Blog
Tigatuzumab: Advancing Cancer Research with Targeted Therapies
Quick Facts About TigatuzumabWhat is Tigatuzumab?Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the death receptor 5 (DR5) pathway, inducing apoptosis in cancer cells.What is the mechanism of action for Tigatuzumab?Tigatuzumab binds to DR5, activating apoptotic pathways in cancer cells, making it a targeted therapy for solid tumors and hematological malignancies.What are the clinical applications of Tigatuzumab?Tigatuzumab has been investigated for treating various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer. Emerging research highlights its potential in combination therapies.1.) Understanding MagrolimabTigatuzumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibo
…
23rd Jan 2025
Rituximab: Mechanism, Applications, and Research Potential
Quick Facts About RituximabWhat is Rituximab?Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20, a protein found on the surface of B cells. It plays a crucial role in treating autoimmune diseases and certain cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.What is the mechanism of action for Rituximab?Rituximab works by binding to CD20, leading to B cell destruction through immune-mediated processes such as complement activation and apoptosis.What are the clinical applications of Rituximab?Rituximab is used to treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It’s also being explored for multiple sclerosis (MS) and lupus.What are the cl
…
12th Dec 2024
Girentuximab: Exploring Its Mechanism, Clinical Potential, and Research Advancements
Quick Facts About GirentuximabWhat is Girentuximab?Girentuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), predominantly expressed in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. It is designed to enhance tumor-specific immune responses.What is the mechanism of action for Girentuximab?Girentuximab binds to CAIX on RCC cells, promoting antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), crucial for its therapeutic efficacy.What are the clinical applications of Girentuximab?It has shown promise in treating advanced RCC and is being explored in combination with radioisotopes for precision oncology.1.) Understanding GirentuximabGi
…
10th Dec 2024
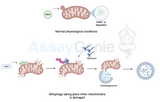
Mitophagy: The Cell's Cleanup Crew for Healthy Living
Mitophagy, a term derived from the fusion of "mitochondria" and "autophagy," represents a vital cellular process responsible for the targeted degradation and recycling of dysfunctional mitochondria. Mitochondria, often hailed as the powerhouses of the cell, play a crucial role in energy production, calcium homeostasis, and apoptosis regulation. However, their functionality can be compromised due to various stressors, leading to the accumulation of damaged mitochondria. To maintain cellular health and functionality, cells employ mitophagy as a mechanism to rid themselves of these dysfunctional organelles. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of mitophagy, exploring its molecu
…
26th Mar 2024
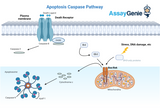
Apoptosis Caspase Pathways: A Closer Look at Cellular Suicide
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a fundamental process that plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of healthy tissues. Central to this process are caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that, once activated, orchestrate the cell's orderly demise. Understanding the caspase pathways not only sheds light on how our bodies maintain cellular balance but also provides insights into the mechanisms underlying various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. The Initiation of Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways Apoptosis can be triggered through two primary pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic, both of which eventually converge on the act
…
8th Feb 2024
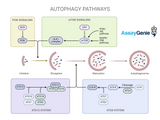
Understanding the Autophagy Pathway: A Critical Process in Cellular Maintenance
Autophagy, a fundamental cellular process, is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stressors. This self-eating mechanism involves the degradation and recycling of cellular components, playing a pivotal role in numerous physiological and pathological contexts. What is Autophagy? Autophagy, derived from the Greek words 'auto' (self) and 'phagy' (eating), is a process where cells degrade and recycle their own components. This process is essential for removing damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and pathogens, and for providing nutrients during starvation. Types of Autophagy: There are three main types of autophagy: Macroautophagy: The m
…
31st Jan 2024
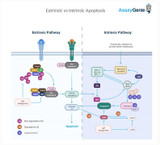
Apoptosis (Intrinsic & Extrinsic Pathways)
At Assay Genie we have created a comprehensive guide outlining everything you need to know about apoptosis! Key Takeaways: Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process, vital for tissue maintenance and disease prevention. Distinct from necrosis, apoptosis involves cellular shrinkage, nuclear breakdown, membrane disruption, and fragmentation into apoptotic bodies. p53 pathway, intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, and caspase cascades are key mechanisms in apoptosis. Apoptosis vs. Necrosis: Apoptosis is controlled and natural, while necrosis is uncontrolled and harmful. p53 Pathway: Activated by DNA damage, involves proteins like Bax, Bak, Bad. Intrinsic Apoptosis: Triggered intern
…
24th Jan 2024
A Comprehensive Overview of Cell Death
Cell death is an essential aspect of cellular biology that plays a crucial role in development, homeostasis, and disease. In this blog, we try to focus on mechanisms and various types of cell death, shedding light on the scientific underpinnings of apoptosis, necrosis, and regulated necrosis variants.
Table of Contents
Jump to a section:
- Apoptosis
- How to Measure Apopto
…
23rd Aug 2023
Cleaved Caspase-3 and Apoptosis
Delve into the role of Cleaved Caspase-3 in programmed cell death and its implications in disease pathologies, unraveling its regulatory mechanisms and potential as a therapeutic target. Key Takeaways: Cleaved Caspase-3 is a central enzyme in apoptosis, orchestrating cell dismantling. It's activated by initiator caspases and is key in executing the apoptotic process. Cleaved Caspase-3 has roles in diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Its regulation involves various factors, including IAPs and the Bcl-2 family. Targeting Cleaved Caspase-3 offers potential therapeutic strategies for various diseases. Table of Contents Jump
…
18th Jul 2023