Description
Urea Assay Kit
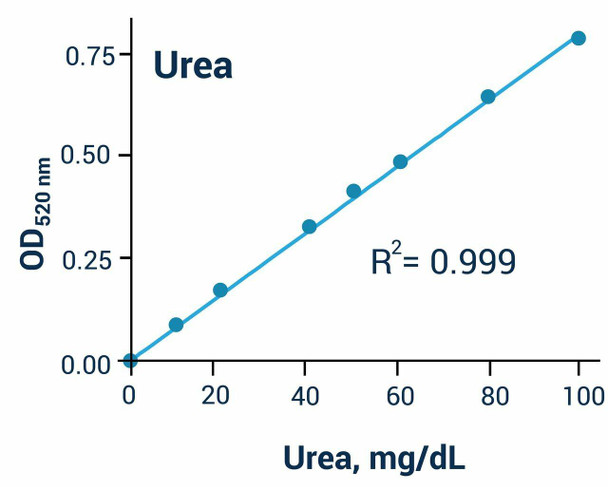
The Assay Genie Urea Assay Kit is designed to measure urea directly in biological samples without any pretreatment. The improved Jung method utilizes a chromogenic reagent that forms a colored complex specifically with urea. The intensity of the color, measured at 520nm, is directly proportional to the urea concentration in the sample. The optimized formulation substantially reduces interference by substances in the raw samples.
| Product Name: | Urea Assay Kit |
| Product Code: | BA0050 |
| Size: | 100 tests |
| Application: | For quantitative determination of urea and evaluation of drug effects on urea metabolism |
| Species: | Universal |
| Sample Type: | Serum, plasma, urine, milk, cell/tissue culture, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), food, beverage and environment |
| Method of Detection: | OD520nm (Chemical) |
| Detection Limit: | 0.08 mg/dL (13 µM) |
| Note: | For research use only |
| Sensitive and accurate. Use 5 samples. Linear detection range 0.08 mg/dL (13µM) to 100 mg/dL (17 mM) urea in 96-well plate assay. | |
| Simple and high-throughput. The procedure involves addition of a single working reagent and incubation for 20 min. Can be readily automated as a high-throughput assay for thousands of samples per day. | |
| Improved reagent stability and versatility. The optimized formulation has greatly enhanced reagent and signal stability. Cuvet or 96-well plate assay. | |
| Low interference in biological samples. No pretreatments are needed. Assays can be directly performed on raw biological samples i.e., in the presence of lipid and protein. |
| Protocol Length: | 30 minutes |
| Storage: | Store all components at 2-8°C. For long-term storage, keep standard at -20°C. |
| Shelf Life: | 12 months |
| Kit Components: |
|
| Kit Requires: |
|
Reagent Preparation
Equilibrate reagents to room temperature. Prepare enough working reagent for all samples and standards by combining equal volumes of Reagent A and Reagent B shortly prior to assay. Use working reagent within 20 min after mixing.
Procedure for 96-well Plate
| Step | Protocol |
| 1. | Serum and plasma samples can be assayed directly (n = 1). Urine samples should be diluted 50-fold in distilled water prior to assay (n = 50). Transfer 5 µL water (blank), 5 µL standard (50mg/dL) and 5 µL samples in duplicate into wells of a clear bottom 96-well plate. For low urea samples (< 5 mg/dL), e.g. tissue/cell extract, culture medium, BAL etc, transfer 50 µL water (blank), 50 µL 5 mg urea/dL (the 50 mg/dL standard diluted in water) and 50 µL samples in duplicate into separate wells. |
| 2. | Add 200 µL working reagent and tap lightly to mix. |
| 3. | Incubate 20 min (50 min for low urea samples) at room temperature. |
| 4. | Read optical density at 520 nm. For low urea samples, read OD at 430 nm. |
Procedure for Cuvettes
Prepare samples as described for 96-well plate assay. Transfer 20 µL water, standard (50 mg/dL) and samples to appropriately labeled tubes. For low urea samples, use 5 mg/dL standard and 200 µL instead of 20 µL. Add 1000 µL working reagent and tap lightly to mix. Incubate 20 min (50 min) and read OD520nm (OD430nm).
Urea is primarily produced in the liver and secreted by the kidneys. Urea is the major end product of protein catabolism in animals. It is the primary vehicle for removal of toxic ammonia from the body. Urea determination is very useful for the medical clinician to assess kidney function of patients.
In general, increased urea levels are associated with nephritis, renal ischemia, urinary tract obstruction, and certain extrarenal diseases, e.g., congestive heart failure, liver diseases and diabetes. Decreased levels indicate acute hepatic insufficiency or may result from over-vigorous parenteral fluid therapy.
Simple, direct and automation-ready procedures for measuring urea concentration or blood urea nitrogen BUN in biological samples are becoming popular in Research and Drug Discovery.
Citations
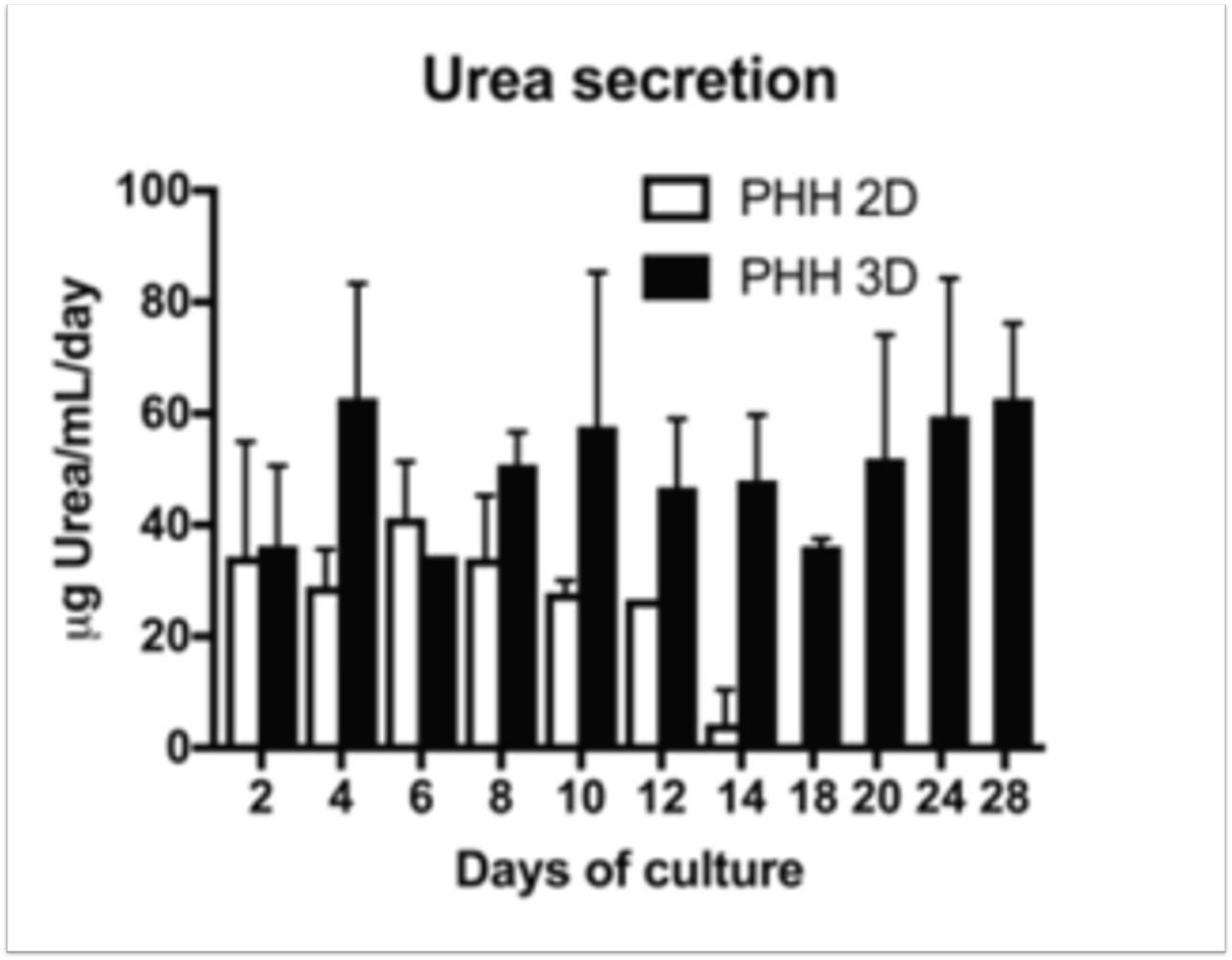
| Cuvellier et al. | 3D culture of HepaRG cells in GelMa and its application to bioprinting of a multicellular hepatic model | Biomaterials (2021) | PubMed: 33385685 |
| Cuvellier et al. | In vitro long term differentiation and functionality of three-dimensional bioprinted primary human hepatocytes: application for in vivo engraftment | Biofabrication (2022) | PubMed ID: 35696992 |
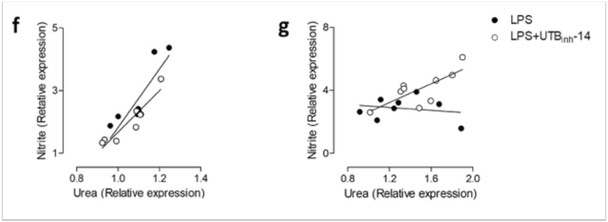
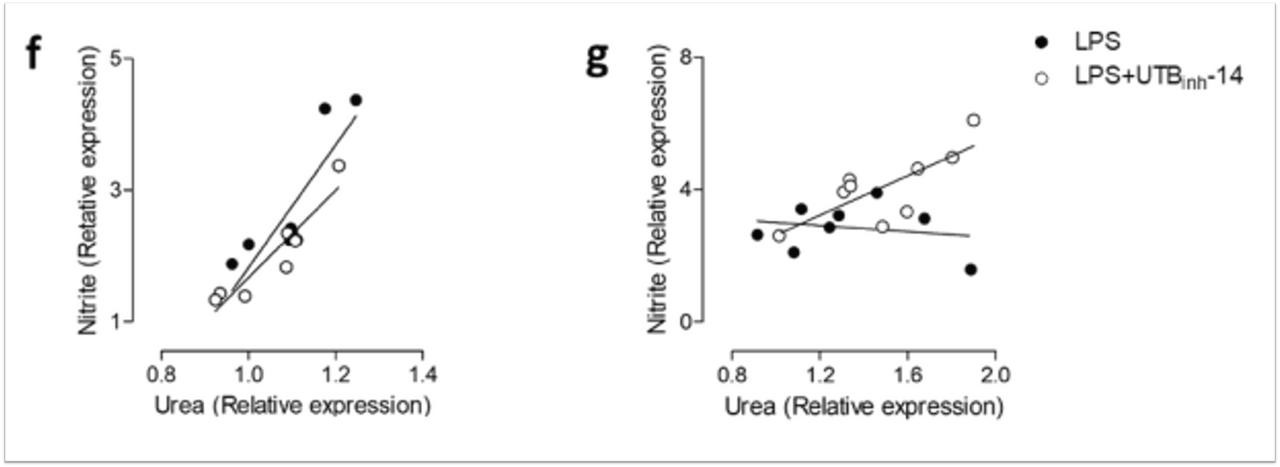
| Jones et al. | Inhibition of Urea Transporter (UT)-B Modulates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in BV2 Microglia and N2a Neuroblastoma Cells | Neurochemical Research (2021) | PubMed: 33675462 |
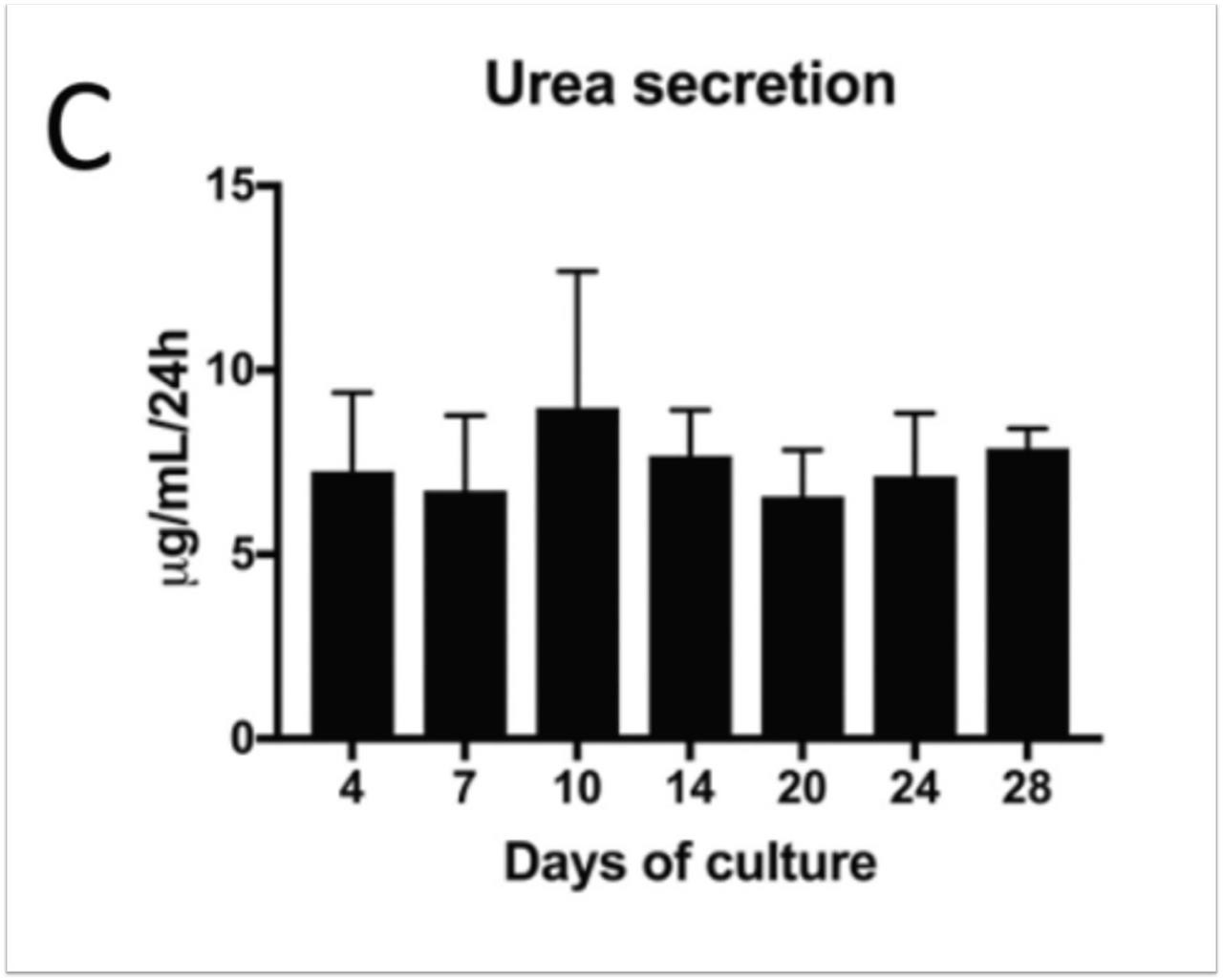
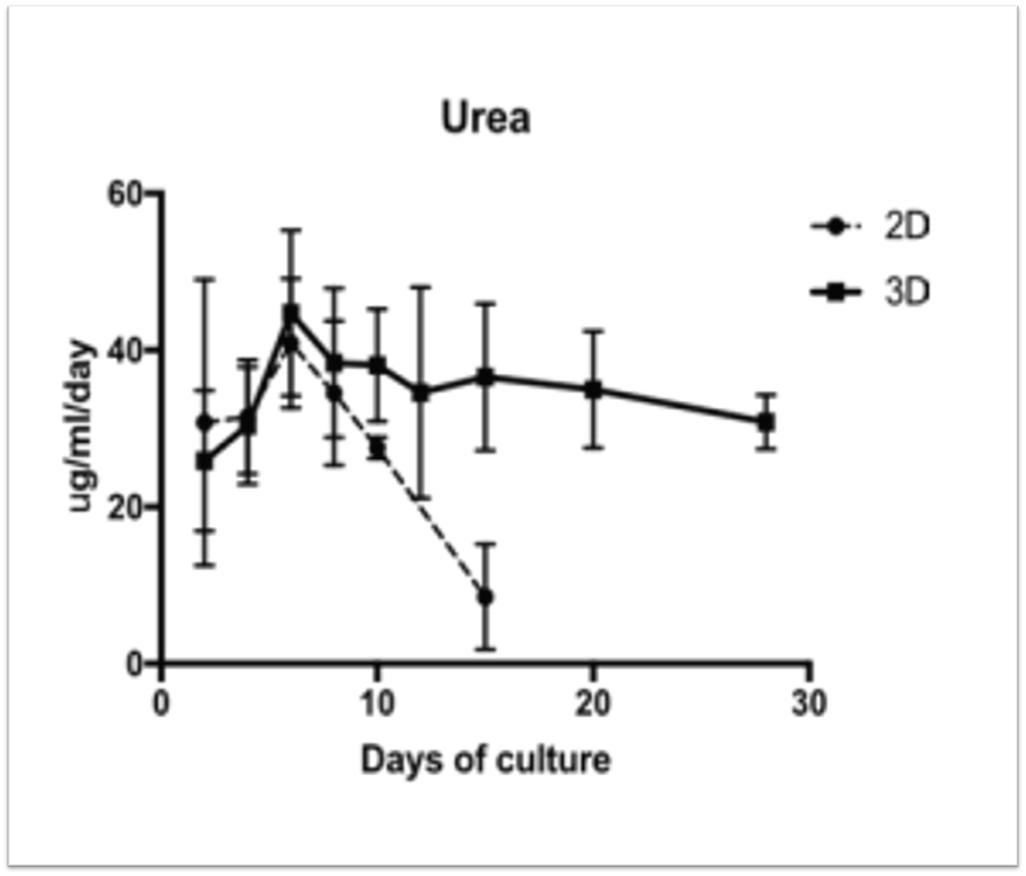
| Rose et al. | DMSO-free highly differentiated HepaRG spheroids for chronic toxicity, liver functions and genotoxicity studies | Archives of Toxicology (2021) | PubMed: 34762139 |
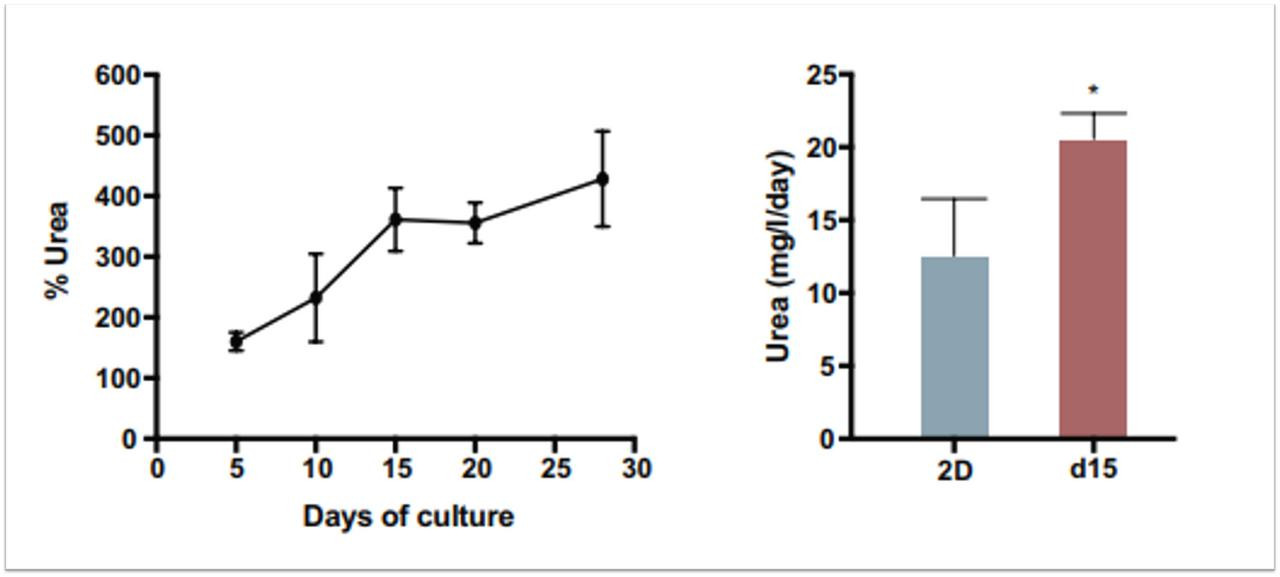
| Rose et al. | Generation of proliferating human adult hepatocytes using optimized 3D culture conditions | Scientific reports (2021) | PubMed: 33436872 |
Data from Citations
| Cuvellier et al. | 3D culture of HepaRG cells in GelMa and its application to bioprinting of a multicellular hepatic model | Biomaterials 2021 | PMID: 33385685 |
| Rose et al. | Generation of proliferating human adult hepatocytes using optimized 3D culture conditions | Scientific Reports 2021 | PMID: 33436872 |
| Jones et al. | Inhibition of Urea Transporter (UT)-B Modulates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in BV2 Microglia and N2a Neuroblastoma Cells | Neurochemical Research 2021 | PMID: 33675462 |
| Cuvellier et al. | In vitro long term differentiation and functionality of three-dimensional bioprinted primary human hepatocytes: application for in vivo engraftment | Biofabrication 2022 | PubMed ID: 35696992 |
| Rose et al. | DMSO-free highly differentiated HepaRG spheroids for chronic toxicity, liver functions and genotoxicity studies | Archives of Toxicology 2022 | PMID: 34762139 |
| Chowdhury et al. | Hepatotoxicity of cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in human: Insights into mechanisms of action in the 3D culture model Hepoid-HepaRG | Environmental Pollution 2023 | PubMed ID: 38036087 |
| Riju R. Chowdhury et al. | Hepatotoxicity of cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in human: Insights into mechanisms of action in the 3D culture model Hepoid-HepaRG | Environmental Pollution 2024 | View Citation |