Blog
MAPK Oxidative Stress Pathway: A Journey through Cellular Signaling
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-e5394be4-6636-4558-9e32-20ef2f209b2b' })
In the intricate world of cellular signaling, the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes. One facet of this pathway that has garnered significant attention is its involvement in managing oxidative stress—a condition marked by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the cell's antioxidant defense mechanisms. In this article, we embark on a journey through the MAPK oxidative stress pathway, exploring its intri
…
18th Jan 2024
Adipokines and Insulin Signaling Pathways: An In-Depth Exploration
The prevalence of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders has risen dramatically in recent decades, presenting a significant global health challenge. Adipose tissue, once considered merely a storage site for excess energy, is now recognized as an active endocrine organ secreting a myriad of bioactive molecules known as adipokines. Among these adipokines, a key player in metabolic regulation is insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Adipokines: Key Regulators of Metabolism Adipokines function as critical mediators between adipose tissue and various organs, influencing metabolic processes such as glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and inflammation. Lep
…
18th Jan 2024
VEGF-A VEGFR-2 Signaling: Decoding the Blueprint of Angiogenesis for Therapeutic Insights
The orchestration of angiogenesis, the process by which new blood vessels form from pre-existing ones, is a complex symphony regulated by various molecular players. At the forefront of this intricate dance is the VEGF-A VEGFR-2 signaling pathway, a pivotal mechanism that propels the growth and maintenance of blood vessels. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the molecular details of this pathway, shedding light on its fundamental role in angiogenesis and its implications in both health and disease. VEGF-A: A Master Regulator of Angiogenesis: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A) stands as a beacon among the VEGF family of growth factors. Produced
…
18th Jan 2024
Unraveling the Complexity of the Notch Signaling Pathway: A Key Player in Development and Disease
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cellular communication system that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and immune system function. Discovered over a century ago, the Notch pathway has since emerged as a complex and versatile signaling network that regulates cell fate decisions and maintains tissue integrity. This article aims to provide an overview of the Notch signaling pathway, its components, and its diverse roles in development and disease. Basic Components of the Notch Signaling Pathway: The Notch pathway consists of a family of transmembrane receptors, known as Notch receptors, a
…
17th Jan 2024
Unlocking Cellular Adaptation: The HIF Enhancer Pathway and Its Implications in Hypoxia Response
Hypoxia, or low oxygen levels, poses a significant challenge to cells, necessitating rapid and efficient adaptation mechanisms. The Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) pathway is a well-known regulator of cellular responses to hypoxia, orchestrating the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, and glycolysis. It plays a pivotal role in cellular adaptation to low oxygen conditions, ensuring survival and homeostasis in diverse physiological and pathological settings. Recent studies have uncovered an additional layer of complexity in HIF regulation, known as the HIF enhancer pathway. This article explores the mechanisms, regulation, and significance of the HIF enhancer pa
…
12th Jan 2024
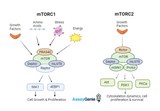
Understanding the mTOR Signaling Pathway: A Key Player in Cell Growth and Metabolism
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway is a crucial regulator of cell growth and metabolism, responding to environmental cues and cellular energy status. This pathway's significance lies in its role in various physiological processes and its implications in numerous pathologies, including cancer, neurological diseases, and metabolic disorders.
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-84730463-591d-4e27-a9ad-0dd265e606e9' })
Figure: An overview of mTORC signaling pathways. Overview of mTOR Signaling: mTOR, a serine/threonine kinase, functions as a part
…
5th Jan 2024
MAPK Signaling: Unraveling the Pathway of Mitogen Stimulation
Introduction to MAPK Signaling in Cellular Processes Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways are crucial in transmitting signals from the cell surface to the DNA in the cell nucleus. These pathways play a pivotal role in various cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and response to environmental stress. Understanding the intricacies of the MAPK signaling pathway, especially in response to mitogen stimulation, is fundamental for advancing our knowledge in cell biology and therapeutic strategies. The Mechanism of MAPK Signaling Pathway
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
wi
…
5th Jan 2024
Deciphering the Intricacies of TGF-Beta Signaling Pathway
Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in orchestrating various cellular processes, ranging from embryonic development to tissue homeostasis and immune response modulation. This intricate pathway is crucial for maintaining cellular balance, and dysregulation can contribute to a myriad of diseases, including cancer, fibrosis, and immune disorders. In this article, we delve into the key components and mechanisms that characterize the TGF-β signaling pathway. Key Components of TGF-Beta Signaling Pathway: TGF-β Ligands: The TGF-β family comprises multifunctional cytokines, with TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 being
…
24th Aug 2023
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis, a dynamic bi-directional communication system linking the gastrointestinal (GI) tract with the central nervous system (CNS), has emerged as a focal point in scientific research. This intricate network underscores the interconnectedness of physiological processes, revealing how the gut microbiota interfaces with cognitive functions. Beyond its conventional digestive role, the gut plays a pivotal role in shaping neurological processes, emotions, and behavior. Through neural pathways, hormonal signaling, and immune mediators, the gut and brain engage
…
24th Aug 2023
The role of IFN gamma in inflammation, cancer and autoimmune disease
Interferons are key cytokines in the immune system, crucial for combating viral and bacterial infections, with significant roles in both innate and adaptive immunity responses. Key Takeaways Interferons (IFNs) are crucial cytokines in immune responses against viral and bacterial challenges. There are two main types: Type I (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and Type II (IFN-gamma), each with unique roles and receptor interactions. IFN-gamma, a Type II interferon, is pivotal in innate and adaptive immunity, produced mainly by T cells and NK cells. What are Interferons? Interferons (IFN) are a family of cytokines which, upon secretion, play a central role in mediating the innate an
…
22nd Aug 2023
Characteristics of scaffold protein
Scaffold Proteins Environmental stimuli result in different biological responses including cell growth, proliferation or apoptosis. How cells translate specific stimuli into a specific cellular response is not well understood. Scaffold proteins are evolutionarily conserved proteins that play important roles in coordinating signalling events in eukaryotic cells. These proteins, conserved through evolution, serve as essential organizers, helping cells translate external cues into specific actions. This blog post delves into the practical world of scaffold proteins, exploring their fundamental functions and shedding light on how they influence cellular signaling pathways. Key T
…
18th Aug 2023
JAK-STAT Signalling and Cytokines: The What, How, and Why
In the intricate landscape of cellular communication, lies a sophisticated system known as JAK-STAT signaling. JAK-STAT stands for Janus kinase's and signals transducer and activator of transcription proteins This cellular dialogue plays a vital role in relaying messages between cells, ensuring our body responds accurately to a myriad of signals. Think of cytokines as molecular couriers in this intricate conversation. These specialized couriers bind to specific cell receptors, triggering a series of events that culminate in the activation of specific genes. These activa
…
16th Aug 2023
CXCL16 – Review
CXCL16
CXCL16, a unique member of the CXC chemokine family, stands at the crossroads of immune modulation and vascular biology. Initially discovered as a chemokine, CXCL16 operates beyond its chemotactic role by serving as a transmembrane protein that can bind to its receptor, CXCR6. This dual functionality endows CXCL16 with the ability to regulate immune cell trafficking, particularly those expressing CXCR6, and to participate in diverse physiological processes such as inflammation, atherosclerosis, and tissue repair. CXCL16's intriguing capacity to bridge immune responses with vascular dynamics underscores its significance as a multifaceted player
…
15th Aug 2023
TNF cytokines and their Receptors
The human body is a complex and intricate system where various components work together to maintain health and combat potential threats. Among these essential players are the TNF cytokines, a superfamily of cell-signaling proteins that play a crucial role in regulating the immune system and other critical physiological processes. These cytokines, along with their corresponding receptors, form a dynamic network that orchestrates immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and much more. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of TNF cytokines and their receptors, exploring their struc
…
27th Jul 2023
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF)
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a cytokine that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. It has gained significant attention in the field of leukemia research due to its multifaceted functions and potential therapeutic applications. In this blog the molecular structure, biological sources, signaling pathways, and the role of LIF in leukemia will be discussed.
Table of Contents
…
13th Jul 2023
VEGF: Inflammation and Tumourigenesis
What is VEGF?
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (VEGFs) are a group of homodimeric polypeptides, and are master regulators of vascular development, maintenance and angiogenesis. VEGF is also a potent growth factor, and is produced by macrophages and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Members of the VEGF family include 5 structurally related proteins (VEGFA-D, and placental growth factor (PIGF), which are further individually subdivided based on alternative splicing. VEGF acts as a potent stimulator of angiogenesis, promoting the growth and survival of endothelial cells, and is essential for embryonic development and tissue re
…
12th Jul 2023
Growth Factors: Key Players in Biological Processes
Growth factors play a vital role in the complex web of biological processes, serving as key regulators in various essential events. They exert significant influence over crucial cellular behaviors such as proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
Acting as molecular messengers, growth factors facilitate communication between cells and tissues, ensuring coordinated functionality.
By exploring the defining characteristics and functions of growth factors, we gain a deeper understanding of their profound contributions to embryonic development, tissue re
…
20th Jun 2023
An Introduction into EV Markers
Extracellular Vesicles
What are Extracellular Vesicles?
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny, spherical structures that are released by cells into the extracellular environment. They are usually composed of a lipid bilayer membrane and contain various biomolecules, such as proteins, lipids, and RNA. EVs play a critical role in intercellular communication, as they are capable of transferring functional molecules and information between cells. This allows cells to coordinate their activities, pro
…
22nd Feb 2023
A Quick Guide To Mycoprotein
Mycoprotein is an alternative source of protein that can be used in place of meat. It is made from a fungi called Fusarium venenatum, and is consumed by vegetarians and vegans as a meat substitute. It is also a good source of iron and B vitamins. Mycoprotein has a chewy texture and can be used in many different recipes. Mycoprotein can be found in many different stores and can be found in the refrigerated or frozen section. Mycoprotein is also available online. Mycoprotein can be used in many different recipes. It can be cooked and used as a meat substitute in burgers, tacos, stir-fries, and more. Mycoprotein can also be used as an ingredient in pasta dishes, soups, and salads. If
…
4th Aug 2022
Protein Kinases: Overview, Classification and Therapeutic Potential
Kinases, key enzymes in cellular signaling, phosphorylate proteins to regulate crucial processes, and their modulation has significant implications in disease treatment. Key Takeaways: Kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate proteins, influencing cell processes. They are categorized into serine/threonine, tyrosine, and dual specificity kinases. Kinases are crucial in cell signaling, growth, metabolism, and homeostasis. Dysregulation of kinases is linked to diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Protein kinase inhibitors hold therapeutic potential in treating various diseases. What are Kinases? Understanding their Functions, Types and Structure Kinases are
…
13th Jun 2022
EGF Family
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) which triggers ligand-induced dimerization which activates the intrinsic protein-tyrosine kinase activity of EGFR. This in turn initiates a signal transduction cascade that results in various biochemical changes within the cell being targeted by EGF. This ultimately leads to DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Members of this protein family are all similar due to their shared structural and functional characteristics.
Each member of the EGF family have at least one common structural motif, the EGF domain, which is character
…
23rd May 2022
The Notch Signalling Pathway: Its Steps and Impacts
Notch signalling pathway review
The Notch signalling pathway is a highly conserved intercellular signalling pathway that regulates various cellular processes. The Notch receptor is a transmembrane protein that is activated by the binding of Notch ligands, which are secreted proteins. There are four known Notch ligands: Jagged, Delta, Serrate, and Lag-related protein. Notch receptors are activated by the binding of a Notch ligand to the receptor's extracellular domain. This binding results in the proteolytic cleavage of the receptor by furin-like proteases. The cleaved Notch intracellular domain (NICD) of the receptor translocates to the nucleus where it interacts with transcri
…
4th Mar 2022
Insulin Signaling and RTK: An Overview
Explore the intricate world of Insulin Signaling and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs), pivotal in regulating metabolism and influencing diseases like cancer and atherosclerosis. Key Takeaways: Insulin signaling involves receptor activation, signal transduction, and gene expression. Insulin receptors, a type of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK), regulate metabolism and cell responses. The Ras/MAP kinase and PI3K pathways are crucial in insulin signaling. Insulin signaling impacts atherosclerosis and cancer, with RTK inhibitors showing therapeutic potential.
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_E
…
23rd Feb 2022
Exosomes - Discovery, Cargo, Biogenesis & Functions
by Ryan Wallis, PhD student, QMUL, Blizard Institute
The microscopic world of cell biology was first explored by Robert Hooke in the 17th century and published in his work, Micrographia, in 1665. He marvelled at the revelation that an organism such as a cork plant was actually comprised of tiny “Cellula” resembling the small chambers occupied by monks. His insight into this invisible domain was the first in a line of discoveries which have transformed our understanding of biology, health and disease. As technology has progressed, scientific discovery has flourished, and the invention of electron microscopy has allowed us to observe the world on an even smaller
…
20th Jan 2022