Blog
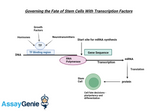
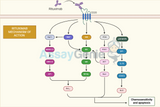
Governing the Fate of Stem Cells With Transcription Factors
The intricate process of stem cell differentiation and self-renewal is a cornerstone of developmental biology and regenerative medicine. At the heart of this complex regulatory mechanism are transcription factors (TFs), which play a pivotal role in determining the fate of stem cells. These proteins bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the transcription of genes, thereby influencing cell fate decisions and maintaining the delicate balance between pluripotency and differentiation. The Essence of Stem Cells and Their Importance: Stem cells are the architects of development, possessing the unique abilities of self-renewal and differentiation. They serve as a foundational eleme
…
16th Feb 2024
Unraveling the Synergy: How Growth Factors Cooperate to Promote Tumorigenesis
In the intricate ballet of cellular communication and regulation, growth factors play pivotal roles in guiding the processes of cell growth, division, and differentiation. These proteins are essential for normal development and tissue repair. However, when their signaling pathways become co-opted or dysregulated, they can also act as key players in the development and progression of cancer. This article delves into the complex interplay of growth factors and their cooperation in promoting tumorigenesis, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms that underlie cancer development and offering insights into potential therapeutic interventions. The Fundamental Role of Growth Factors in C
…
15th Feb 2024
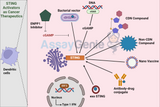
STING Activators As Cancer Therapeutics
The STING (Stimulator of Interferon Genes) pathway plays a pivotal role in the innate immune system's response to cancerous cells and DNA viruses. Exploiting this pathway through STING activators presents a promising avenue for cancer therapeutics. This article delves into the mechanism of action of STING activators, their therapeutic potential, challenges in their development, and the latest advancements in the field. Understanding the STING Pathway The Biological Role of STING The STING pathway is integral to the innate immune response, detecting cytosolic DNA to trigger the production of type I interferons and other cytokines. This response is crucial for the immune syst
…
15th Feb 2024
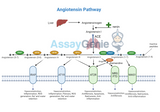
Angiotensin Pathways: Unlocking the Secrets to Blood Pressure Regulation and Beyond
The angiotensin pathway is a pivotal hormonal system that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance within the body. This complex biochemical cascade not only underpins essential physiological processes but also serves as a target for therapeutic interventions in conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. Understanding the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): At the heart of the angiotensin pathway lies the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), a regulatory circuit that influences systemic vascular resistance and, consequently, arterial blood pressure. The RAS pathway initiates with the synthesis of angio
…
14th Feb 2024
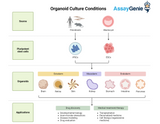
Optimizing Organoid Culture Conditions: Paving the Way for Revolutionary Advances in Biomedical Research
In the dynamic landscape of biomedical research, organoids have emerged as a groundbreaking tool, offering three-dimensional (3D) models that mimic the complex architecture and functionality of human organs. These miniature, self-organizing structures have revolutionized our approach to understanding human development, disease modeling, and drug discovery. However, the key to harnessing their full potential lies in optimizing organoid culture conditions. This intricate process involves fine-tuning the biochemical and physical environment to support the growth, differentiation, and maturation of organoids. This article delves into the critical aspects of organoid culture, including the se
…
14th Feb 2024
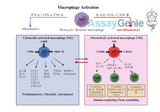
Macrophage Activation: A Keystone in Immune Response and Therapeutic Potential
In the intricate tapestry of the immune system, macrophages play a pivotal role, orchestrating a wide range of biological responses that protect the body against pathogens, remove cellular debris, and promote tissue repair. Macrophage activation is a complex process, integral to both innate and adaptive immunity, influencing disease outcomes and offering promising avenues for therapeutic intervention. This comprehensive exploration delves into the mechanisms of macrophage activation, its dualistic nature, and the implications for disease treatment and immune modulation. The Fundamentals of Macrophage Activation: Macrophages, derived from monocytes, are versatile cells present in
…
13th Feb 2024
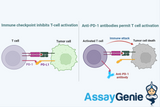
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
The advent of immune checkpoint targeting marks a significant milestone in the oncological field, offering a beacon of hope for patients battling cancer. This innovative approach leverages the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells, a method that stands in stark contrast to traditional therapies. This article delves deep into the essence of immune checkpoint therapy, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and the horizon it promises for future cancer treatments. Introduction to Immune Checkpoints Immune checkpoints are critical regulators of the immune system's response to various cells, including cancer cells. They are designed to prevent the immune s
…
13th Feb 2024
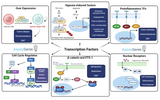
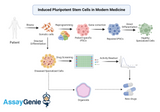
The Transformative Era of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Modern Medicine
The inception of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) has heralded a new dawn in the realm of biomedical research and regenerative medicine, setting the stage for groundbreaking advancements in disease treatment, drug discovery, and the prospect of personalized medicine. This pioneering technology, which allows the reprogramming of adult somatic cells back to an embryonic-like pluripotent state, has not only expanded our understanding of cellular biology but also opened up new avenues for therapeutic interventions, challenging the very paradigms of medical science. The Genesis of iPSC Technology: The journey of iPSC technology began with the landmark discovery by Shinya Yamanak
…
12th Feb 2024
Deciphering B Cell Cancers With a Rituximab Biosimilar
The fight against B cell cancers, a challenging spectrum of hematologic malignancies, has entered a new era with the introduction of rituximab biosimilars. These biosimilars promise to extend the revolutionary benefits of rituximab, a cornerstone in the treatment of diseases like non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), to a broader patient population. This detailed exploration covers the complex nature of B cell cancers, the therapeutic mechanism of rituximab, and the significant potential of its biosimilars. Introduction B cell cancers represent a diverse group of malignancies that require nuanced therapeutic approaches. The advent of biosimilar thera
…
5th Feb 2024
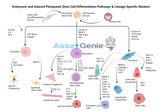
Embryonic Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation: Pathways and Lineage-Specific Markers
Embryonic induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) hold immense potential in the field of regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types. Understanding the differentiation pathways and identifying lineage-specific markers are crucial for advancing stem cell research and therapy. Overview of Embryonic iPSC Differentiation: Embryonic iPSCs are characterized by their pluripotency, the ability to differentiate into any cell type of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This pluripotency is maintained through specific transcription factors such as Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog. The differentiation process involves a complex interpl
…
29th Jan 2024
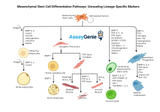
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Pathways: Unraveling Lineage-Specific Markers
The intricate process of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation is a cornerstone of developmental biology and regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells, renowned for their self-renewal capacity and multipotency, can differentiate into various cell types, contributing significantly to tissue repair and homeostasis. This article delves into the differentiation pathways of MSCs, focusing on lineage-specific markers that are pivotal in identifying and understanding these pathways. Understanding Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Mesenchymal stem cells are characterized by their ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and other cell types. Found in numerous
…
27th Jan 2024
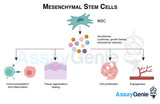
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Navigating the Frontiers of Regenerative Medicine
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as pivotal players in the realm of regenerative medicine due to their unique properties and versatile potential. Originally discovered in the bone marrow, MSCs are now known to reside in various tissues, including adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and dental pulp. This article delves into the characteristics, therapeutic applications, and challenges surrounding mesenchymal stem cells, shedding light on their promising role in advancing medical treatments. Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: MSCs are multipotent progenitor cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. T
…
23rd Jan 2024
VEGF-A VEGFR-2 Signaling: Decoding the Blueprint of Angiogenesis for Therapeutic Insights
The orchestration of angiogenesis, the process by which new blood vessels form from pre-existing ones, is a complex symphony regulated by various molecular players. At the forefront of this intricate dance is the VEGF-A VEGFR-2 signaling pathway, a pivotal mechanism that propels the growth and maintenance of blood vessels. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the molecular details of this pathway, shedding light on its fundamental role in angiogenesis and its implications in both health and disease. VEGF-A: A Master Regulator of Angiogenesis: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A) stands as a beacon among the VEGF family of growth factors. Produced
…
18th Jan 2024
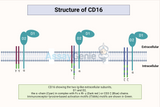
Understanding CD16: A Comprehensive Overview
CD16, also known as FcγRIII (Fc gamma receptor III), plays a crucial role in the immune system, serving as a receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). This receptor is a key player in mediating various immune responses and has implications in both innate and adaptive immunity. In this article, we will delve into the structure, functions, and significance of CD16 in the context of immune regulation. Key Takeways CD16, also known as FcγRIII, is crucial in both innate and adaptive immunity. There are two isoforms: CD16A on NK cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, and CD16B mainly on neutrophils. Functions include Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxi
…
5th Jan 2024
The role of IFN gamma in inflammation, cancer and autoimmune disease
Interferons are key cytokines in the immune system, crucial for combating viral and bacterial infections, with significant roles in both innate and adaptive immunity responses. Key Takeaways Interferons (IFNs) are crucial cytokines in immune responses against viral and bacterial challenges. There are two main types: Type I (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and Type II (IFN-gamma), each with unique roles and receptor interactions. IFN-gamma, a Type II interferon, is pivotal in innate and adaptive immunity, produced mainly by T cells and NK cells. What are Interferons? Interferons (IFN) are a family of cytokines which, upon secretion, play a central role in mediating the innate an
…
22nd Aug 2023
The Lenti Viral Vector System: A New Way to Deliver Genetic Therapies
A new way to deliver genetic therapies is making waves in the medical world. The lenti virus vector system has been shown to be more effective than traditional methods of gene therapy delivery. This system uses a virus to carry the therapeutic genes into the cells of the patient's body. Researchers have found that this method results in fewer side effects and higher success rates. In this blog post, we will discuss the lenti virus vector system and its benefits for patients with genetic disorders.
Lentiviruses
The
…
18th Aug 2023
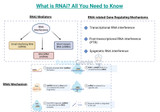
What is RNAi? All You Need to Know
RNA interference (RNAi), also referred to as Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS), is the process by which RNA molecules silence genes in response to double-stranded RNA. RNA interference (RNAi) causes the downregulation or silencing of specific genes at the post-transcriptional level. It can lead to several effects depending on the targeted gene and its biological function.This article discusses RNAi, the various types of RNAi, its mechanism of action and RNAi therapeutics.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.assaygenie.com/blog/what-is-rna-interference-all-you-need-to-kno
…
13th Jul 2023
Immunometabolism – A therapeutic perspective
What is Immunometabolism?
Immunometabolism is an exponentially growing, multi-disciplinary field of research aiming at deciphering the dynamic cellular and molecular mechanisms that interweave metabolic and immunological processes together. Although the term “immunometabolism” first appeared in the literature in 2011, the first studies investigating the connection between immune and metabolic disorders date back to the late 19th century. Our expanding understanding of how different immune cell functions correlate with particular metabolic configurations during home
…
10th Jul 2023
How do different types of vaccines work?
What is a vaccine?
A vaccine is a pharmacological product that gives the recieving patient's immune system a chance to learn how to fight infection with decreased risk of illness. Vaccination involves administering antigenic material (the vaccine), resulting in immunity to the disease.
Vaccine dosing and the need for boosters
Certain vaccines require boosters at appropriate intervals to maintain effective immunity. Boosters simulate pathogen re-infection, providing antibody-producing cells with another chance to build up immunity. For example, the 6 in 1 (diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, Hib, Hep B) vaccine needs to be given at 2 months, 4 months, and 6 months. This is
…
21st Apr 2022
What is pharmacogenomics?
What is pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is how DNA variation and drugs interact and how this can optimise patient health; this involves studying pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacokinetics is the variability of how the drug interacts with the body, e.g., absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. Pharmacodynamics is the variability of the drug interactions with its effector molecules and variability in disease mechanisms. There are many different reasons for individual variability in drug response, although we will focus on examples of how the genome affects drug response. A patient with one of these variants may experience severe and life-threatening
…
10th Apr 2022
Novel Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis
Novel Gene Therapies for Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive, life-limiting disease resulting from gene mutations that encode the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). This gene is comprised of 27 exons and is located on chromosome 7. CFTR is a cAMP-regulated chloride channel located on the apical membrane of exocrine epithelial cells. CFTR is involved in regulating the epithelial sodium channel and bicarbonate transport. There are many different types of CFTR mutations that result in CF; lack of production; failure to reach the site of action; defects in gating; conductance; abnormally low channel numbers; and
…
6th Apr 2022
Pyroptosis: A Promising Target for Immunotherapy
Pyroptosis is an immunogenic form of cell death, meaning that it triggers an immune response. This makes pyroptosis a potentially promising target for immunotherapies that aim to boost the immune system's response to cancer cells and other invaders. In this article, we will discuss pyroptosis in more detail, compare it to apoptosis and explore its potential as a therapeutic target.
What is Pyroptosis ?
Pyroptosis is a type of programmed cell death that occurs in response to infection or other cellular stresses. It is characterized by inflammatory cytokine release, membrane rupture, and cell lysis. Pyroptosis was first described in 2004 by Steinman and
…
22nd Mar 2022
PD-1 & PD-L1 Inhibitors
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS.push({ hoverImage: '', uuid: 's-9d0e3f85-cf60-457e-b32a-268d931a22ba' })
PD-1 & PD-L1 interaction between T-cells and tumour cells.
What are PD-1 and PD-L1?
PD-1, also known as programmed cell death 1, is a receptor expressed on the surface of T cells and plays a pivotal role in immune homeostasis, by keeping overstimulated responses at bay while safeguarding tissues from any unintended destruction. In essence, Programme
…
21st Jan 2022
Anti-CTLA-4 Immunotherapy
CD Markers
Cluster of Differentiation (CD) markers play an important role in the differentiation of B cells, T cells and NK (natural killer) cells. These markers are often responsible for the identification of certain cancers and tumors, resulting in CD markers being good candidates for cancer therapies.
CTLA-4
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4)(CD152) is a protein receptor found on T cells. Both CTLA-4 and CD28 bind to B7-1/2 on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells and B cells. CTLA-4 has been shown to bind B7-1/2 with a higher affinity than CD28 d
…
11th Jan 2022