Blog
TNFR2: Taming Regulatory T Cells to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity
In recent years, cancer immunotherapy has become a powerful tool for treating various malignancies. One promising approach involves targeting the tumor microenvironment, particularly regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play a key role in suppressing the immune response against tumors. TNFR2 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2) is highly expressed on Tregs within the tumor, making it an attractive target for immunotherapy. Antibodies such as https://www.assaygenie.com/tnfr2-taming-regulatory-t-cells-to-enhance-anti-tumor-immunity/, which block TNFR2, have the potential to enhance anti-tumor immunity by reducing the suppressive function of Tregs and promoting a more robust immune resp
…
14th Oct 2024
CD27 Activation: Strengthening the Immune Army Against Cancer
Harnessing the immune system to fight cancer has become a pivotal strategy in modern oncology. A key component in this fight is CD27, a receptor that plays a crucial role in T-cell activation and immune memory. CD27 stimulation can enhance the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells, making it an attractive target for immunotherapy. Antibodies such as AT124-5 are being developed to activate CD27, offering new hope for strengthening the immune response against cancer. What is CD27? CD27 is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, expressed primarily on T cells and B cells. Its primary function is to enhance T-cell activation, support the formation of
…
14th Oct 2024
B7-H4: A New Frontier in Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
The recent advances in cancer immunotherapy have brought new opportunities to harness the body’s immune system against tumors. Among these advancements is the targeting of immune checkpoints, which play a significant role in immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment. A relatively new target of interest is B7-H4, a member of the B7 family of immune-regulatory proteins. Emerging research indicates that blocking B7-H4 with antibodies such as MIH43 may offer promising therapeutic benefits in various cancers. This article explores the role of B7-H4, its biological functions, and how anti-B7-H4 therapies may improve cancer treatment outcomes.Assay Genie · B7 - H4 A New Fron
…
14th Oct 2024
LILT: A Novel Immune Checkpoint for Cancer Therapy
Recent advances in immunotherapy have highlighted the importance of targeting immune checkpoints to enhance the immune system’s ability to combat cancer. A new potential target in this growing field is LILT (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript), an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. Blocking LILT with antibodies like 3G4 offers a promising strategy to restore immune surveillance and improve the effectiveness of cancer therapies.Assay Genie · LILT-A Novel Immune Checkpoint For Cancer TherapyWhat is LILT?Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript (LILT) is a family of receptors expressed predominantly on immune cells, particular
…
14th Oct 2024
ICOS: Stimulating the Immune System for Superior Cancer Therapy
Immunotherapy has transformed the landscape of cancer treatment by leveraging the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. A key player in this process is Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS), a molecule that enhances T-cell activation and function. Anti-ICOS antibodies, such as C398.4A, are being explored to amplify the immune response, making them a promising addition to cancer therapy strategies. Assay Genie · ICOS Stimulating The Immune System For Superior Cancer TherapyWhat is ICOS? Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS) is a member of the CD28 family of co-stimulatory receptors, which are critical for T-cell activation and survival. ICOS is expres
…
14th Oct 2024
PVR: Balancing Immune Activation and Suppression in Cancer
PVR (Poliovirus receptor), also known as CD155, is a molecule that plays a dual role in regulating the immune response within the tumor microenvironment. While initially discovered as a receptor for poliovirus, PVR is now recognized for its involvement in modulating immune cell interactions, particularly in cancer. Its expression on tumor cells can both activate and suppress the immune system, making it an intriguing target for cancer immunotherapy. Antibodies such as Anti-PVR (e.g., D172) are being explored as potential therapeutic agents to restore immune function and improve tumor clearance. Assay Genie · PVR Balancing Immune Activation And Suppression In CancerPVR: An O
…
10th Oct 2024
CD28: Amplifying T Cell Responses for Better Tumor Clearance
The CD28 molecule plays a crucial role in amplifying T cell activation, which is critical for mounting effective immune responses against tumors. By engaging with co-stimulatory molecules, CD28 enhances T cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production, making it an important target in cancer immunotherapy. In particular, Anti-CD28 antibodies, such as 37.51, are being explored to boost the immune system’s ability to fight cancer, offering a promising avenue for improved tumor clearance.Assay Genie · CD28: Amplifying T Cell Responses For Better Tumor ClearanceCD28 Overview: A Key Co-Stimulatory MoleculeCD28 is a co-stimulatory receptor expressed on T cells, essential for fu
…
10th Oct 2024
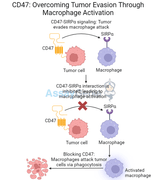
CD47: Overcoming Tumor Evasion Through Macrophage Activation
One of the greatest challenges in cancer therapy is how tumors evade immune detection. Among the mechanisms cancer cells exploit, the CD47 pathway has emerged as a major player in helping tumors avoid immune attack. CD47, known as the “don’t eat me” signal, interacts with immune cells to prevent their destruction by the body’s defense systems. However, novel therapies targeting CD47, such as anti-CD47 antibodies like MIAP301, are showing promising results in reversing this evasion strategy by activating macrophages and enhancing the body's ability to eliminate tumor cells.Assay Genie · CD47 Overcoming Tumor Evasion Through Macrophage ActivationWhat is CD47?CD7 is a transmembrane
…
8th Oct 2024
4-1BB: Energizing Immune Cells to Overcome Tumor Resistance
Immunotherapy has become a central pillar in the fight against cancer, with a focus on enhancing the body’s natural defenses. Among the molecules at the forefront of immunotherapeutic research is 4-1BB (CD137), a co-stimulatory receptor that plays a key role in amplifying immune cell responses. Agonists like 1D8 target 4-1BB, unleashing potent anti-tumor immunity. This article delves into the function of 4-1BB, how agonists enhance immune responses, and their potential in https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/targetting-immune-checkpoints-as-cancer-therapyAssay Genie · 4 - 1BB Energizing Immune Cells To Overcome Tumor ResistanceWhat is 4-1BB (CD137)?4-1BB, also known as CD137, is a co
…
8th Oct 2024
OX40 Agonists: Revitalizing the Immune Response in Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment options, offering strategies to harness the immune system to target and destroy tumors. One emerging area of interest is the use of OX40 agonists, like OX86, which play a crucial role in amplifying the immune response against cancer cells. OX40 agonists show promise in several cancer models, potentially improving the efficacy of existing immunotherapies. This article will explore the mechanism of OX40, the role of OX40 agonists in cancer treatment, and ongoing clinical developments. Understanding OX40 and Its Role in Immunity OX40, also known as CD134, is a costimulatory receptor that belongs to the tumor necrosis facto
…
8th Oct 2024
Targeting CD200: Unlocking Immune Suppression in Tumors
Immune evasion is one of the hallmarks of cancer, where tumor cells employ various strategies to suppress immune responses and prevent destruction by the body’s defense systems. CD200, a transmembrane protein, has emerged as a key player in mediating immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Targeting CD200 with therapies like OX90 is a promising approach to disrupt this immune evasion, allowing the immune system to mount a more effective attack against cancer cells. This article delves into the role of CD200 in tumors, the therapeutic potential of CD200-targeting agents, and the ongoing research surrounding this pathway. Assay Genie · Targeting CD200 Unlocking Immu
…
8th Oct 2024
SIRPα Inhibition: Clearing Tumors by Promoting Phagocytosis
Cancer cells are adept at avoiding destruction by the immune system, often exploiting specific pathways to escape detection and elimination. One of these key mechanisms involves the SIRPα-CD47 axis, which prevents macrophages and other phagocytic cells from attacking tumor cells. SIRPα inhibitors, such as P84, are emerging as novel immunotherapies that block this protective signal, allowing the immune system to recognize and engulf cancer cells. This article explores the role of SIRPα inhibition in enhancing phagocytosis, promoting anti-tumor immunity, and the therapeutic potential of anti-SIRPα agents like P84 in cancer treatment. Assay Genie · SIRPα Inhibition Clearing Tu
…
8th Oct 2024
Harnessing CD40 for Potent Anti-Tumor Immune Responses
CD40, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily, plays a pivotal role in regulating immune responses, particularly in activating antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and promoting T cell activation. Over the past decade, CD40 has emerged as a promising target in cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to stimulate both the innate and adaptive immune systems, driving potent anti-tumor responses. By activating CD40, researchers aim to amplify immune reactions that enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This article explores the biology of CD40, its role in anti-tumor immunity, and its potential in cancer immunotherapy.What is
…
4th Oct 2024
Targeting VISTA: Unleashing the Power of T Cells in Cancer Therapy
V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) is an emerging immune checkpoint receptor that plays a key role in suppressing T cell activity within the tumor microenvironment (TME). As a negative regulator of immune responses, VISTA helps tumors evade detection by dampening the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells. Recent research into targeting VISTA has highlighted its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer immunotherapy. By inhibiting VISTA, scientists aim to unleash the full power of T cells and other immune cells to attack and destroy tumors. This article explores VISTA’s function in immune regulation, its role in cancer progression, and the potential o
…
3rd Oct 2024
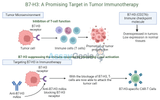
B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor Immunotherapy
B7-H3, also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules that has emerged as a compelling target in tumor immunotherapy. Initially recognized for its role in regulating immune responses, B7-H3 has gained increasing attention due to its overexpression in various cancers and its ability to promote immune evasion. As a result, B7-H3 has become a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, offering new hope for treatments aimed at improving patient outcomes by enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight tumors. AudioAssay Genie · B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor ImmunotherapyWhat is B7-H3? B7-H3 is an immune regulatory molecule expres
…
3rd Oct 2024
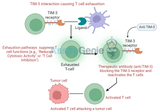
TIM-3: Targeting T Cell Exhaustion for Better Immunotherapy Outcomes
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3) is an immune checkpoint receptor that plays a pivotal role in T cell exhaustion, a state where T cells lose their ability to effectively combat cancer or infections. As a result, TIM-3 has gained significant attention as a therapeutic target to enhance immunotherapy outcomes. This article delves into the biological functions of TIM-3, its involvement in T cell exhaustion, and the potential of TIM-3 inhibitors in improving cancer immunotherapy and treatments for chronic diseases.What is TIM-3?TIM-3 is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on various immune cells, including CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, regulatory T cells
…
3rd Oct 2024
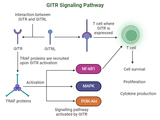
GITR: Boosting T Cell Activation for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy
Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) is an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a crucial role in regulating T cell activation and survival. In recent years, GITR has emerged as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to enhance immune responses against tumors. By stimulating T cells, particularly effector T cells, and inhibiting the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), GITR-based therapies aim to boost the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells. This article explores the function of GITR in immune regulation and its potential for enhancing cancer immunotherapy.Assay Genie · GITR Boosting T Cell Activation Fo
…
3rd Oct 2024
CD25 and Tregs: Understanding the Role of Regulatory T Cells in Tumor Immunity
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a crucial role in maintaining immune balance by suppressing excessive immune responses that could lead to tissue damage. However, in the context of cancer, Tregs can be problematic because they also suppress the immune system’s ability to attack and eliminate tumors. One of the key markers of Tregs is CD25, which is the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. This article explores the role of CD25 and Tregs in tumor immunity, shedding light on how these cells contribute to tumor growth and how they can be targeted to improve cancer immunotherapy outcomes.Assay Genie · CD25 And Tregs Understanding The Role Of Regulatory T Cells In Tumor ImmunityWhat Are
…
3rd Oct 2024
NK Cells: Unlocking the Potential of Natural Killer Cells in Cancer Therapy
Natural killer (NK) cells are a crucial component of the innate immune system and play a significant role in eliminating tumor cells. Unlike T cells, NK cells can recognize and kill cancer cells without prior sensitization, which makes them particularly valuable in cancer immunotherapy. As research progresses, novel therapies aim to harness and enhance NK cells' innate ability to fight cancer. This article explores NK cells' function, their role in cancer immunosurveillance, and the innovative therapeutic strategies being developed to improve cancer treatment outcomes.Assay Genie · NK Cells: Unlocking the Potential of Natural Killer Cells in Cancer TherapyWhat Are NK Cells?NK ce
…
3rd Oct 2024
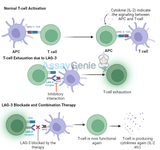
LAG-3: Revitalizing T Cells in Exhaustion for Combination Therapies
Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3 (LAG-3) is an immune checkpoint receptor that plays a critical role in regulating T cell function. In recent years, LAG-3 has emerged as a potential target for combination therapies aimed at overcoming T cell exhaustion, particularly in the context of cancer immunotherapy. By revitalizing exhausted T cells, LAG-3 inhibitors offer a new avenue for enhancing the efficacy of existing therapies like PD-1 inhibitors. This article explores LAG-3’s role in immune modulation and its potential as a therapeutic target.Understanding T Cell Exhaustion and LAG-3T cell exhaustion is a state in which T cells progressively lose their functionality after prolonged ex
…
2nd Oct 2024
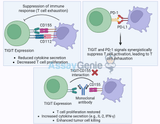
TIGIT: A New Frontier in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Immunotherapy
TIGIT (T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains) has emerged as a promising target in cancer immunotherapy and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. As a checkpoint receptor, TIGIT plays a critical role in regulating immune responses by inhibiting the activity of immune cells, especially T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. By manipulating TIGIT pathways, scientists aim to develop therapies that enhance immune responses against cancer or dampen harmful immune activity in autoimmune disorders.Understanding TIGIT's Role in Immune RegulationTIGIT belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is primarily expressed on T cells, including regulatory T cells (Tregs), activated
…
1st Oct 2024
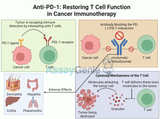
Anti-PD-1: Restoring T Cell Function in Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment landscape for various malignancies. One of the most promising therapeutic strategies is the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly anti-PD-1 (programmed death-1) antibodies. These drugs enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells by restoring the function of T cells, which are often suppressed in cancer patients.Assay Genie · Anti-PD-1: Restoring T Cell Function in Cancer ImmunotherapyIntroduction to PD-1 and Its Role in Immune EvasionPD-1 is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on T cells. It plays a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis by preventing overactivation of T
…
24th Sep 2024
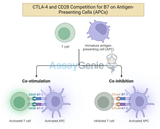
Anti-CTLA-4: Unleashing the Power of T Cells in Combination Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the body's immune system to fight malignancies. Among the notable advancements in this field is the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors. One of the key players is anti-CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), a monoclonal antibody that disrupts immune checkpoints and enhances T cell activation. Anti-CTLA-4 has shown immense promise, especially when used in combination immunotherapy. This article delves into how anti-CTLA-4 works, its role in unleashing the power of T cells, and its synergistic effects in combination therapies.Assay Genie · Anti - CTLA - 4 Unleashing The Power Of T Cells In Combi
…
24th Sep 2024
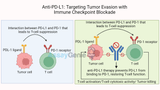
Anti-PD-L1: Targeting Tumor Evasion with Immune Checkpoint Blockade
IntroductionCancer cells have developed sophisticated mechanisms to evade the immune system, particularly through the inhibition of T-cell responses. One such mechanism involves the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which binds to its receptor PD-1 on T cells, leading to the suppression of immune activity. Anti-PD-L1 therapies, as part of the broader category of immune checkpoint inhibitors, have transformed cancer treatment by restoring immune system function and enhancing the body's ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. This article explores the role of PD-L1 in immune evasion and how its inhibition can significantly impact cancer therapy outcomes.Assay Genie · Anti
…
22nd Sep 2024