Blog
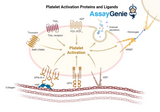
Platelet Adhesion Proteins and Ligands: Key Players in Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Platelet adhesion is a critical process in the maintenance of hemostasis, the body's response to bleeding. This intricate process involves a series of interactions between platelets, the cellular components of blood, and the vascular endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. At the core of this process are specific proteins and ligands that mediate the initial steps of platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation, ultimately leading to the formation of a platelet plug that aids in the cessation of bleeding. This article delves into the vital roles of platelet adhesion proteins and their ligands, shedding light on their significance in both physiological and pathological contexts.
…
13th Feb 2024
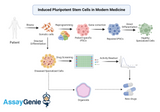
The Transformative Era of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Modern Medicine
The inception of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) has heralded a new dawn in the realm of biomedical research and regenerative medicine, setting the stage for groundbreaking advancements in disease treatment, drug discovery, and the prospect of personalized medicine. This pioneering technology, which allows the reprogramming of adult somatic cells back to an embryonic-like pluripotent state, has not only expanded our understanding of cellular biology but also opened up new avenues for therapeutic interventions, challenging the very paradigms of medical science. The Genesis of iPSC Technology: The journey of iPSC technology began with the landmark discovery by Shinya Yamanak
…
12th Feb 2024
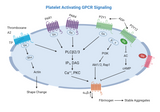
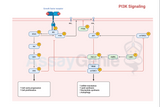
Unraveling the Mysteries of Platelet-Activating GPCR Signaling
Platelet activation plays a pivotal role in hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding and initiates wound healing. Central to this process is the activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which serve as key signal transducers on the surface of platelets. These receptors detect extracellular signals and initiate a cascade of intracellular events leading to platelet activation. This article delves into the mechanisms of platelet-activating GPCR signaling, highlighting its significance in thrombosis and potential therapeutic implications. The Role of GPCRs in Platelet Activation: GPCRs represent a vast and diverse family of receptors that are critical in various physiolog
…
9th Feb 2024
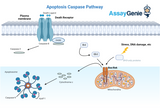
Apoptosis Caspase Pathways: A Closer Look at Cellular Suicide
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a fundamental process that plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of healthy tissues. Central to this process are caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that, once activated, orchestrate the cell's orderly demise. Understanding the caspase pathways not only sheds light on how our bodies maintain cellular balance but also provides insights into the mechanisms underlying various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. The Initiation of Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways Apoptosis can be triggered through two primary pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic, both of which eventually converge on the act
…
8th Feb 2024
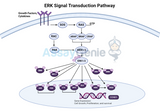
The ERK Signal Transduction Pathway: A Keystone in Cellular Communication and Response
The ERK signal transduction pathway stands as a fundamental mechanism in cellular biology, orchestrating a wide array of physiological processes, including cell division, differentiation, and survival. This pathway, part of the larger mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, is instrumental in conveying signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, thereby influencing gene expression and cellular outcomes in response to external stimuli. Understanding the ERK Pathway: The Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) pathway is initiated by the binding of growth factors, cytokines, and other extracellular ligands to their respective receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) on the ce
…
8th Feb 2024
The Battle of Antibiotics: Penicillin vs. Streptomycin
In the realm of medicine, antibiotics are akin to superheroes, combating bacterial infections with unwavering efficacy. Among these, two stalwarts stand out: penicillin and streptomycin. These antibiotics revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives since their discovery. However, understanding their differences and applications is crucial for effective medical management. Let's delve into the fascinating world of penicillin versus streptomycin and explore the unique properties of Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution. Penicillin: The Pioneer Discovered accidentally by Alexander Fleming in 1928, penicillin marked the dawn of the antibiotic era. Fl
…
8th Feb 2024
What is the difference between PBS and dPBS?
In the realm of biological and biochemical research, solutions play a pivotal role in various experimental procedures, from cell culture to molecular biology assays. Among the plethora of solutions utilized, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) stand out as crucial components. While both solutions share similarities, they possess distinct compositions and applications that merit exploration and understanding. Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS): A Versatile Solution PBS, a staple in laboratories worldwide, serves as a fundamental isotonic buffer solution utilized across diverse applications. Its composition typically consists of
…
8th Feb 2024
Transduction vs Transfection: Understanding Gene Delivery Techniques
In the realm of molecular biology and genetic engineering, the ability to deliver genetic material into cells is fundamental for various research and therapeutic purposes. Two common methods employed for this purpose are transduction and transfection. While both techniques facilitate the introduction of exogenous genetic material into cells, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and applications. This article aims to elucidate the distinctions between transduction and transfection, highlighting their respective advantages, limitations, and applications. Transduction: Transduction is a process by which genetic material is transferred into a cell via a viral vector.
…
8th Feb 2024
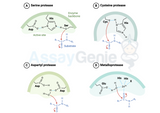
Protease vs Peptidase: Understanding Enzymatic Digestion
In the complex world of biochemical processes, enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing various reactions necessary for life. Among these enzymes, proteases and peptidases are fundamental players involved in the breakdown of proteins and peptides, respectively. While their names might sound similar and their functions somewhat overlap, they serve distinct purposes in the realm of enzymatic digestion. Let's delve deeper into their definitions, functions, and types to gain a comprehensive understanding. Protease: The Protein Digesters Proteases, also known as proteolytic enzymes or proteinases, are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds within proteins. These
…
6th Feb 2024
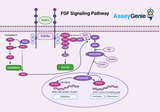
FGF Signaling Pathways: Unraveling the Complexities
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are pivotal in regulating cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and survival. The FGF signaling pathways play a critical role in embryonic development, tissue repair, metabolism, and cancer progression. This article delves into the mechanisms of FGF signaling, highlighting its significance in biological processes and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding FGF Signaling: FGF signaling is mediated through the interaction of FGFs with their cell-surface receptors, known as FGFRs. This interaction leads to receptor dimerization and activation, initiating a cascade of downstream signaling events. The specificity of FG
…
3rd Feb 2024
Innate Lymphoid Cells Differentiation: Guardians of Immune Homeostasis
Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs) represent a fascinating component of the immune system, playing a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and mounting rapid responses against pathogens. These cells lack antigen-specific receptors, distinguishing them from their adaptive counterparts, yet their ability to rapidly respond to environmental cues is vital for effective immune surveillance. One of the key aspects of ILCs' functionality lies in their differentiation process, a complex series of events that shape these cells into distinct subsets with specialized functions. Understanding ILC Differentiation: ILCs are broadly categorized into three main subsets based on their cy
…
2nd Feb 2024
p38 MAPK Signaling Review
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular responses to various stressors and inflammatory stimuli. It is a part of the larger MAPK superfamily, which also includes ERK and JNK pathways. The p38 MAPK pathway is involved in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune responses. Key Takeaways: p38 MAPK, part of the MAPK family, is key in cellular responses to stress and inflammation. This pathway regulates cell processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. The MAPK family includes ERKs, JNKs, and p38
…
1st Feb 2024
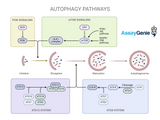
Understanding the Autophagy Pathway: A Critical Process in Cellular Maintenance
Autophagy, a fundamental cellular process, is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stressors. This self-eating mechanism involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components, playing a pivotal role in numerous physiological and pathological contexts. What is Autophagy? Autophagy, derived from the Greek words 'auto' (self) and 'phagy' (eating), is a process where cells degrade and recycle their own components. This process is essential for removing damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens, and for providing nutrients during starvation. Types of Autophagy: There are three main types of autophagy: Macroautophagy: The m
…
31st Jan 2024
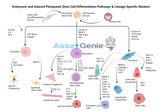
Embryonic Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Embryonic induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold immense potential in the field of regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types. Understanding the differentiation pathways and identifying lineage-specific markers are crucial for advancing stem cell research and therapy. Overview of Embryonic iPSC Differentiation: Embryonic iPSCs are characterized by their pluripotency, the ability to differentiate into any cell type of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This pluripotency is maintained through specific transcription factors such as Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog. The differentiation process involves a complex interpl
…
29th Jan 2024
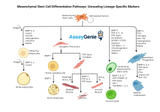
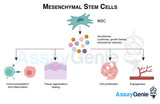
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Pathways: Unraveling Lineage-Specific Markers
The intricate process of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation is a cornerstone of developmental biology and regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells, renowned for their self-renewal capacity and multipotency, can differentiate into various cell types, contributing significantly to tissue repair and homeostasis. This article delves into the differentiation pathways of MSCs, focusing on lineage-specific markers that are pivotal in identifying and understanding these pathways. Understanding Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Mesenchymal stem cells are characterized by their ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and other cell types. Found in numerous
…
27th Jan 2024
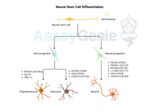
Neural Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Understanding the differentiation pathways of neural stem cells (NSCs) and the identification of lineage-specific markers is a cornerstone in the field of neurobiology and regenerative medicine. This knowledge is pivotal in unraveling the complexities of brain development and for advancing therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders. Introduction to Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Neural stem cells are unique in their ability to self-renew and differentiate into various neural lineages. This process is tightly regulated through intricate signaling pathways and the expression of specific lineage markers. NSC differentiation involves a stepwise progression into multipotent p
…
26th Jan 2024
Serum vs. Plasma: A Deep Dive into Their Molecular Makeup and Implications for ELISA
Blood plasma and serum are essential components of blood and have distinct molecular compositions and uses in the medical and research fields. This article aims to elucidate the differences between serum and plasma and respond to the most frequently asked questions. Key Takeaways: Serum is blood fluid without clotting factors; plasma contains these factors. They're crucial in medical research, including ELISA, to measure various analytes. Different collection methods are used for serum and plasma. What is Serum vs Plasma? Blood consists of red and white cells, platelets, and a liquid portion, known as plasma. When blood is collected and coagulates, the solid components,
…
24th Jan 2024
Articular Cartilage Extracellular Matrix
Articular cartilage, a key player in joint function, owes its unique properties to its extracellular matrix (ECM). This complex, highly specialized structure is not only fundamental in maintaining joint integrity but also in ensuring smooth and efficient movement. The ECM of articular cartilage is a masterful creation of nature, intricately designed to withstand compressive forces while providing a lubricated surface for articulation. Understanding the Composition of ECM in Articular Cartilage Proteoglycans: The Hydration Masters: The ECM of articular cartilage is rich in proteoglycans, primarily aggrecan. These macromolecules play a crucial role in retaining water, giving
…
23rd Jan 2024
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Navigating the Frontiers of Regenerative Medicine
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as pivotal players in the realm of regenerative medicine due to their unique properties and versatile potential. Originally discovered in the bone marrow, MSCs are now known to reside in various tissues, including adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and dental pulp. This article delves into the characteristics, therapeutic applications, and challenges surrounding mesenchymal stem cells, shedding light on their promising role in advancing medical treatments. Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: MSCs are multipotent progenitor cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. T
…
23rd Jan 2024
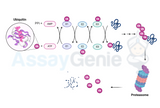
Ubiquitin and Its Role in Cellular Regulation: A Comprehensive Overview of Modifiers and Pathways
Ubiquitin is a small, highly conserved protein found in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes. The process of ubiquitination involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin molecules to target proteins, marking them for degradation, localization, or signaling. This post-translational modification is a dynamic and tightly regulated process that influences numerous cellular pathways. In this article, we will explore the structure and function of ubiquitin, its related modifiers, and the intricate pathways involved in ubiquitin-mediated cellular regulation. Structure and Function of Ubiquitin: Ubiquitin, a 76-amino acid protein, i
…
23rd Jan 2024
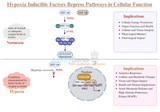
HIF Repress Pathways: An Insight into Cellular Oxygen Homeostasis
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are pivotal in the cellular response to oxygen deprivation. These transcription factors regulate various aspects of cellular and systemic homeostasis in response to hypoxia. Central to their role is the activation of genes that aid in adaptation to low oxygen conditions. However, equally important, yet less emphasized, is their ability to repress certain pathways. This article delves into the mechanisms and implications of HIF-mediated repression pathways in cells. Mechanisms of HIF-Mediated Repression Transcriptional Repression Through HIF: HIFs function primarily as transcriptional activators. However, they can indirectly repress gene expr
…
22nd Jan 2024
MAPK Oxidative Stress Pathway: A Journey through Cellular Signaling
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-e5394be4-6636-4558-9e32-20ef2f209b2b' })
In the intricate world of cellular signaling, the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes. One facet of this pathway that has garnered significant attention is its involvement in managing oxidative stress—a condition marked by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the cell's antioxidant defense mechanisms. In this article, we embark on a journey through the MAPK oxidative stress pathway, exploring its intri
…
18th Jan 2024
Adipokines and Insulin Signaling Pathways: An In-Depth Exploration
The prevalence of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders has risen dramatically in recent decades, presenting a significant global health challenge. Adipose tissue, once considered merely a storage site for excess energy, is now recognized as an active endocrine organ secreting a myriad of bioactive molecules known as adipokines. Among these adipokines, a key player in metabolic regulation is insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Adipokines: Key Regulators of Metabolism Adipokines function as critical mediators between adipose tissue and various organs, influencing metabolic processes such as glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and inflammation. Lep
…
18th Jan 2024
Unraveling the Complexity of the Notch Signaling Pathway: A Key Player in Development and Disease
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cellular communication system that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and immune system function. Discovered over a century ago, the Notch pathway has since emerged as a complex and versatile signaling network that regulates cell fate decisions and maintains tissue integrity. This article aims to provide an overview of the Notch signaling pathway, its components, and its diverse roles in development and disease. Basic Components of the Notch Signaling Pathway: The Notch pathway consists of a family of transmembrane receptors, known as Notch receptors, a
…
17th Jan 2024