Blog
MAPK Oxidative Stress Pathway: A Journey through Cellular Signaling
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-e5394be4-6636-4558-9e32-20ef2f209b2b' })
In the intricate world of cellular signaling, the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes. One facet of this pathway that has garnered significant attention is its involvement in managing oxidative stress—a condition marked by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the cell's antioxidant defense mechanisms. In this article, we embark on a journey through the MAPK oxidative stress pathway, exploring its intri
…
18th Jan 2024
Adipokines and Insulin Signaling Pathways: An In-Depth Exploration
The prevalence of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders has risen dramatically in recent decades, presenting a significant global health challenge. Adipose tissue, once considered merely a storage site for excess energy, is now recognized as an active endocrine organ secreting a myriad of bioactive molecules known as adipokines. Among these adipokines, a key player in metabolic regulation is insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Adipokines: Key Regulators of Metabolism Adipokines function as critical mediators between adipose tissue and various organs, influencing metabolic processes such as glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and inflammation. Lep
…
18th Jan 2024
Unraveling the Complexity of the Notch Signaling Pathway: A Key Player in Development and Disease
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cellular communication system that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and immune system function. Discovered over a century ago, the Notch pathway has since emerged as a complex and versatile signaling network that regulates cell fate decisions and maintains tissue integrity. This article aims to provide an overview of the Notch signaling pathway, its components, and its diverse roles in development and disease. Basic Components of the Notch Signaling Pathway: The Notch pathway consists of a family of transmembrane receptors, known as Notch receptors, a
…
17th Jan 2024
Unlocking Cellular Adaptation: The HIF Enhancer Pathway and Its Implications in Hypoxia Response
Hypoxia, or low oxygen levels, poses a significant challenge to cells, necessitating rapid and efficient adaptation mechanisms. The Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) pathway is a well-known regulator of cellular responses to hypoxia, orchestrating the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, and glycolysis. It plays a pivotal role in cellular adaptation to low oxygen conditions, ensuring survival and homeostasis in diverse physiological and pathological settings. Recent studies have uncovered an additional layer of complexity in HIF regulation, known as the HIF enhancer pathway. This article explores the mechanisms, regulation, and significance of the HIF enhancer pa
…
12th Jan 2024
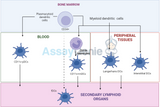
Dendritic Cells: Tracing the Developmental Lineage Pathway
Dendritic cells (DCs) are pivotal in the immune system, orchestrating innate and adaptive immune responses. Understanding their developmental lineage pathway is crucial in immunology, particularly in the context of cancer and infection responses. Introduction to Dendritic Cells Dendritic cells are unique antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that play a crucial role in the immune system. They are known for their ability to capture and present antigens, thereby bridging innate and adaptive immunity. DCs are heterogeneous, comprising various subsets with distinct phenotypes and functions. This diversity is a result of their complex developmental lineage. Origin and Early Development
…
5th Jan 2024
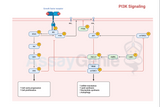
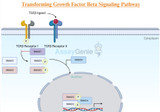
Deciphering the Intricacies of TGF-Beta Signaling Pathway
Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in orchestrating various cellular processes, ranging from embryonic development to tissue homeostasis and immune response modulation. This intricate pathway is crucial for maintaining cellular balance, and dysregulation can contribute to a myriad of diseases, including cancer, fibrosis, and immune disorders. In this article, we delve into the key components and mechanisms that characterize the TGF-β signaling pathway. Key Components of TGF-Beta Signaling Pathway: TGF-β Ligands: The TGF-β family comprises multifunctional cytokines, with TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 being
…
24th Aug 2023
Xeroderma pigmentosum: Causes, Inheritance, Treatment and Diagnosis
What is Xeroderma Pigmentosum? Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) also known De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin, eyes and central nervous system. It is caused by a defect in the Xeroderma pigmentosum gene, which results in an inability to repair DNA damage caused by ultraviolet light. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including sunburns, freckles, skin cancer and neurological problems. XP is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Till date about 8 inherited forms of Xeroderma pigmentosum has been identified XP-A to XP-G. Diagnosis of Xeroderma pigmentosum can be difficult, as there is no single definitive test. A combination of test
…
23rd Aug 2023
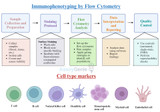
Immunophenotyping by Flow Cytometry and Cell Type Markers
Immunophenotyping by Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping is a technique used in the field of immunology and cell biology to identify and classify cells based on the specific proteins or molecules found on their surfaces, known as cell surface markers or antigens. These markers provide valuable information about the type, state, and characteristics of individual cells within a larger population. Immunophenotyping is particularly important in fields such as immunology, hematology, oncology, and infectious diseases, where understanding cell populations and their properties is crucial. The primary tool used for immunophenotyping is flow cytometry, although other methods like immu
…
23rd Aug 2023
Oxidative Stress: Causes, Biomarkers & Disease
Oxidative Stress Definition
Oxidative stress is a condition that results when the body produces or consumes more reactive oxygen species (ROS) than it can neutralize. ROS are unstable molecules that can damage cells, proteins, and DNA. Oxidative stress has been implicated in a wide range of diseases, including heart disease, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease. In this article, we will discuss oxidative stress and explore its role in disease. We will also look at some of the most common oxidative stress markers.
Oxidants and reductants can be formed in cells by losing or gaining a single electron, which
…
23rd Aug 2023
Waardenburg Syndrome and Klein-Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg Syndrome: A Rare Genetic Disorder Affecting Pigmentation, Hearing, and More
Waardenburg Syndrome (WS) is a fascinating and rare genetic disorder that impacts various aspects of an individual's appearance and sensory abilities. First described by Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg in the 1950s, WS is characterized by distinctive features, including changes in pigmentation, hearing loss, and facial abnormalities.
Table of Contents
…
24th Jul 2023
A Quick Guide to Myelin
The myelin sheath is an insulating layer around nerve cells. It is made up of a substance called myelin, which is produced by special cells called oligodendrocytes. Myelin protects the nerve cells and to keep them maintain their function. Myelin is important for the proper function of the nervous system. It helps to speed up nerve impulses and prevents them from becoming mixed up. Without myelin, nerve impulses would move slowly and would be easily confused. Myelin is also important for the repair of damaged nerves. When a nerve is damaged, the myelin sheath around it is also damaged. The oligodendrocytes that produce myelin can also repair the myelin sheath. This process is called myeli
…
19th Jul 2023
Sepsis and Immune Dysregulation
Exploring sepsis: a critical imbalance in the immune response to infection. Key Takeaways: Sepsis is a severe, immune-driven response to infection causing systemic inflammation and potential organ damage. It progresses through stages: initial sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock, each with increasing severity. Complications include organ failure, septic shock, ARDS, blood clots, and long-term impairments. Immune responses in sepsis vary from hypo-inflammation (weak) to hyper-inflammation (excessive). Understanding these responses is key for effective sepsis treatment and management. What is Sepsis? Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that arises when the bod
…
29th Jun 2023
Biomarkers in sepsis: Their Role in Early Detection and Management
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition, is characterized by a dysregulated immune response to an infection, leading to systemic inflammation and organ dysfunction. Biomarkers, as measurable indicators of biological processes, hold immense potential in the field of sepsis diagnosis, prognosis, and management. In this article, we explore the critical role that biomarkers play in sepsis, particularly their significance in early detection and diagnosis. We delve into the latest research and advancements in biomarker identification, their association with the immune response duri
…
28th Jun 2023
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
Understanding Beta-Oxidation: A Comprehensive Overview Fatty acids provide a highly efficient energy storage mechanism, delivering more energy per gram than common carbohydrates like glucose. This becomes particularly vital in tissues with high energy requirements, such as the heart, where 50–70% of energy is derived from fatty acid beta-oxidation. During this process, long-chain acyl-CoA molecules, the main components of fatty acids, are broken down into acetyl-CoA molecules. Key Takeaways: Beta-oxidation is a metabolic process breaking down fatty acids for energy. It occurs primarily in mitochondria and involves four critical steps. Beta-oxidation generates acet
…
28th May 2023
Renal and Hepatic Function Assays
Hepatic Function Assays
Liver function assays are a suite of tests designed to assess the health and efficacy of our vital organ: The liver. This hardworking powerhouse is responsible for creating bile, eliminating toxins, and breaking down fats, carbohydrates and proteins – all necessary elements that keep us ticking!
To evaluate the liver's health, there are various hepatic function assays that can be performed. These tests measure the organ's capacity to produce bile, metabolize toxins and drugs, as well as synthesize proteins and carbohydrates. By assessing these three factors of liver performance with an
…
7th Mar 2023
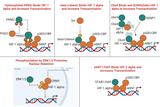
Protein Kinases: Overview, Classification and Therapeutic Potential
Kinases, key enzymes in cellular signaling, phosphorylate proteins to regulate crucial processes, and their modulation has significant implications in disease treatment. Key Takeaways: Kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate proteins, influencing cell processes. They are categorized into serine/threonine, tyrosine, and dual specificity kinases. Kinases are crucial in cell signaling, growth, metabolism, and homeostasis. Dysregulation of kinases is linked to diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Protein kinase inhibitors hold therapeutic potential in treating various diseases. What are Kinases? Understanding their Functions, Types and Structure Kinases are
…
13th Jun 2022
Spanish Flu: The Deadliest Pandemic in History
The Spanish flu pandemic of 1918-1919 was the deadliest in history. It is estimated that up to 100 million people died from the virus, which is more than three times the number who died in World War I. The pandemic began in Spain, but quickly spread around the world. Despite the fact that the 1918 flu was not concentrated to one location, it became known throughout the world as the Spanish flu because Spain was severely affected by it. In some areas, as many as one out of every four people contracted the virus and died. The cause of the Spanish flu remains a mystery to this day, but scientists believe it may have been a mutated form of H1N1 influenza. In 1918, a new influen
…
24th Mar 2022
The Ebola Virus: What You Need to Know
The Ebola virus has been in the news a lot lately, but many people still don't know what it is or how it spreads. In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of the Ebola virus: what it is, how it is spread, and the symptoms. The Ebola virus is a virus that causes hemorrhagic fever, which is a severe and often fatal illness. The Ebola virus is spread through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected animal, such as a monkey, chimpanzee, or bat. It can also be spread to humans through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person.
'Zaire ebolavirus' commonly known as 'Ebola virus', is one of six recognized species in the genus Ebolavirus. EBOV, al
…
22nd Mar 2022
Influenza Hemagglutinin (HA) Subtypes and Flu Virus Strains: What You Need to Know
The flu is a highly contagious virus that affects the respiratory system. It can cause fever, muscle aches, and coughing. In some cases, it can lead to more serious health complications such as pneumonia. Each year, the flu virus mutates, meaning people must recieve a new vaccine against new strains of the virus. One important factor in determining how severe the coming flu season will be is the type of hemagglutinin (HA) subtype involved. In this blog post, we will discuss influenza HA subtypes and flu virus strains.
Flu virus Strains:
There are three types of flu viruses: A, B, and C. Influenza A is the most prevalent variety of flu virus. It causes
…
9th Mar 2022
Insulin Signaling and RTK: An Overview
Explore the intricate world of Insulin Signaling and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs), pivotal in regulating metabolism and influencing diseases like cancer and atherosclerosis. Key Takeaways: Insulin signaling involves receptor activation, signal transduction, and gene expression. Insulin receptors, a type of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK), regulate metabolism and cell responses. The Ras/MAP kinase and PI3K pathways are crucial in insulin signaling. Insulin signaling impacts atherosclerosis and cancer, with RTK inhibitors showing therapeutic potential.
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_E
…
23rd Feb 2022
What Causes Acute Pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a condition in which activated enzymes and inflammatory mediators released from the pancreas cause damage to the pancreas and surrounding tissues. AP is further divided into two main categories, a mild form called interstitial oedematous pancreatitis or a severe form called necrotising pancreatitis. Interstitial oedematous pancreatitis accounts for 80% of AP cases and the pancreatic inflammation involved usually resolves itself. However, necrotising pancreatitis resembles necrosis of the pancreas which can result in further complications.
AP starts with inflammation which can lead to damage of affected organs through multiple organ failure (MOF) and
…
15th Feb 2022
Fenofibrate Usage for Diabetes Damage
Fenofibrate, also known as FEN, is a drug that is used to lower cholesterol levels. It works by blocking the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the small intestine and therefore, reduces the amount of cholesterol that enters the bloodstream. Fenofibrate has been shown to be effective in reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by up to 20% and it is approved for use in the United States and Europe. Fenofibrate is a safe and effective drug and it can be used in conjunction with other medications to help reduce LDL levels.
The mechanism of action of fenofibrate is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by inhibiting the activity of a protein called Niemann-Pick C1-Like
…
15th Feb 2022
Cyclophosphamide Side Effects
Ovarian cancer is a set of malignancies that start in the ovaries, as well as adjacent portions of the fallopian tubes and peritoneum. Women have two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries produce reproductive hormones and egg cells. Thousands of women each year get an ovarian cancer diagnosis and this type of cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths among women.
Cyclophosphamide is an effective alkylating chemotherapy agent used to treat ovarian cancer. Although cyclophosphamide has many benefits cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian toxicity is a side effect of treatment with this drug. This type of toxicity can cause infertility and increase the risk of developing can
…
15th Feb 2022
Everything You Need to Know About Preeclampsia: A Guide
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is marked by high blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine and can cause serious problems for both mother and baby if it is not treated. A recent study found that preeclampsia is associated with an increased risk of heart disease in later life. It can lead to high blood pressure and diabetes, which both increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. It may also cause damage to arteries and reduce blood flow to the placenta (leading to low birth weight). Therefore, it’s essential that pregnant women should be screened for preeclampsia at their first prenatal visit so that treatment can
…
9th Feb 2022