Blog
Vorsetuzumab: Advancing Cancer Research with CD70 Targeting
What You Need to Know About VorsetuzumabWhat is Vorsetuzumab?Vorsetuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD70, a protein found in various cancers. It shows promise for advancing cancer immunotherapy due to its tumor-specific activity.What is Vorsetuzumab mafodotin?Vorsetuzumab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate combining vorsetuzumab with a cytotoxic agent. This combination delivers targeted therapy, killing CD70-positive cancer cells.Why is Vorsetuzumab significant?Its high specificity for cancer cells and potential to enhance immune response make it a key focus in emerging oncology research.1.) Understanding VorsetuzumabVorsetuzumab is a targeted therapeutic age
…
27th Nov 2024
Talacotuzumab: Exploring CD123-Targeting Therapies in AML and MDS Research
Key Facts About TalacotuzumabWhat is Talacotuzumab?Talacotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target CD123, a protein commonly found on the surface of certain blood cancer cells.How does Talacotuzumab work?It binds to CD123, recruiting the body’s immune cells to destroy cancer cells, making it a targeted and innovative approach in cancer therapy.What are Talacotuzumab’s potential uses?Talacotuzumab has been studied for treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), offering hope for patients with these challenging conditions.1.) Understanding TalacotuzumabTalacotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody developed to target CD123, a key marker
…
27th Nov 2024
Magrolimab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research and Beyond
What You Need to Know About MagrolimabWhat is Magrolimab?Magrolimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody that targets the "don't eat me" signal on cancer cells, promoting their destruction by the immune system.Is Magrolimab safe?Magrolimab has shown a manageable safety profile in clinical trials, though side effects such as anemia and infusion reactions have been reported.What is the mechanism of action for Magrolimab?Magrolimab works by blocking CD47, a protein that helps cancer cells evade immune attack, thereby enabling macrophages to target and eliminate these cells.1.) Understanding MagrolimabMagrolimab is a groundbreaking therapeutic antibody developed to target CD47, a pr
…
27th Nov 2024
Elotuzumab: Revolutionizing Multiple Myeloma Treatment and Research Applications
Quick Facts About ElotuzumabWhat is Elotuzumab?Elotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to enhance the immune system's ability to detect and destroy multiple myeloma cells. It targets the SLAMF7 protein, which is present on both myeloma and immune natural killer (NK) cells.How does Elotuzumab work?Elotuzumab activates NK cells by binding to SLAMF7, boosting their ability to attack cancer cells. It also directly marks myeloma cells for immune system destruction, making it a dual-action therapy.What is Elotuzumab used for?Primarily, Elotuzumab is used in combination therapies for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. These include pairings with drugs like lenalidomide, pom
…
26th Nov 2024
Pembrolizumab: Unveiling Its Mechanism and Research Applications with Biosimilars
Key Facts: PembrolizumabIs Pembrolizumab Safe?Pembrolizumab is widely recognized as safe for most patients, with side effects ranging from mild to severe. Commonly reported side effects include fatigue, rash, and immune-related complications such as colitis or pneumonitis.What is the Mechanism of Action for Pembrolizumab?Pembrolizumab functions by inhibiting the PD-1 pathway, a mechanism that tumors often exploit to evade immune detection. By blocking this pathway, Pembrolizumab enhances the immune system’s ability to identify and destroy cancer cells.Does Pembrolizumab Lower IgG4 Levels?Research has shown that Pembrolizumab can reduce IgG4 levels, which may influence immune mo
…
26th Nov 2024
Daratumumab: Advancing Research in Multiple Myeloma and Beyond
Key Facts About DaratumumabWhat is Daratumumab?Daratumumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD38, a protein highly expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells.How does Daratumumab work?It binds to CD38, triggering immune-mediated destruction of cancer cells through mechanisms like complement-dependent cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.What are the clinical applications of Daratumumab?Daratumumab is primarily used in the treatment of multiple myeloma, both as a monotherapy and in combination with other therapies. Research is also exploring its potential in other hematologic cancers.1.) Understanding DaratumumabDaratumumab is a groundbreaking t
…
26th Nov 2024
Phosphorothioate: Enhancing Stability in Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies
Phosphorothioate is a chemical modification commonly used in oligonucleotide-based therapies to enhance the stability and efficacy of therapeutic nucleic acids. In this modification, one of the non-bridging oxygen atoms in the phosphate backbone of a nucleotide is replaced by a sulfur atom. This seemingly small change provides a significant benefit: phosphorothioate oligonucleotides are far more resistant to enzymatic degradation, which is critical for maintaining their activity in the body. The modification is widely used in antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), RNA interference (RNAi), and aptamer therapies to improve cellular uptake, bioavailability, and stability .1. Structure
…
15th Nov 2024
TREM2: Exploring Its Role in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to TREM2 and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in CancerTREM2 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2) is an immunoregulatory receptor primarily expressed on macrophages, microglia, monocytes, and dendritic cells. In the context of cancer, TREM2 is highly expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), a major immune cell population in the tumor microenvironment (TME) that supports tumor growth and immune evasion. TREM2 signaling in TAMs promotes immunosuppressive functions, limiting the ability of the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.Research has shown that blocking TREM2 can shift TAMs from an immunosuppressive state to a more pro-inflamm
…
31st Oct 2024
Dual PD-1/PD-L2 Blockade: Expanding the Horizons of Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Cancer ImmunotherapyThe PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway has been instrumental in cancer immunotherapy, with PD-1 (programmed death-1) inhibitors showing success across various cancers by restoring T cell function and enhancing immune responses. PD-1, a receptor on T cells, interacts with its ligand PD-L1, which is commonly expressed on tumor cells and tumor-associated immune cells. This binding suppresses T cell activity, allowing tumors to evade immune destruction. However, PD-L1 is not the only ligand for PD-1—PD-L2 also binds to PD-1 and can significantly contribute to immune evasion in certain tumors.While most current therapies
…
29th Oct 2024
BTLA: A Key Player in Immune Regulation and Cancer Therapy
Introduction to BTLA in Immune Regulation B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) is an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a critical role in regulating immune responses by suppressing T cell activity. Structurally similar to other inhibitory receptors like CTLA-4 and PD-1, BTLA functions as a negative regulator of immune activation, maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive inflammation. While this is essential for avoiding autoimmune diseases, it can also be exploited by tumors to escape immune surveillance. BTLA's role in immune regulation has made it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, where blocking its inhibitory effects can restore T cell activit
…
16th Oct 2024
B7-H4: A New Frontier in Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
The recent advances in cancer immunotherapy have brought new opportunities to harness the body’s immune system against tumors. Among these advancements is the targeting of immune checkpoints, which play a significant role in immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment. A relatively new target of interest is B7-H4, a member of the B7 family of immune-regulatory proteins. Emerging research indicates that blocking B7-H4 with antibodies such as MIH43 may offer promising therapeutic benefits in various cancers. This article explores the role of B7-H4, its biological functions, and how anti-B7-H4 therapies may improve cancer treatment outcomes.Assay Genie · B7 - H4 A New Fron
…
14th Oct 2024
LILT: A Novel Immune Checkpoint for Cancer Therapy
Recent advances in immunotherapy have highlighted the importance of targeting immune checkpoints to enhance the immune system’s ability to combat cancer. A new potential target in this growing field is LILT (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript), an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. Blocking LILT with antibodies like 3G4 offers a promising strategy to restore immune surveillance and improve the effectiveness of cancer therapies.Assay Genie · LILT-A Novel Immune Checkpoint For Cancer TherapyWhat is LILT?Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript (LILT) is a family of receptors expressed predominantly on immune cells, particular
…
14th Oct 2024
ICOS: Stimulating the Immune System for Superior Cancer Therapy
Immunotherapy has transformed the landscape of cancer treatment by leveraging the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. A key player in this process is Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS), a molecule that enhances T-cell activation and function. Anti-ICOS antibodies, such as C398.4A, are being explored to amplify the immune response, making them a promising addition to cancer therapy strategies. Assay Genie · ICOS Stimulating The Immune System For Superior Cancer TherapyWhat is ICOS? Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS) is a member of the CD28 family of co-stimulatory receptors, which are critical for T-cell activation and survival. ICOS is expres
…
14th Oct 2024
Targeting CD200: Unlocking Immune Suppression in Tumors
Immune evasion is one of the hallmarks of cancer, where tumor cells employ various strategies to suppress immune responses and prevent destruction by the body’s defense systems. CD200, a transmembrane protein, has emerged as a key player in mediating immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Targeting CD200 with therapies like OX90 is a promising approach to disrupt this immune evasion, allowing the immune system to mount a more effective attack against cancer cells. This article delves into the role of CD200 in tumors, the therapeutic potential of CD200-targeting agents, and the ongoing research surrounding this pathway. Assay Genie · Targeting CD200 Unlocking Immu
…
8th Oct 2024
Targeting VISTA: Unleashing the Power of T Cells in Cancer Therapy
V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) is an emerging immune checkpoint receptor that plays a key role in suppressing T cell activity within the tumor microenvironment (TME). As a negative regulator of immune responses, VISTA helps tumors evade detection by dampening the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells. Recent research into targeting VISTA has highlighted its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer immunotherapy. By inhibiting VISTA, scientists aim to unleash the full power of T cells and other immune cells to attack and destroy tumors. This article explores VISTA’s function in immune regulation, its role in cancer progression, and the potential o
…
3rd Oct 2024
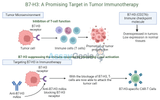
B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor Immunotherapy
B7-H3, also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules that has emerged as a compelling target in tumor immunotherapy. Initially recognized for its role in regulating immune responses, B7-H3 has gained increasing attention due to its overexpression in various cancers and its ability to promote immune evasion. As a result, B7-H3 has become a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, offering new hope for treatments aimed at improving patient outcomes by enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight tumors. AudioAssay Genie · B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor ImmunotherapyWhat is B7-H3? B7-H3 is an immune regulatory molecule expres
…
3rd Oct 2024
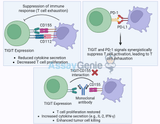
TIGIT: A New Frontier in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Immunotherapy
TIGIT (T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains) has emerged as a promising target in cancer immunotherapy and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. As a checkpoint receptor, TIGIT plays a critical role in regulating immune responses by inhibiting the activity of immune cells, especially T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. By manipulating TIGIT pathways, scientists aim to develop therapies that enhance immune responses against cancer or dampen harmful immune activity in autoimmune disorders.Understanding TIGIT's Role in Immune RegulationTIGIT belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and is primarily expressed on T cells, including regulatory T cells (Tregs), activated
…
1st Oct 2024
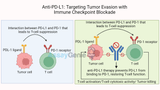
Anti-PD-L1: Targeting Tumor Evasion with Immune Checkpoint Blockade
IntroductionCancer cells have developed sophisticated mechanisms to evade the immune system, particularly through the inhibition of T-cell responses. One such mechanism involves the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which binds to its receptor PD-1 on T cells, leading to the suppression of immune activity. Anti-PD-L1 therapies, as part of the broader category of immune checkpoint inhibitors, have transformed cancer treatment by restoring immune system function and enhancing the body's ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. This article explores the role of PD-L1 in immune evasion and how its inhibition can significantly impact cancer therapy outcomes.Assay Genie · Anti
…
22nd Sep 2024
Biomarker Testing: Advancements, Applications, and Future Directions
Biomarkers, measurable indicators of biological processes or responses to therapeutic interventions, play a pivotal role in modern healthcare. They provide clinicians with valuable information for disease detection, prognosis assessment, and treatment optimization. Biomarker testing encompasses a wide array of techniques and platforms, ranging from simple immunoassays to sophisticated genomic analyses. Over the past few decades, significant advancements in biomarker research have revolutionized clinical practice, leading to more personalized and precise approaches to patient care. Types of Biomarkers: Biomarkers encompass a diverse array of molecular entities that reflect v
…
14th Apr 2024
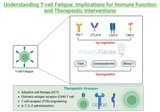
Understanding T Cell Fatigue: Implications for Immune Function and Therapeutic Interventions
T cells are central players in adaptive immunity, responsible for recognizing and eliminating infected or aberrant cells. Upon encountering antigens, T cells undergo clonal expansion and differentiation into effector or memory cells, executing various functions to eliminate the threat. However, in scenarios of persistent antigen exposure, such as chronic infections or cancer, T cells can become functionally exhausted, leading to compromised immune responses. This phenomenon, known as T cell fatigue or exhaustion, has garnered significant attention due to its implications for immune function and therapeutic interventions. Mechanisms of T Cell Fatigue: T cell fatigue is chara
…
9th Apr 2024
Labeling Non-Antibody Proteins and Small Molecules: An Advanced Guide
In the evolving landscape of biochemical research and diagnostic assay development, the ability to label non-antibody proteins and small molecules with high precision has become indispensable. This advanced guide delves into the methodologies, challenges, and applications of labeling these crucial biomolecules, providing insights for researchers and developers aiming to enhance the specificity and sensitivity of their assays. Understanding the Basics of Biomolecule Labeling Biomolecule labeling encompasses a set of techniques used to attach detectable tags or labels to proteins, peptides, and small molecules. These tags can be fluorescent dyes, biotin, radioactive isotopes, or en
…
18th Mar 2024
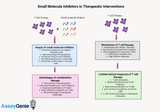
Advantages of Small Molecule Inhibitors in Therapeutic Interventions
Small molecule inhibitors represent a significant advancement in the field of therapeutic interventions, offering a versatile approach to treating a myriad of diseases, including cancer, viral infections, and chronic inflammatory conditions. These compounds, typically with a molecular weight of less than 900 daltons, can modulate biological processes by interacting with specific protein targets within the cell. This article explores the multifaceted advantages of small molecule inhibitors, highlighting their role in the development of targeted therapies. Target Specificity and Selectivity: One of the paramount advantages of small molecule inhibitors is their ability to selectivel
…
13th Mar 2024
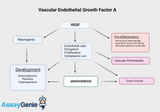
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA): A Cornerstone in Angiogenesis and Beyond
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) is a pivotal signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, processes essential for the formation of blood vessels during embryonic development and the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones. As a member of the VEGF family, VEGFA plays a critical role in the regulation of endothelial cell function, affecting vascular permeability and endothelial cell proliferation. The Molecular Biology of VEGFA VEGFA is characterized by its gene located on chromosome 6p21.1, encoding a heparin-binding protein that promotes endothelial cell growth, migration, and survival. The VEGFA protein undergoes complex post-transl
…
9th Mar 2024
Targeting Immune Checkpoints as Cancer Therapy
In recent years, the field of oncology has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of immunotherapy, a treatment modality that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer. Among the most promising approaches in immunotherapy is the targeting of immune checkpoints. These molecular pathways are crucial for maintaining self-tolerance and modulating the immune response to prevent autoimmunity. However, cancer cells cleverly exploit these pathways to evade immune detection and destruction. This article delves into the mechanisms of immune checkpoint pathways, their role in cancer evasion, and the therapeutic strategies designed to inhibit these checkpoints, thereby reactivating the
…
16th Feb 2024