Description
Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/SDF-1 Protein
The Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/SDF-1 Protein is a high-quality recombinant protein designed for murine biological research applications. This protein serves as an essential reagent in mouse model studies, comparative immunology research, and preclinical therapeutic evaluations, enabling scientists to investigate CXCL12/SDF-1 biology and its relevance to human disease mechanisms through translational research approaches.
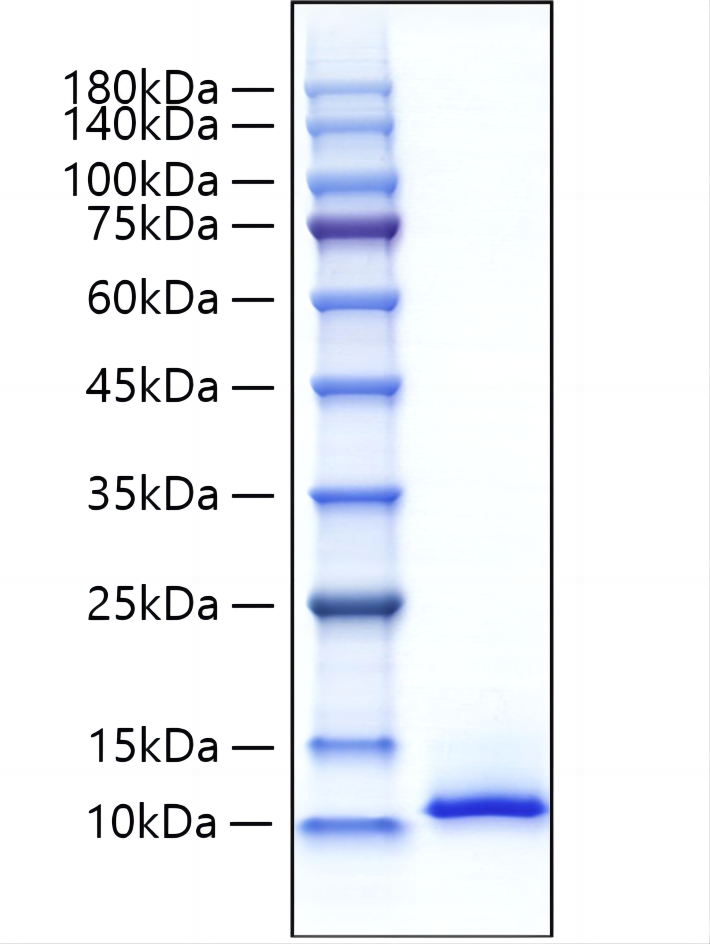
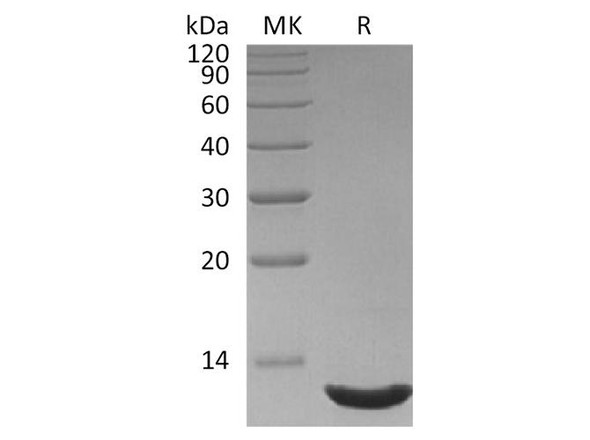
This product (SKU: RPCB1876) is produced using Pichia and features a NO-tag tag for convenient detection and purification. The protein exhibits a calculated molecular weight of 7.98 kDa with an observed molecular weight of 10-12 kDa under denaturing conditions, achieving ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE.. Functional bioactivity has been validated through rigorous quality control assays, confirming its suitability for demanding research applications.
Key Features
| High Purity by Affinity Chromatography | |
| Mammalian & Bacterial Expression Systems | |
| High lot-to-lot consistency via strict QC |
| Product Name: | Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/SDF-1 Protein |
| SKU: | RPCB1876 |
| Size: | 10 μg , 20 μg , 50 μg |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Synonyms: | Cxcl12, Stromal cell-derived factor 1, SDF-1, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate repressedprotein 1, TPAR1, C-X-C motif chemokine 12, Pre-B cell growth-stimulating factor, PBSF, Thymiclymphoma cell-stimulating factor, TLSF, Sdf1 |
| Tag: | NO-tag |
| Expression Host: | Pichia |
| Calculated MW: | 7.98 kDa |
| Observed MW: | 10-12 kDa |
| Gene ID: | 20315 |
| Protein Description: | High quality, high purity and low endotoxin recombinant Recombinant Mouse CXCL12/SDF-1 Protein (RPCB1876), tested reactivity in Pichia and has been validated in SDS-PAGE.100% guaranteed. |
| Endotoxin: | < 1 EU/μg of the protein by LAL method. |
| Purity: | ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.22 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
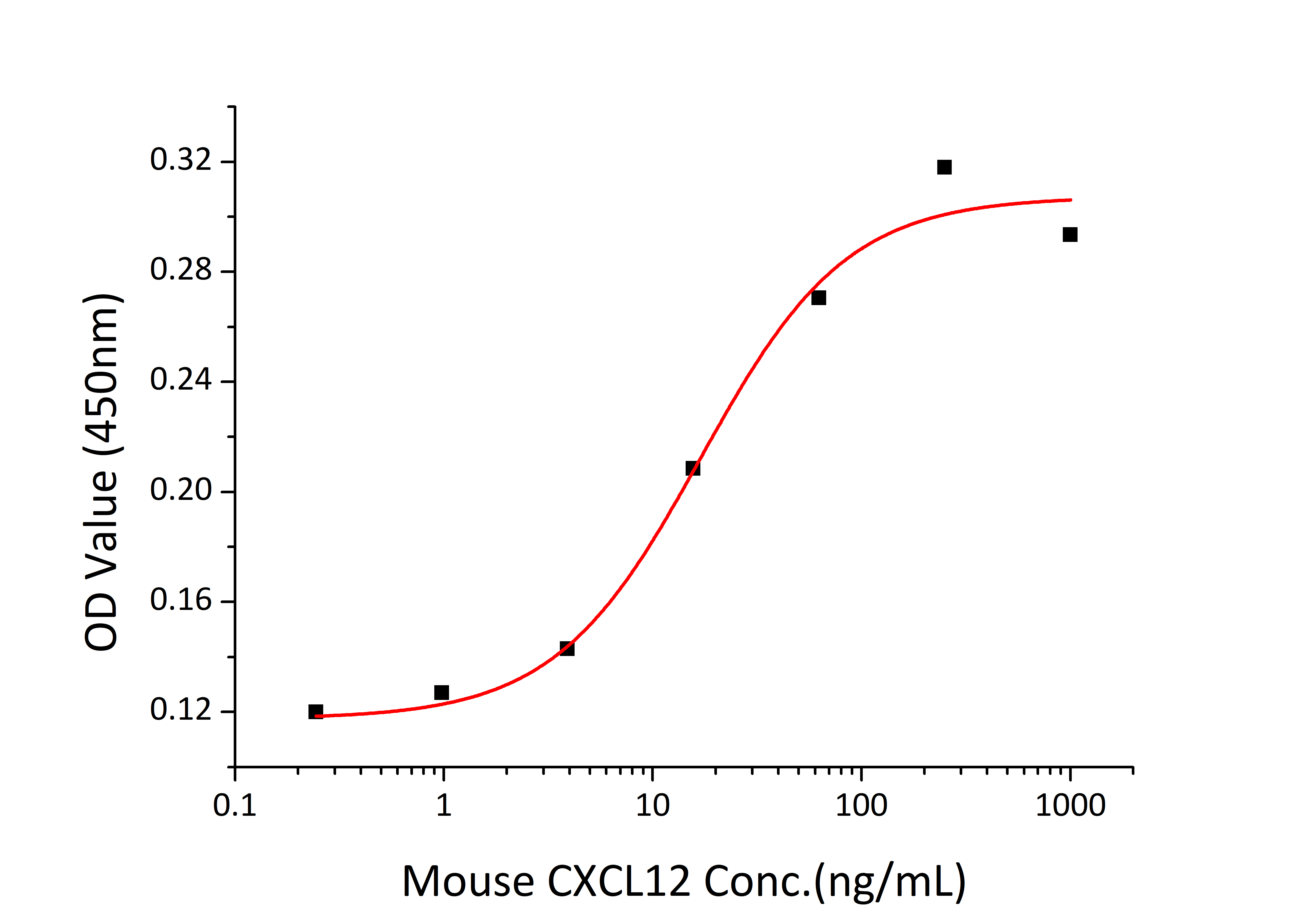
| Bio-Activity: | Measured by its ability to chemoattract MOLT4 cells. The ED 50 for this effect is 8.49-33.94 ng/mL, corresponding to a specific activity of 2.95×10 4 ~1.18×10 5 units/mg. |
| Reconstitution: | Centrifuge the vial before opening. Reconstitute to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile distilled water. Avoid vortex or vigorously pipetting the protein. For long term storage, it is recommended to add a carrier protein or stablizer (e.g. 0.1% BSA, 5% HSA, 10% FBS or 5% Trehalose), and aliquot the reconstituted protein solution to minimize free-thaw cycles. |
| Storage: | Store at -20℃.Store the lyophilized protein at -20℃ to -80 ℃ up to 1 year from the date of receipt. After reconstitution, the protein solution is stable at -20℃ for 3 months, at 2-8℃ for up to 1 week. |
Mouse Cxcl12 is a secreted and highly conserved protein which belongs to the intercrine alpha (chemokine CxC)family.CXCL12 is widely expressed in various organs including brain, kidney, skeletal muscle, heart, liver, and lymphoidorgans. Cxcl12 activates the C-X-C chemokine receptor CXCR4 to induce a rapid and transient rise in the level ofintracellular calcium ions and chemotaxis. It also binds to atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3 which activates the beta-arrestin pathway and acts as a scavenger receptor for SDF-1. Cxcl12 has several critical functions during embryonicdevelopment such as B-cell lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis in bone marrow and heart ventricular septum formation. Cxcl12plays an important role in acting as a positive regulator of monocyte migration and a negative regulator of monocyteadhesion via the LYN kinase. It stimulates migration of monocytes and T-lymphocytes through its receptors, CXCR4 andACKR3, and decreases monocyte adherence to surfaces coated with ICAM-1, a ligand for beta-2 integrins. SDF1A/CXCR4signaling axis inhibits beta-2 integrin LFA-1 mediated adhesion of monocytes to ICAM-1 through LYN kinase. It also plays aprotective role after myocardial infarction, induces down-regulation and internalization of ACKR3 expressed in various cellsand stimulates the proliferation of bone marrow-derived b progenitor cells in the presence of IL-7 as well as growth of thestromal cell-dependent B-cell clone DW34 cells.