Blog
Guselkumab: Advancing Psoriasis and Autoimmune Disease Research Through IL-23 Targeting
Quick Facts About GuselkumabWhat is Guselkumab?Guselkumab is a biologic therapy that selectively targets the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23), playing a critical role in inflammatory autoimmune conditions.What is the mechanism of action for Guselkumab?It inhibits IL-23 signaling by binding to the p19 subunit, disrupting downstream inflammatory pathways involved in diseases like psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.Is Guselkumab safe?Clinical trials have shown Guselkumab to have a favorable safety profile, with most side effects being mild to moderate, such as upper respiratory infections and injection-site reactions.What conditions does Guselkumab treat?Guselkumab is FDA-appr
…
27th Mar 2025
Canakinumab: Unraveling Its Role in Inflammatory Disease and Cancer Research
Quick Facts About CanakinumabWhat is Canakinumab?Canakinumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), reducing inflammation associated with various diseases.How Does Canakinumab Work?It neutralizes IL-1β, a key inflammatory mediator, preventing downstream inflammatory responses that contribute to conditions like systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), periodic fever syndromes, and cardiovascular disease.What Are the Clinical Applications of Canakinumab?Canakinumab is FDA-approved for treating autoinflammatory syndromes, including sJIA, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS), and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF). It has also shown
…
5th Feb 2025
Dupilumab: Transforming Immunotherapy and Skin Disease Management
What You Need to Know About DupilumabWhat is Dupilumab?Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody designed to treat various chronic inflammatory diseases by inhibiting key cytokines involved in immune responses.How does Dupilumab work?It targets the interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor α subunit, blocking IL-4 and IL-13 signaling pathways that drive inflammation.What are the clinical applications of Dupilumab?Approved for atopic dermatitis, asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP), and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), Dupilumab addresses several unmet medical needs.Is Dupilumab safe?Yes, Dupilumab has a well-established safety profile, with mild injection-site r
…
1st Feb 2025
Inebilizumab: Advancing Research and Clinical Applications
What You Need to Know About InebilizumabWhat is Inebilizumab?Inebilizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets CD19, a protein expressed on B cells, to treat autoimmune diseases.How does Inebilizumab work?It depletes B cells by binding to CD19, reducing inflammation and modulating immune responses.What are the clinical applications of Inebilizumab?It is primarily approved for treating Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD) in adults.Is Inebilizumab safe?Yes, it has demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with common side effects being mild-to-moderate and manageable.1.) Understanding InebilizumabInebilizumab represents a groundbreaking advancement in the tre
…
1st Feb 2025
Fezakinumab: Exploring Its Mechanism and Clinical Potential
Quick Facts About FezakinumabWhat is Fezakinumab?Fezakinumab is a human IgG1-lambda monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-22 (IL-22), a cytokine involved in inflammatory responses. What is the mechanism of action for Fezakinumab?By binding to IL-22, Fezakinumab inhibits its activity, thereby reducing inflammation associated with various diseases. What are the clinical applications of Fezakinumab?Fezakinumab has been investigated in clinical trials for conditions such as atopic dermatitis and rheumatoid arthritis. 1.) Understanding FezakinumabThe development of Fezakinumab was initiated by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and later continued by Pfizer following their
…
29th Jan 2025
Tocilizumab: Advancing Therapeutics and Research with Biosimilars
What You Need to Know About TocilizumabWhat is Tocilizumab?Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor, widely used for managing autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.What is the mechanism of action for Tocilizumab?Tocilizumab works by inhibiting the IL-6 receptor, thereby reducing inflammation and immune response.What are the clinical applications of Tocilizumab?It is approved for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and giant cell arteritis (GCA).1.) Understanding TocilizumabTocilizumab, marketed under the brand name Actemra, is a groundbreaking biologic drug that functions as an IL-6 receptor antagoni
…
22nd Jan 2025
Siltuximab: Exploring IL-6 Inhibition in Castleman’s Disease and Research
Quick Facts About SiltuximabWhat is Siltuximab?Siltuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6), a cytokine involved in inflammation and immune regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Siltuximab?Siltuximab binds to IL-6, preventing it from interacting with its receptor and mitigating downstream pro-inflammatory signaling.What are the clinical applications of Siltuximab?Siltuximab is approved for treating multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD) in patients negative for HIV and HHV-8.1.) Understanding SiltuximabWhat Makes Siltuximab Unique?Siltuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody specifically designed to neutralize interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammat
…
16th Jan 2025
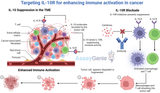
Targeting IL-10R: Enhancing Immune Activation in Cancer
Introduction to IL-10R and Immune Suppression in CancerThe interleukin-10 receptor (IL-10R) is a key player in regulating immune responses, particularly in suppressing inflammation and maintaining immune tolerance. IL-10R is activated by its ligand, interleukin-10 (IL-10), an anti-inflammatory cytokine that is critical in controlling excessive immune activation and preventing tissue damage during infection or inflammation. However, in the context of cancer, IL-10 signaling can be exploited by tumor cells to suppress immune responses, particularly by inhibiting the activity of T cells and dendritic cells, creating a microenvironment conducive to tumor growth.Targeting IL-10R with
…
12th Dec 2024
IL-1 Family Signaling: Unraveling the Molecular Orchestra of Immune Regulation
The Interleukin-1 (IL-1) family represents a crucial group of signaling molecules that play a pivotal role in regulating the immune system and inflammatory responses. Comprising 11 members, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33, the IL-1 family members exhibit diverse functions in immune homeostasis, tissue repair, and disease pathogenesis. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the IL-1 family signaling pathway, shedding light on its components, activation mechanisms, and physiological significance. Components of the IL-1 Family Signaling Pathway: IL-1 Receptors (IL-1Rs): The IL-1 family signaling cascade begins with the binding of
…
2nd Feb 2024
IL-9 Signaling and Its Impact on Immune Cell Regulation
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) plays a critical role in the immune system, influencing a variety of biological functions across different immune cell types. This article provides an in-depth look at the signaling mechanisms of IL-9 and its widespread effects on immune regulation, specifically focusing on its impact on T cells, mast cells, basophils, B cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). IL-9 Signaling Pathway Overview of IL-9 Receptor Activation IL-9 interacts with the IL-9 receptor (IL-9R), composed of the IL-9Rα chain and the common gamma chain (γc), initiating the JAK-STAT signaling cascade. This activation promotes the transcription of genes that regulate cell proliferation, d
…
1st Feb 2024
The Intricacies of IL-21 Signaling: Impact on Diverse Immune Cell Types
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) stands out as a pivotal cytokine in the complex network of immune system communication. Its role in regulating various immune cell types has drawn considerable attention from researchers seeking to unravel the intricate web of signaling pathways and biological effects it elicits. In this article, we will delve into the nuanced world of IL-21 signaling and explore its profound impacts on different immune cell populations. IL-21: An Overview IL-21 belongs to the family of cytokines, which are small proteins crucial for intercellular communication. Produced mainly by activated CD4+ T cells, particularly T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and Th17 cells, IL-
…
31st Jan 2024
The role of key Interleukins
Interleukin signaling is involved in a number of biological processes, including cell growth and differentiation, inflammation and immunity. Interleukins are glycoproteins which act on hematopoietic cells to regulate immune responses or target cells for destruction by the immune system. Interleukins mediate communication between cells through a complex network of receptors. Interleukin receptors are members of a large family of cell surface molecules called cytokine receptors. Interleukins bind to the receptor and cause it to dimerize with another interleukin receptor, which in turn stimulates activity within the target cells. Interleukins play a major role in host defense against
…
11th Jan 2022
Physiological and Pathological functions of IL-36
By Charlotte O'Donnell PhD
Similar to IL-33, IL-36R ligands are involved in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. Analogous to IL-33, d is localised to the nuclei of intestinal epithelial cells [1]. The presence of IL-36γ in the nucleus may be due to its role as an “alarmin”.
In murine models of intestinal damage such as the DSS colitis model and also in mechanical mucosal injury model, IL-36γ was released by the intestinal epithelial cells and shown to enhance mucosal healing. The effects of IL-36γ on colonic fibroblasts have been examined in a recent study. It was demonstrated that IL-36γ induced pr
…
6th Oct 2021
Interferons
Interferons (IFNs) are a group of signalling proteins that are produced and released from cells in response to viral infection and other stimuli such as normal and tumour cell survival and death. IFNs interact with specific cellular receptors, thereby promoting production of secondary messengers which leads to the expression of antiviral and immune modulatory genes. There are three groups of IFNs, Type I IFNs, Type II IFNs and Type III IFNs. Type I IFNs include IFN-alpha, -beta, -omega, -kappa and IFN-zeta. These are essential for regulating the immune response to viral infections. The Type II IFN group only includes IFN-gamma. IFN-gamma is a versatile cytokine that plays an essen
…
6th Mar 2021
Physiological Roles for IL-33 | Assay Genie
By Charlotte O'Donnell PhD
A role for IL-33 in Barrier Function and Epithelial Wound Healing
IL-33 is constitutively expressed by cells involved in the maintenance of mechanical barriers, including keratinocytes, lung and gut epithelial cells, fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells [1]. In these cells IL-33 is localized to the nucleus and mediates gene transcription. It is believed to maintain a quiescent state as it is only produced in barrier cells when they are senescent. Indeed, downregulation of IL-33 has been linked to the initiation of cellular proliferation in barrier cells. Once
…
1st Jan 1970