Ipilimumab and Nivolumab: Advancing Research on CTLA-4 in Cancer Therapy
What You Need to Know About Ipilimumab
What is Ipilimumab?
Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets CTLA-4, a protein involved in downregulating the immune system, to boost the body's immune response against cancer cells.
How does Ipilimumab work?
By inhibiting CTLA-4, ipilimumab enhances T-cell activation and proliferation, enabling a stronger immune response to attack tumors.
What are the side effects of Ipilimumab?
Common side effects include fatigue, diarrhea, rash, and more severe immune-related adverse events like colitis and hepatitis.
What is the role of Ipilimumab in combination with Nivolumab?
The combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab has shown enhanced efficacy in treating advanced melanoma and other cancers by targeting two different immune checkpoints.
1.) Understanding Ipilimumab
Ipilimumab, marketed under the brand name Yervoy, represents a transformative advancement in cancer treatment and is widely regarded as a cornerstone of immuno-oncology. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2011, lipilimumab became the first immune checkpoint inhibitor to revolutionize the management of metastatic melanoma and later other cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Its mechanism of action focuses on CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), a receptor on T-cells that acts as an immune "brake" to prevent overactivation.
Cancer cells often exploit CTLA-4 to suppress the immune system, allowing unchecked tumor growth. Ipilimumab blocks this receptor, lifting the immune system’s inhibition and enabling T-cells to mount a more robust attack against cancer cells. This breakthrough approach, termed immune checkpoint blockade, has significantly enhanced survival rates and spurred further research into combination therapies.
While ipilimumab has shown remarkable efficacy, it is associated with immune-related adverse events (irAEs) due to heightened immune activation. Despite these challenges, ipilimumab has reshaped cancer therapy, paving the way for other immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting molecules like PD-1 and PD-L1. Its success continues to inspire innovations in immunotherapy, offering new hope to patients worldwide.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Ipilimumab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Ipilimumab
Ipilimumab’s mechanism of action revolves around targeting CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), a pivotal immune checkpoint that regulates T-cell activity. Under normal physiological conditions, CTLA-4 acts as a "brake" to maintain immune homeostasis and prevent excessive immune responses, which could damage healthy tissues. It achieves this by competing with CD28, a costimulatory receptor on T-cells, for binding to B7 ligands (CD80 and CD86) expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). When CTLA-4 binds to B7, it suppresses T-cell activation, leading to immune downregulation.
Ipilimumab disrupts this inhibitory pathway by specifically blocking CTLA-4, thereby preventing it from binding to B7 ligands. This blockade shifts the balance in favor of CD28-B7 interaction, which delivers a crucial costimulatory signal required for full T-cell activation. The result is the proliferation and activation of cytotoxic T-cells, which are then unleashed to recognize and attack tumor cells more effectively.
This immune enhancement makes ipilimumab particularly effective against cancers like melanoma, where immune evasion is a hallmark. By reactivating the immune system's natural ability to fight tumors, ipilimumab represents a groundbreaking approach in cancer immunotherapy, though it also underscores the need for careful management of immune-related side effects.

3.) Clinical Applications of Ipilimumab
Ipilimumab’s clinical utility was first recognized in the treatment of metastatic melanoma, where it became the first immune checkpoint inhibitor to demonstrate significant survival benefits. Its approval marked a pivotal advancement in cancer immunotherapy. Beyond metastatic melanoma, ipilimumab has exhibited efficacy in treating other challenging cancers, including renal cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability (MSI-high), and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
One of the most transformative applications of ipilimumab has been its combination with nivolumab, a PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor. Together, these agents target complementary pathways to amplify the immune response against cancer. Clinical trials have shown that this combination significantly improves progression-free survival and overall survival in advanced melanoma, NSCLC, and renal cell carcinoma compared to monotherapy. This dual-blockade approach exemplifies the synergistic potential of checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy.
Ongoing research continues to explore ipilimumab's potential in combination therapies with other immunotherapies, targeted therapies, and even conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation. It is also being investigated in earlier-stage disease settings, including adjuvant therapy for resected high-risk melanoma. As studies progress, ipilimumab is poised to play a broader role in oncology, offering hope for more effective treatments across a wide range of cancers.
4.) Advancing Research on Ipilimumab
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic medical products highly similar to an original reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, purity, and potency. They offer a cost-effective alternative for research and therapeutic purposes while maintaining rigorous standards.
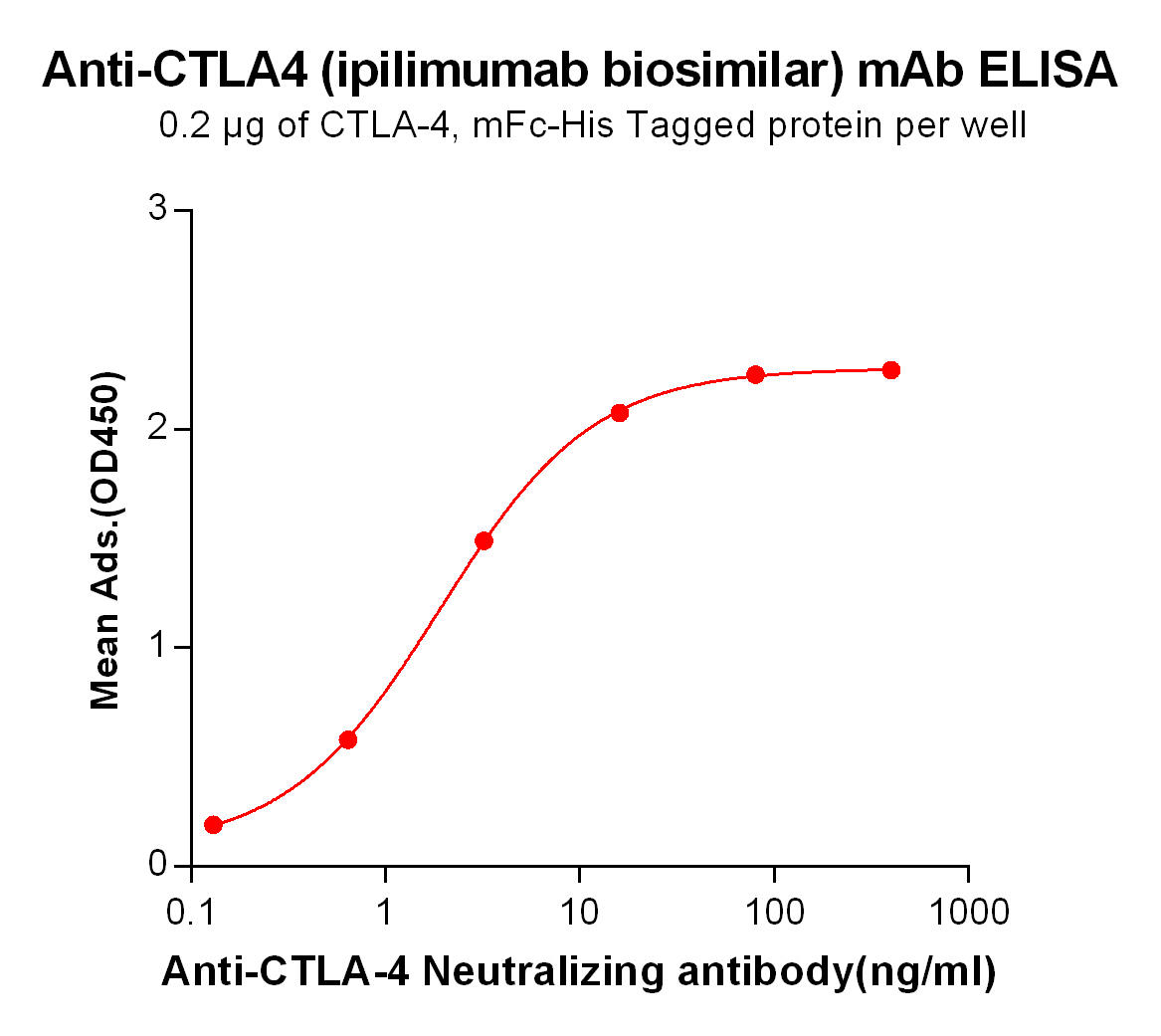
| Ipilimumab (Anti-CTLA-4) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CTLA-4 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Our Ipilimumab Biosimilar Contributes to Research
Our Ipilimumab biosimilar is designed for research use only, providing scientists with a valuable tool to advance their studies. By mimicking the structure and function of the original drug, it enables exploration of CTLA-4 inhibition and its effects in various experimental models.
Benefits of Ipilimumab Biosimilar for Research
Cost-Effective Access: Enables extensive preclinical research without the high costs associated with branded drugs.
High Quality: Maintains rigorous standards to ensure reliability in research settings.
Versatile Applications: Useful for studying immune checkpoint pathways, drug interactions, and combination therapies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer
Our ipilimumab biosimilar is intended strictly for research purposes and is not approved for clinical or patient use. This distinction ensures its application is focused on advancing scientific knowledge and innovation.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Metabolic Exhaustion: How Mitochondrial Dysfunction Sabotages CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
Imagine engineering a patient's own immune cells into precision-guided missiles against cancer—cells …8th Dec 2025 -
The Powerhouse of Immunity: How Mitochondrial Fitness Fuels the Fight Against Cancer
Why do powerful cancer immunotherapies work wonders for some patients but fail for others? The answe …5th Dec 2025 -
How Cancer Cells Hijack Immune Defenses Through Mitochondrial Transfer
Imagine a battlefield where the enemy doesn't just hide from soldiers—it actively sabotages their we …5th Dec 2025