Blog
Histamine Receptors: Gatekeepers of Immunological and Neurological Responses
Histamine, a biogenic amine, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including immune responses, gastric acid secretion, and neurotransmission. Central to the action of histamine are histamine receptors, which are distributed broadly across different tissues and cell types. This article delves into the nature, types, and functions of histamine receptors, highlighting their significance in immunological and neurological processes. Understanding Histamine Receptors: Histamine exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors on the surfaces of target cells. These receptors are part of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, characterized by their seven tran
…
15th Mar 2024
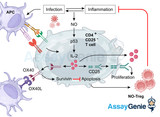
Exploring the Frontier of Immunotherapy: T Cell Expansion
In the realm of immunotherapy, T cell expansion has emerged as a pivotal strategy, holding promise in the treatment of various diseases, particularly cancer. T cells are a critical component of the adaptive immune system, orchestrating immune responses against pathogens and malignant cells. Harnessing the potential of T cells through expansion techniques offers a novel avenue for enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. This article delves into the mechanisms, applications, and advancements in T cell expansion, illuminating its transformative impact on medical science. Understanding T Cell Expansion T cells, a type of lymphocyte, play a central role in adaptive immunity by rec
…
8th Mar 2024
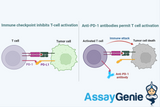
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
In recent years, the field of oncology has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of immunotherapy, a treatment modality that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer. Among the most promising approaches in immunotherapy is the targeting of immune checkpoints. These molecular pathways are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and modulating the immune response to prevent autoimmunity. However, cancer cells cleverly exploit these pathways to evade immune detection and destruction. This article delves into the mechanisms of immune checkpoint pathways, their role in cancer evasion, and the therapeutic strategies designed to inhibit these checkpoints, thereby reactivating the
…
16th Feb 2024
Navigating the Intricacies of Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Key Considerations
In the evolving landscape of cellular biology, intracellular flow cytometry (ICFC) stands out as a powerful technique for analyzing the complexities within cells. This advanced method extends the capabilities of traditional flow cytometry by allowing researchers to investigate intracellular proteins, signaling pathways, and specific gene expressions within individual cells. ICFC has become indispensable in various fields, including immunology, oncology, and drug discovery, offering insights that are pivotal for understanding disease mechanisms and developing therapeutic strategies. However, harnessing the full potential of ICFC requires meticulous attention to several critical considerat
…
16th Feb 2024
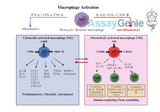
Macrophage Activation: A Keystone in Immune Response and Therapeutic Potential
In the intricate tapestry of the immune system, macrophages play a pivotal role, orchestrating a wide range of biological responses that protect the body against pathogens, remove cellular debris, and promote tissue repair. Macrophage activation is a complex process, integral to both innate and adaptive immunity, influencing disease outcomes and offering promising avenues for therapeutic intervention. This comprehensive exploration delves into the mechanisms of macrophage activation, its dualistic nature, and the implications for disease treatment and immune modulation. The Fundamentals of Macrophage Activation: Macrophages, derived from monocytes, are versatile cells present in
…
13th Feb 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
The advent of immune checkpoint targeting marks a significant milestone in the oncological field, offering a beacon of hope for patients battling cancer. This innovative approach leverages the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells, a method that stands in stark contrast to traditional therapies. This article delves deep into the essence of immune checkpoint therapy, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and the horizon it promises for future cancer treatments. Introduction to Immune Checkpoints Immune checkpoints are critical regulators of the immune system's response to various cells, including cancer cells. They are designed to prevent the immune s
…
13th Feb 2024
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: A Key to Innate Immunity
In the intricate landscape of the immune system, toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a fundamental role in the first line of defense against pathogens. These receptors, essential components of the innate immune response, are adept at recognizing specific microbial patterns, initiating signaling pathways that lead to the activation of immune responses. This article delves into the toll-like receptor signaling pathways, underscoring their importance in immunology and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding Toll-Like Receptors Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune system by detecting microbial infections and activating the immune r
…
5th Feb 2024
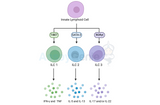
Innate Lymphoid Cells Differentiation: Guardians of Immune Homeostasis
Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs) represent a fascinating component of the immune system, playing a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and mounting rapid responses against pathogens. These cells lack antigen-specific receptors, distinguishing them from their adaptive counterparts, yet their ability to rapidly respond to environmental cues is vital for effective immune surveillance. One of the key aspects of ILCs' functionality lies in their differentiation process, a complex series of events that shape these cells into distinct subsets with specialized functions. Understanding ILC Differentiation: ILCs are broadly categorized into three main subsets based on their cy
…
2nd Feb 2024
IL-1 Family Signaling: Unraveling the Molecular Orchestra of Immune Regulation
The Interleukin-1 (IL-1) family represents a crucial group of signaling molecules that play a pivotal role in regulating the immune system and inflammatory responses. Comprising 11 members, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33, the IL-1 family members exhibit diverse functions in immune homeostasis, tissue repair, and disease pathogenesis. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the IL-1 family signaling pathway, shedding light on its components, activation mechanisms, and physiological significance. Components of the IL-1 Family Signaling Pathway: IL-1 Receptors (IL-1Rs): The IL-1 family signaling cascade begins with the binding of
…
2nd Feb 2024
IL-9 Signaling and Its Impact on Immune Cell Regulation
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) plays a critical role in the immune system, influencing a variety of biological functions across different immune cell types. This article provides an in-depth look at the signaling mechanisms of IL-9 and its widespread effects on immune regulation, specifically focusing on its impact on T cells, mast cells, basophils, B cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). IL-9 Signaling Pathway Overview of IL-9 Receptor Activation IL-9 interacts with the IL-9 receptor (IL-9R), composed of the IL-9Rα chain and the common gamma chain (γc), initiating the JAK-STAT signaling cascade. This activation promotes the transcription of genes that regulate cell prol
…
1st Feb 2024
The role of IL-18 in health and disease
Exploring IL-18: A key cytokine in inflammation and disease. Key Takeaways: IL-18, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, plays a pivotal role in immune responses, particularly in inducing Type II interferon and activating macrophages. It's produced as an inactive form and activated by caspase-1, signaling through IL-18 receptors to trigger inflammation. IL-18's regulation involves IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP) and IL-37, which modulate its activity and prevent excessive inflammation. It contributes to T cell differentiation and NK cell cytotoxicity, influencing various immune functions. IL-18 is implicated in several diseases, including Crohn's disease and sepsis, making it a potential
…
1st Feb 2024
The Intricacies of IL-21 Signaling: Impact on Diverse Immune Cell Types
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) stands out as a pivotal cytokine in the complex network of immune system communication. Its role in regulating various immune cell types has drawn considerable attention from researchers seeking to unravel the intricate web of signaling pathways and biological effects it elicits. In this article, we will delve into the nuanced world of IL-21 signaling and explore its profound impacts on different immune cell populations. IL-21: An Overview IL-21 belongs to the family of cytokines, which are small proteins crucial for intercellular communication. Produced mainly by activated CD4+ T cells, particularly T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and Th17 cells, IL-
…
31st Jan 2024
Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway: A Keystone in Innate Immunity
The innate immune system, a primary line of defense against pathogens, comprises various cellular and molecular mechanisms. Among these, the Nod-like Receptor (NLR) signaling pathways play a critical role. They are central to the immune response, acting as intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This article delves into the basic components of NLR signaling pathways, their key steps, roles in development, and implications in disease. Basic Components of Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: Nod-like receptors (NLRs) belong to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family and are primarily located in
…
30th Jan 2024
Decoding the Language of Cells: Chemokine Signaling Pathways Unveiled
Chemokines are small signaling proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system by directing the movement of cells, orchestrating immune responses, and maintaining tissue homeostasis. The intricate network of chemokine signaling pathways governs the trafficking and positioning of immune cells throughout the body, contributing to various physiological and pathological processes. This article aims to delve into the complexity of chemokine signaling pathways, shedding light on their diverse functions and significance in cellular communication. Chemokines and Their Receptors: Chemokines belong to a family of chemotactic cytokines that guide the migration of immune cells b
…
28th Jan 2024
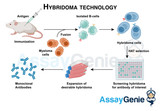
Hybridoma Technology: Revolutionizing Antibody Production
Hybridoma technology, a revolutionary method in immunology pioneered by Georges Köhler and César Milstein in the 1970s, has transformed the landscape of antibody production. This groundbreaking technique has had a profound impact on various scientific domains, from diagnostics to therapeutics and basic research. In this essay, we explore the intricacies of hybridoma technology, its diverse applications, and its pivotal role in advancing our understanding and treatment of diseases. The Birth of Hybridoma Technology: The genesis of hybridoma technology lies in the fusion of two distinct cell types: B cells, responsible for antibody production, and myeloma cells, which p
…
23rd Jan 2024
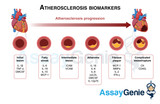
Biomarkers & Inflammatory markers of atherosclerosis
As atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease, there are many influential biomarkers that contribute to the disease’s progression as well as biomarkers from atherosclerosis related diseases such as periodontal disease and autoimmune diseases i.e. Diabetes, RA, SLE. Biomarkers can be proteins, DNA and mRNA which are measured to asses biological, pathological processes and pharmacological responses. Biomarkers can be classified as early, predictive and prognostic biomarkers depending on disease stage (Huang et al., 2010). Identifying biomarkers for disease and finding therapeutic targets is crucial to research and treatment and overall a populations mortality and morbidi
…
23rd Jan 2024
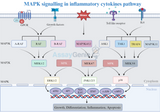
MAPK Signaling in Inflammatory Cytokines Pathways
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway is a pivotal signaling cascade that plays a crucial role in mediating cellular responses to various external stimuli. This pathway is intricately involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokines, key signaling molecules in the immune system. Understanding the MAPK signaling pathway in the context of inflammatory cytokines is essential for grasping the molecular basis of inflammation and its related disorders. Overview of MAPK Signaling Fundamental Components and Activation: MAPK signaling encompasses a series of protein kinases that transmit signals from the cell surface to the nucleus. These kinases include the Extrac
…
22nd Jan 2024
CD25 Marker
CD25, a key molecule in immune regulation, is integral to the function of activated lymphocytes and regulatory T cells. It's central in mediating immune responses, with implications in autoimmune diseases and cancer. Key Takeaways: CD25, part of the IL-2 receptor, is crucial in immune response regulation. Found on T cells, NK cells, Tregs, and others; upregulated during immune activation. Vital for cellular immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Serves as a biomarker in autoimmune diseases, allergies, and certain cancers. Targeted in immunotherapy for diseases like multiple sclerosis and various cancers. What is CD25? CD25, also known as Cluster o
…
22nd Jan 2024
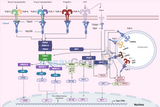
JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway: A Comprehensive Exploration
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-45124fd5-9a75-444d-b680-b8339e2a814d' })
Progression of the JAK STAT Signalling Pathway Cellular communication is a complex network of molecular interactions that govern various physiological processes. Among the many signaling pathways, the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway plays a pivotal role in mediating signals from the cell surface to the nucleus. This pathway is essential for regulating immune responses, cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. In this article, we will delv
…
18th Jan 2024
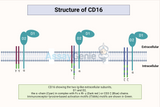
Understanding CD16: A Comprehensive Overview
CD16, also known as FcγRIII (Fc gamma receptor III), plays a crucial role in the immune system, serving as a receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). This receptor is a key player in mediating various immune responses and has implications in both innate and adaptive immunity. In this article, we will delve into the structure, functions, and significance of CD16 in the context of immune regulation. Structure of CD16: CD16 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It exists in two main isoforms: CD16A (FcγRIIIA) and CD16B (FcγRIIIB). CD16A is expressed on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and
…
5th Jan 2024
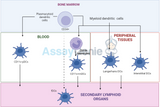
Dendritic Cells: Tracing the Developmental Lineage Pathway
Dendritic cells (DCs) are pivotal in the immune system, orchestrating innate and adaptive immune responses. Understanding their developmental lineage pathway is crucial in immunology, particularly in the context of cancer and infection responses. Introduction to Dendritic Cells Dendritic cells are unique antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that play a crucial role in the immune system. They are known for their ability to capture and present antigens, thereby bridging innate and adaptive immunity. DCs are heterogeneous, comprising various subsets with distinct phenotypes and functions. This diversity is a result of their complex developmental lineage. Origin and Early Development
…
5th Jan 2024
Understanding CD16: A Comprehensive Overview
CD16, also known as FcγRIII (Fc gamma receptor III), plays a crucial role in the immune system, serving as a receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). This receptor is a key player in mediating various immune responses and has implications in both innate and adaptive immunity. In this article, we will delve into the structure, functions, and significance of CD16 in the context of immune regulation. Key Takeways CD16, also known as FcγRIII, is crucial in both innate and adaptive immunity. There are two isoforms: CD16A on NK cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, and CD16B mainly on neutrophils. Functions include Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxi
…
5th Jan 2024
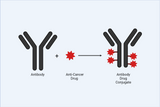
Positive Control vs Negative Control
T cell activation is a crucial process in the immune response, playing a pivotal role in how the body responds to pathogens and maintains immune homeostasis. This intricate process involves several key stages and molecules, each contributing to the effective functioning of T cells in the immune system. Understanding the Basics of T Cell Activation Direct conjugation involves the direct covalent attachment of the molecule to the antibody. This method is straightforward but requires careful control of reaction conditions to ensure specificity and retain antibody functionality. Indirect Conjugation Indirect conjugation uses a two-step process. Initially, a reactive group is
…
24th Aug 2023
PCR : Types and Applications
PCR stands as a cornerstone in molecular biology, enabling scientists to magnify and analyze fragments of DNA with incredible precision. In this blog, we'll embark on understanding of PCR – from its fundamental principles to the diverse techniques that have revolutionized research, diagnostics, and beyond. Key Takeaways PCR is a pivotal technique for DNA amplification, crucial in research, diagnostics, and forensics. Variants like Hot Start PCR, RT-PCR, and qPCR enhance specificity, analyze RNA, and quantify nucleic acids. Advances like High Fidelity Polymerase and Digital PCR offer precision in detecting mutations and low-abundance genes. Table of C
…
23rd Aug 2023