Blog
Zilovertamab: Unlocking the Potential of ROR1-Targeted Therapy
Quick Facts About ZilovertamabWhat is Zilovertamab?Zilovertamab is a monoclonal antibody targeting ROR1, a receptor tyrosine kinase overexpressed in hematologic cancers and solid tumors.How does Zilovertamab work?It binds to ROR1, disrupting tumor cell survival pathways and enhancing immune-mediated cancer cell destruction.What are the clinical applications of Zilovertamab?It has been investigated for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and other malignancies.Are there biosimilars for Zilovertamab?Yes, biosimilars are being explored to enhance research accessibility and further therapeutic advancements.1.) Understanding ZilovertamabZilo
…
6th Feb 2025
Brodalumab: A Breakthrough in IL-17 Receptor Blockade for Psoriasis and Beyond
Quick Facts About BrodalumabWhat is Brodalumab?Brodalumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-17 receptor to treat immune-mediated conditions like moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.What is the mechanism of action of Brodalumab?It blocks IL-17 receptor A, inhibiting downstream signaling pathways involved in inflammatory responses.What conditions does Brodalumab treat?Brodalumab is approved for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and is being studied for other autoimmune disorders.Is Brodalumab safe?While generally well-tolerated, it carries a REMS program due to risks of suicidal ideation in some patients. Always consult healthcare professionals for guidance.1.) Understan
…
29th Jan 2025
Cetuximab: A Revolutionary Drug in Cancer Therapy
Quick Facts About CetuximabWhat is Cetuximab?Cetuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), widely used in cancer therapy.How does Cetuximab work?Cetuximab binds to EGFR on cancer cells, inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis, making it a powerful tool in oncology.What are the clinical uses of Cetuximab?It is commonly prescribed for metastatic colorectal cancer and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, often in combination with chemotherapy or radiation.Is Cetuximab safe?Cetuximab is generally well-tolerated, but common side effects include skin rash and infusion reactions.1.) Understanding CetuximabCetuximab, a c
…
29th Jan 2025
Utomilumab: Advancing Immuno-Oncology Research
Quick Facts About UtomilumabWhat is Utomilumab?Utomilumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting 4-1BB (CD137), a co-stimulatory receptor on T-cells, designed to enhance anti-tumor immunity.What is the mechanism of action for Utomilumab?Utomilumab binds to 4-1BB, stimulating T-cell activation and proliferation while promoting an enhanced immune response against cancer cells.What are the clinical applications of Utomilumab?It has been investigated in combination therapies for cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and melanoma, aiming to improve immune checkpoint therapy outcomes.1.) Understanding UtomilumabUtomilumab represents a pivotal development in immuno-oncology a
…
29th Jan 2025
Enapotamab: Advancing Cancer Research with Innovative Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnapotamabWhat is Enapotamab?Enapotamab is an experimental antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed to target tumor cells selectively, offering new hope in cancer treatment.How does Enapotamab work?Enapotamab combines a monoclonal antibody with a cytotoxic agent to selectively bind to tumor-associated antigens, delivering a potent anti-cancer payload directly to cancer cells.What are the clinical applications of Enapotamab?This ADC has shown potential in treating solid tumors such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), melanoma, and head-and-neck cancers.1.) Understanding EnapotamabEnapotamab vedotin represents a groundbreaking advance in oncology therapeutics
…
29th Jan 2025
Tarextumab: Unlocking the Potential of Cancer Therapeutics
Quick Facts About TarextumabWhat is Tarextumab?Tarextumab is a novel therapeutic antibody designed to target the Notch signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in tumor progression and resistance to treatment.How does Tarextumab work?Tarextumab inhibits the Notch2/3 receptors, disrupting critical cellular communication pathways in cancer, thereby impeding tumor growth and promoting apoptosis.What are the clinical applications of Tarextumab?Tarextumab has been studied in treating pancreatic cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), showcasing its potential in addressing treatment-resistant tumors.Is Tarextumab safe?Safety profiles from e
…
21st Jan 2025
Murlentamab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research with Targeted Therapy
Quick Facts About MurlentamabWhat is Murlentamab?Murlentamab is a novel monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a "don’t eat me" signal that helps cancer cells evade the immune system.What is the mechanism of action for Murlentamab?Murlentamab binds to CD47 on cancer cells, blocking its interaction with SIRPα on macrophages. This promotes phagocytosis, enabling the immune system to eliminate cancer cells more effectively.What are the clinical applications of Murlentamab?Murlentamab is primarily being explored for treating solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Emerging research suggests its potential in combination therapies for enhanced efficacy.1.) Understanding Mu
…
21st Jan 2025
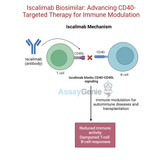
Iscalimab: Advancing Research in Autoimmune Diseases and Transplantation
What You Need to Know About IscalimabWhat is Iscalimab?Iscalimab (CFZ533) is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD40, a key protein involved in immune system regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Iscalimab?Iscalimab blocks the CD40-CD40L pathway, preventing the activation of T cells and B cells, which are central to autoimmune responses and transplant rejection.What are the clinical applications of Iscalimab?Iscalimab is under investigation for treating autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome, lupus nephritis, and for improving outcomes in organ transplantation.1.) Understanding IscalimabIscalimab (CFZ533) is an innovative monoclonal antibody developed by Novartis to
…
15th Jan 2025
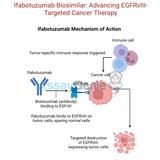
Ifabotuzumab: Exploring the Role of Anti-EphA3 in Cancer Research
What You Need to Know About IfabotuzumabWhat is Ifabotuzumab?Ifabotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting EphA3, a receptor tyrosine kinase overexpressed in certain cancers. It plays a critical role in tumor angiogenesis and microenvironment regulation.What is the mechanism of action for Ifabotuzumab?Ifabotuzumab binds to EphA3, disrupting tumor-supportive interactions and potentially reducing tumor growth and spread.What are the clinical applications of Ifabotuzumab?This antibody is being studied for its therapeutic potential in treating various cancers, including glioblastoma and solid tumors.1.) Understanding IfabotuzumabIfabotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody des
…
15th Jan 2025
Inflammasome Activation Pathways: A Comprehensive Overview
Inflammasomes are complex intracellular structures that play a pivotal role in the immune response by detecting pathogenic microorganisms and sterile stressors. Their activation is a critical step in the host defense system, leading to the maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18. This article provides a detailed examination of the mechanisms underlying inflammasome activation. Understanding the Inflammasome: Structure and Function Inflammasomes are multiprotein oligomers, primarily composed of a sensor (typically a pattern recognition receptor), the adaptor protein ASC, and the effector protein pro-caspase-1. The most well-studied inflammasomes
…
29th Apr 2024
NRF2 Signaling: A Keystone in Inflammation and Disease Management
Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 (NRF2) orchestrates a principal defense mechanism against oxidative stress and plays a pivotal role in inflammation and disease pathogenesis. This article explores the mechanism of NRF2 signaling, its intricate relationship with inflammation, its implications in various diseases, and the therapeutic potential of NRF2 modulation. Understanding NRF2 Signaling Basic Mechanism of Action NRF2 is a transcription factor that, upon activation, migrates to the nucleus to bind to Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE) in the DNA, promoting the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, detoxification, and cellular homeostasis. Re
…
12th Feb 2024
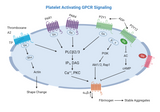
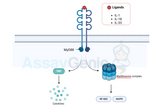
Unraveling the Mysteries of Platelet-Activating GPCR Signaling
Platelet activation plays a pivotal role in hemostasis, the process that stops bleeding and initiates wound healing. Central to this process is the activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which serve as key signal transducers on the surface of platelets. These receptors detect extracellular signals and initiate a cascade of intracellular events leading to platelet activation. This article delves into the mechanisms of platelet-activating GPCR signaling, highlighting its significance in thrombosis and potential therapeutic implications. The Role of GPCRs in Platelet Activation: GPCRs represent a vast and diverse family of receptors that are critical in various physiolog
…
9th Feb 2024
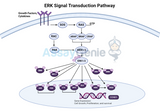
The ERK Signal Transduction Pathway: A Keystone in Cellular Communication and Response
The ERK signal transduction pathway stands as a fundamental mechanism in cellular biology, orchestrating a wide array of physiological processes, including cell division, differentiation, and survival. This pathway, part of the larger mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, is instrumental in conveying signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, thereby influencing gene expression and cellular outcomes in response to external stimuli. Understanding the ERK Pathway: The Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) pathway is initiated by the binding of growth factors, cytokines, and other extracellular ligands to their respective receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) on the ce
…
8th Feb 2024
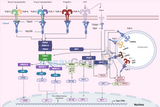
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: A Key to Innate Immunity
In the intricate landscape of the immune system, toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a fundamental role in the first line of defense against pathogens. These receptors, essential components of the innate immune response, are adept at recognizing specific microbial patterns, initiating signaling pathways that lead to the activation of immune responses. This article delves into the toll-like receptor signaling pathways, underscoring their importance in immunology and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding Toll-Like Receptors Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune system by detecting microbial infections and activating the immune r
…
5th Feb 2024
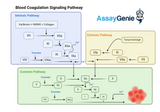
Blood Coagulation Signaling Pathways: A Critical Overview
Blood coagulation is a fundamental physiological process that prevents excessive bleeding when the vascular system is injured. It involves a complex cascade of events that lead to the formation of a stable fibrin clot. This process is tightly regulated by various signaling pathways to ensure that coagulation occurs promptly and appropriately in response to vascular injury, without leading to thrombosis or bleeding disorders. This article delves into the critical signaling pathways involved in blood coagulation, highlighting their roles, mechanisms, and the potential for therapeutic intervention. The Coagulation Cascade: An Overview The coagulation cascade is traditionally divided
…
5th Feb 2024
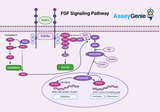
FGF Signaling Pathways: Unraveling the Complexities
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are pivotal in regulating cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and survival. The FGF signaling pathways play a critical role in embryonic development, tissue repair, metabolism, and cancer progression. This article delves into the mechanisms of FGF signaling, highlighting its significance in biological processes and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding FGF Signaling: FGF signaling is mediated through the interaction of FGFs with their cell-surface receptors, known as FGFRs. This interaction leads to receptor dimerization and activation, initiating a cascade of downstream signaling events. The specificity of FG
…
3rd Feb 2024
IL-1 Family Signaling: Unraveling the Molecular Orchestra of Immune Regulation
The Interleukin-1 (IL-1) family represents a crucial group of signaling molecules that play a pivotal role in regulating the immune system and inflammatory responses. Comprising 11 members, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33, the IL-1 family members exhibit diverse functions in immune homeostasis, tissue repair, and disease pathogenesis. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the IL-1 family signaling pathway, shedding light on its components, activation mechanisms, and physiological significance. Components of the IL-1 Family Signaling Pathway: IL-1 Receptors (IL-1Rs): The IL-1 family signaling cascade begins with the binding of
…
2nd Feb 2024
p38 MAPK Signaling Review
The p38 MAPK signaling pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular responses to various stressors and inflammatory stimuli. It is a part of the larger MAPK superfamily, which also includes ERK and JNK pathways. The p38 MAPK pathway is involved in regulating a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune responses. Key Takeaways: p38 MAPK, part of the MAPK family, is key in cellular responses to stress and inflammation. This pathway regulates cell processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. The MAPK family includes ERKs, JNKs, and p38
…
1st Feb 2024
Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway: A Keystone in Innate Immunity
The innate immune system, a primary line of defense against pathogens, comprises various cellular and molecular mechanisms. Among these, the Nod-like Receptor (NLR) signaling pathways play a critical role. They are central to the immune response, acting as intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This article delves into the basic components of NLR signaling pathways, their key steps, roles in development, and implications in disease. Basic Components of Nod-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways: Nod-like receptors (NLRs) belong to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family and are primarily located in
…
30th Jan 2024
Decoding the Language of Cells: Chemokine Signaling Pathways Unveiled
Chemokines are small signaling proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system by directing the movement of cells, orchestrating immune responses, and maintaining tissue homeostasis. The intricate network of chemokine signaling pathways governs the trafficking and positioning of immune cells throughout the body, contributing to various physiological and pathological processes. This article aims to delve into the complexity of chemokine signaling pathways, shedding light on their diverse functions and significance in cellular communication. Chemokines and Their Receptors: Chemokines belong to a family of chemotactic cytokines that guide the migration of immune cells b
…
28th Jan 2024
Ubiquitin and Its Role in Cellular Regulation: A Comprehensive Overview of Modifiers and Pathways
Ubiquitin is a small, highly conserved protein found in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in regulating various cellular processes. The process of ubiquitination involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin molecules to target proteins, marking them for degradation, localization, or signaling. This post-translational modification is a dynamic and tightly regulated process that influences numerous cellular pathways. In this article, we will explore the structure and function of ubiquitin, its related modifiers, and the intricate pathways involved in ubiquitin-mediated cellular regulation. Structure and Function of Ubiquitin: Ubiquitin, a 76-amino acid protein, i
…
23rd Jan 2024
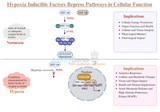
HIF Repress Pathways: An Insight into Cellular Oxygen Homeostasis
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are pivotal in the cellular response to oxygen deprivation. These transcription factors regulate various aspects of cellular and systemic homeostasis in response to hypoxia. Central to their role is the activation of genes that aid in adaptation to low oxygen conditions. However, equally important, yet less emphasized, is their ability to repress certain pathways. This article delves into the mechanisms and implications of HIF-mediated repression pathways in cells. Mechanisms of HIF-Mediated Repression Transcriptional Repression Through HIF: HIFs function primarily as transcriptional activators. However, they can indirectly repress gene expr
…
22nd Jan 2024
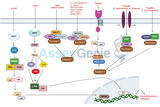
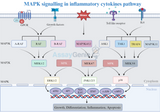
MAPK Signaling in Inflammatory Cytokines Pathways
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway is a pivotal signaling cascade that plays a crucial role in mediating cellular responses to various external stimuli. This pathway is intricately involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokines, key signaling molecules in the immune system. Understanding the MAPK signaling pathway in the context of inflammatory cytokines is essential for grasping the molecular basis of inflammation and its related disorders. Overview of MAPK Signaling Fundamental Components and Activation: MAPK signaling encompasses a series of protein kinases that transmit signals from the cell surface to the nucleus. These kinases include the Extrac
…
22nd Jan 2024
JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway: A Comprehensive Exploration
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS = window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS || new Array();
window.SHOGUN_IMAGE_V2_ELEMENTS.push({ uuid: 's-45124fd5-9a75-444d-b680-b8339e2a814d' })
Progression of the JAK STAT Signalling Pathway Cellular communication is a complex network of molecular interactions that govern various physiological processes. Among the many signaling pathways, the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway plays a pivotal role in mediating signals from the cell surface to the nucleus. This pathway is essential for regulating immune responses, cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. In this article, we will delv
…
18th Jan 2024