Blog
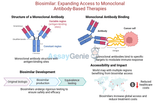
Biosimilar: Expanding Access to Monoclonal Antibody-Based Therapies
1. What is a Biosimilar? A biosimilar is a biologic medical product that is highly similar to an already-approved reference biologic. While minor differences in clinically inactive components may exist, biosimilars match the reference product in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality. HDBS0016 represents one such advancement, offering a cost-effective alternative for biologic therapies. 2. Key Features of HDBS0016 Mechanism of ActionBiosimilar HDBS0016 mimics the mechanism of its reference biologic, targeting specific pathways or antigens depending on its indication. These include:Immune Checkpoint Inhibition: Enhancing T-cell activity by blocking inhibitory recep
…
5th Dec 2024
CB6 Biosimilar: Targeting SARS-CoV-2 with Cost-Effective Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
CB6, also known as Etesevimab, is a monoclonal antibody that targets the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. It neutralizes the virus by preventing it from binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on human cells. CB6 has been studied in combination with other antibodies, such as Bamlanivimab, for treating mild to moderate COVID-19 and preventing disease progression. The biosimilar HDBS0011 replicates CB6’s efficacy and safety while providing a cost-effective option for broader global access.This article explores the mechanism of action, clinical applications, and potential benefits of HDBS0011 in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic.1
…
4th Dec 2024
MHC Class I vs MHC Class II: Key Differences and Functions
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules are essential for immune recognition and response. They are specialized glycoproteins that present antigens to T cells, allowing the immune system to identify and eliminate pathogens or abnormal cells. MHC molecules are classified into Class I and Class II, each with distinct structures, functions, and roles in immune defense.This article explores the differences between MHC class I and MHC class II, highlighting their unique features and immune significance.Assay Genie · MHC Class I vs MHC Class II_ Key Differences and Functions1. Overview of MHC MoleculesMHC molecules play a crucial role in antigen presentation, enabling the ada
…
22nd Nov 2024
SLAMF7: Activating Natural Killer Cells for Potent Anti-Cancer Responses
Introduction to SLAMF7 in Cancer Immunotherapy SLAMF7, also known as Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule F7, is a surface receptor found on natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, plasma cells, and certain immune-regulatory cells. This receptor plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, particularly by enhancing the cytotoxic activity of NK cells, which are a critical part of the body’s first line of defense against tumors. The SLAMF7 receptor, also referred to as CD319, has garnered significant attention as a target for cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to activate NK cells and facilitate tumor destruction.In cancers such as multiple myeloma and solid tum
…
16th Oct 2024
BTLA: A Key Player in Immune Regulation and Cancer Therapy
Introduction to BTLA in Immune Regulation B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) is an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a critical role in regulating immune responses by suppressing T cell activity. Structurally similar to other inhibitory receptors like CTLA-4 and PD-1, BTLA functions as a negative regulator of immune activation, maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive inflammation. While this is essential for avoiding autoimmune diseases, it can also be exploited by tumors to escape immune surveillance. BTLA's role in immune regulation has made it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, where blocking its inhibitory effects can restore T cell activit
…
16th Oct 2024
LILT: A Novel Immune Checkpoint for Cancer Therapy
Recent advances in immunotherapy have highlighted the importance of targeting immune checkpoints to enhance the immune system’s ability to combat cancer. A new potential target in this growing field is LILT (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript), an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. Blocking LILT with antibodies like 3G4 offers a promising strategy to restore immune surveillance and improve the effectiveness of cancer therapies.Assay Genie · LILT-A Novel Immune Checkpoint For Cancer TherapyWhat is LILT?Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Transcript (LILT) is a family of receptors expressed predominantly on immune cells, particular
…
14th Oct 2024
ICOS: Stimulating the Immune System for Superior Cancer Therapy
Immunotherapy has transformed the landscape of cancer treatment by leveraging the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. A key player in this process is Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS), a molecule that enhances T-cell activation and function. Anti-ICOS antibodies, such as C398.4A, are being explored to amplify the immune response, making them a promising addition to cancer therapy strategies. Assay Genie · ICOS Stimulating The Immune System For Superior Cancer TherapyWhat is ICOS? Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator (ICOS) is a member of the CD28 family of co-stimulatory receptors, which are critical for T-cell activation and survival. ICOS is expres
…
14th Oct 2024
Targeting CD200: Unlocking Immune Suppression in Tumors
Immune evasion is one of the hallmarks of cancer, where tumor cells employ various strategies to suppress immune responses and prevent destruction by the body’s defense systems. CD200, a transmembrane protein, has emerged as a key player in mediating immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Targeting CD200 with therapies like OX90 is a promising approach to disrupt this immune evasion, allowing the immune system to mount a more effective attack against cancer cells. This article delves into the role of CD200 in tumors, the therapeutic potential of CD200-targeting agents, and the ongoing research surrounding this pathway. Assay Genie · Targeting CD200 Unlocking Immu
…
8th Oct 2024
SIRPα Inhibition: Clearing Tumors by Promoting Phagocytosis
Cancer cells are adept at avoiding destruction by the immune system, often exploiting specific pathways to escape detection and elimination. One of these key mechanisms involves the SIRPα-CD47 axis, which prevents macrophages and other phagocytic cells from attacking tumor cells. SIRPα inhibitors, such as P84, are emerging as novel immunotherapies that block this protective signal, allowing the immune system to recognize and engulf cancer cells. This article explores the role of SIRPα inhibition in enhancing phagocytosis, promoting anti-tumor immunity, and the therapeutic potential of anti-SIRPα agents like P84 in cancer treatment. Assay Genie · SIRPα Inhibition Clearing Tu
…
8th Oct 2024
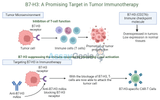
B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor Immunotherapy
B7-H3, also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules that has emerged as a compelling target in tumor immunotherapy. Initially recognized for its role in regulating immune responses, B7-H3 has gained increasing attention due to its overexpression in various cancers and its ability to promote immune evasion. As a result, B7-H3 has become a promising target for cancer immunotherapy, offering new hope for treatments aimed at improving patient outcomes by enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight tumors. AudioAssay Genie · B7-H3: A Promising New Target in Tumor ImmunotherapyWhat is B7-H3? B7-H3 is an immune regulatory molecule expres
…
3rd Oct 2024
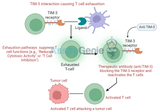
TIM-3: Targeting T Cell Exhaustion for Better Immunotherapy Outcomes
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3) is an immune checkpoint receptor that plays a pivotal role in T cell exhaustion, a state where T cells lose their ability to effectively combat cancer or infections. As a result, TIM-3 has gained significant attention as a therapeutic target to enhance immunotherapy outcomes. This article delves into the biological functions of TIM-3, its involvement in T cell exhaustion, and the potential of TIM-3 inhibitors in improving cancer immunotherapy and treatments for chronic diseases.What is TIM-3?TIM-3 is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on various immune cells, including CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, regulatory T cells
…
3rd Oct 2024
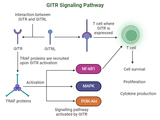
GITR: Boosting T Cell Activation for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy
Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) is an immune checkpoint molecule that plays a crucial role in regulating T cell activation and survival. In recent years, GITR has emerged as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to enhance immune responses against tumors. By stimulating T cells, particularly effector T cells, and inhibiting the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), GITR-based therapies aim to boost the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells. This article explores the function of GITR in immune regulation and its potential for enhancing cancer immunotherapy.Assay Genie · GITR Boosting T Cell Activation Fo
…
3rd Oct 2024
CD25 and Tregs: Understanding the Role of Regulatory T Cells in Tumor Immunity
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a crucial role in maintaining immune balance by suppressing excessive immune responses that could lead to tissue damage. However, in the context of cancer, Tregs can be problematic because they also suppress the immune system’s ability to attack and eliminate tumors. One of the key markers of Tregs is CD25, which is the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. This article explores the role of CD25 and Tregs in tumor immunity, shedding light on how these cells contribute to tumor growth and how they can be targeted to improve cancer immunotherapy outcomes.Assay Genie · CD25 And Tregs Understanding The Role Of Regulatory T Cells In Tumor ImmunityWhat Are
…
3rd Oct 2024
NK Cells: Unlocking the Potential of Natural Killer Cells in Cancer Therapy
Natural killer (NK) cells are a crucial component of the innate immune system and play a significant role in eliminating tumor cells. Unlike T cells, NK cells can recognize and kill cancer cells without prior sensitization, which makes them particularly valuable in cancer immunotherapy. As research progresses, novel therapies aim to harness and enhance NK cells' innate ability to fight cancer. This article explores NK cells' function, their role in cancer immunosurveillance, and the innovative therapeutic strategies being developed to improve cancer treatment outcomes.Assay Genie · NK Cells: Unlocking the Potential of Natural Killer Cells in Cancer TherapyWhat Are NK Cells?NK ce
…
3rd Oct 2024