Blog
Clinical Pathology Labs List: Overview, Services, and Importance
Clinical pathology labs play a crucial role in modern healthcare, providing critical diagnostic testing services for a wide array of diseases and conditions. These laboratories are designed to analyze samples from patients, such as blood, urine, and tissues, to help clinicians make informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.Assay Genie · Clinical Pathology Labs List_ Overview, Services, and Importance1. What is Clinical Pathology?Clinical pathology is a branch of pathology that focuses on diagnosing diseases through laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, including blood, urine, and other specimens. These labs are integral in detecting infections, monitoring diseases, assess
…
19th Nov 2024
Streptococcus pneumoniae: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Streptococcus pneumoniae, commonly known as pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, encapsulated bacterium that is a leading cause of respiratory and invasive diseases worldwide. It is part of the natural flora in the human nasopharynx but can become pathogenic under certain conditions. Diseases caused by S. pneumoniae include pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, and sepsis, particularly in young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals.Assay Genie · Streptococcus pneumoniae_ Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment1. Biology and Characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae Morphology and ClassificationShape: Gram-positive, lancet-shaped diplococci.Encapsulation: Th
…
19th Nov 2024
Horseshoe Crab Blood and Endotoxin Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Horseshoe crabs, often referred to as "living fossils," are invaluable to modern medicine due to their unique blue blood. This blood is the source of Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL), a substance critical for detecting endotoxins in vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices. However, the reliance on horseshoe crabs raises ecological and ethical concerns, prompting the development of sustainable alternatives. This guide explores the science, applications, and future of endotoxin testing.Assay Genie · Horseshoe Crab Blood and Endotoxin Testing_ A Comprehensive Guide1. The Unique Properties of Horseshoe Crab Blood Why Horseshoe Crab Blood is BlueHorseshoe crab blood contain
…
19th Nov 2024
Phosphorothioate: Enhancing Stability in Oligonucleotide-Based Therapies
Phosphorothioate is a chemical modification commonly used in oligonucleotide-based therapies to enhance the stability and efficacy of therapeutic nucleic acids. In this modification, one of the non-bridging oxygen atoms in the phosphate backbone of a nucleotide is replaced by a sulfur atom. This seemingly small change provides a significant benefit: phosphorothioate oligonucleotides are far more resistant to enzymatic degradation, which is critical for maintaining their activity in the body. The modification is widely used in antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), RNA interference (RNAi), and aptamer therapies to improve cellular uptake, bioavailability, and stability .1. Structure
…
15th Nov 2024
Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating NSCLC
Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, representing about 85% of all lung cancer cases. NSCLC includes several subtypes, with distinct biological characteristics that influence treatment options and prognosis. Advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have significantly improved NSCLC treatment, especially in advanced stages.1. What is Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma?NSCLC encompasses a group of lung cancers that arise from different types of lung cells and grow at varying rates. Unlike small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), which is more aggressive, NSCLC generally progresses more slowly. The main types of NSCLC are:Adenocarcinoma:
…
14th Nov 2024
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Kidney Cancer
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of kidney cancer, originating in the lining of the proximal renal tubules. RCC accounts for approximately 90% of all kidney cancers and often develops as a single tumor in one kidney, though it can also appear bilaterally or as multiple tumors. Understanding RCC's causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the role of advanced therapies can guide patients and healthcare providers in managing this complex disease.1. What is Renal Cell Carcinoma?Renal cell carcinoma arises from epithelial cells of the renal tubules in the kidney. RCC can remain undetected until it reaches an advanced stage due to its location and lack of early sympt
…
12th Nov 2024
Melanoma: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating Skin Cancer
Melanoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which gives skin its color. Although it is less common than other types of skin cancer, melanoma is more likely to spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. Understanding melanoma’s risk factors, signs, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention.1. What is Melanoma?Melanoma is a malignant tumor that arises from melanocytes, often appearing as an unusual mole or dark spot on the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and
…
12th Nov 2024
M2 Supplement for Organoid Cell Culture: Enhancing Growth and Differentiation
The use of M2 Supplement in organoid culture has revolutionized the way researchers cultivate and maintain these three-dimensional (3D) cellular models. Organoids—self-organizing cell clusters that mimic the structure and function of actual tissues and organs—are widely used in disease modeling, drug discovery, and regenerative medicine. M2 Supplement enhances organoid culture by providing essential nutrients and growth factors that support the growth, viability, and differentiation of cells within these complex systems.Assay Genie · M2 Supplement for Organoid Cell Culture_ Enhancing Growth and Differentiation1. What is M2 Supplement?M2 Supplement is a cell culture additive spec
…
12th Nov 2024
Freezing Stimulated T Cells: A Detailed Guide
Cryopreservation of stimulated T cells is a common technique in immunology research, allowing for long-term storage while maintaining their functional viability. Stimulated T cells—especially those activated with antigens, cytokines, or co-stimulatory molecules—tend to be more metabolically active than resting cells, which makes them sensitive to the freezing process. Proper cryopreservation techniques ensure that T cells remain viable and functional upon thawing, allowing for consistent experimental results.Assay Genie · Freezing Stimulated T Cells_ A Detailed Guide1. Preparation Before FreezingCell Stimulation and ActivationPrior to freezing, T cells are often stimulated with
…
6th Nov 2024
Typical Workflow of CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing
The CRISPR-Cas9 system is a powerful tool for genome editing, enabling precise modifications to DNA. The typical CRISPR-Cas9 workflow involves several steps, from designing guide RNAs to confirming targeted genetic changes. This guide provides a step-by-step overview of the CRISPR-Cas9 workflow, highlighting best practices for efficient and accurate genome editing.Assay Genie · CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing Workflow1. Design of Guide RNA (gRNA)The first step in the CRISPR-Cas9 workflow is designing a guide RNA (gRNA) that targets the specific DNA sequence for editing.Key Considerations in gRNA DesignTarget Specificity: Ensure the gRNA sequence is highly specific to the target
…
6th Nov 2024
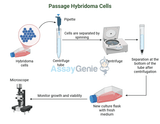
Passaging Hybridoma Cells: A Detailed Guide
Hybridoma cells are essential tools for producing monoclonal antibodies and are derived by fusing B lymphocytes (antibody-producing cells) with myeloma cells (cancer cells) to achieve both targeted antibody production and immortality. Properly maintaining and passaging hybridoma cells is key to their longevity and productivity in culture. This guide provides a step-by-step protocol and best practices for passaging hybridoma cells to ensure optimal health and antibody yield.Assay Genie · Passaging Hybridoma Cells_ A Detailed Guide1. Preparing to Passage Hybridoma CellsMaterials and Equipment NeededHybridoma culture medium: RPMI-1640 or DMEM, typically supplemented with 10-20% fet
…
5th Nov 2024
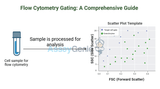
Flow Cytometry Gating: A Comprehensive Guide
Flow cytometry gating is a critical step for isolating and analyzing specific cell populations based on size, granularity, and fluorescence. Proper gating strategies enhance data accuracy by excluding irrelevant or compromised events such as doublets, dead cells, and debris, ensuring that the analysis focuses on relevant, viable cells.1. Introduction to Flow Cytometry GatingGating is the process of setting criteria to identify cell populations of interest based on specific parameters in flow cytometry. Gating helps:Exclude unwanted events: Filters out dead cells, debris, and doublets.Focus on single cells: Isolates single, viable cells for precise data analysis.Identify specific
…
5th Nov 2024
Excluding Doublets in FACS Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Overview: Doublet discrimination is essential in Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) to ensure accurate results, as doublets (two cells sticking together) can resemble single cells or falsely increase fluorescence signals. By following a systematic approach to exclude doublets, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your data. This guide covers the steps for identifying and excluding doublets based on signal characteristics, with a focus on forward scatter (FSC), side scatter (SSC), and fluorescence parameters.Assay Genie · Excluding Doublets in FACS Analysis_ A Comprehensive Guide1. Importance of Doublet Exclusion in FACSDoublets, often appearing as clusters or
…
5th Nov 2024
TREM2: Exploring Its Role in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to TREM2 and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in CancerTREM2 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2) is an immunoregulatory receptor primarily expressed on macrophages, microglia, monocytes, and dendritic cells. In the context of cancer, TREM2 is highly expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), a major immune cell population in the tumor microenvironment (TME) that supports tumor growth and immune evasion. TREM2 signaling in TAMs promotes immunosuppressive functions, limiting the ability of the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.Research has shown that blocking TREM2 can shift TAMs from an immunosuppressive state to a more pro-inflamm
…
31st Oct 2024
FoxP3: Understanding Regulatory T Cell Control in Tumor Immunity
Introduction to FoxP3 and Regulatory T Cells in CancerFoxP3 (forkhead box P3) is a transcription factor critical for the development and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), a specialized subset of CD4+ T cells responsible for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune reactions. Tregs play a key role in regulating the immune response, preventing excessive immune activation that can damage normal tissues. However, in the context of cancer, Tregs, marked by high FoxP3 expression, often accumulate in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and suppress anti-tumor immune responses, creating an environment that enables tumors to evade immune surveillance.The presence of FoxP
…
30th Oct 2024
CD155: Breaking Immune Suppression in Tumor Environments
Introduction to CD155 in Cancer ImmunotherapyCD155, also known as Poliovirus Receptor (PVR), is a transmembrane protein that plays a pivotal role in tumor immune evasion. While CD155 is normally involved in cell adhesion and migration, its overexpression on tumor cells creates an immunosuppressive environment by engaging inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells and T cells. Through these interactions, CD155 contributes to the suppression of the body's natural immune responses, helping tumors evade detection and destruction.Targeting CD155 has emerged as a promising strategy to break immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment, allowing immune cells to regain their
…
29th Oct 2024
TNFRSF9: Enhancing Immune Cell Activity Against Tumors
Introduction to TNFRSF9 and Its Role in Immune ActivationTNFRSF9, also known as 4-1BB or CD137, is a co-stimulatory receptor expressed on the surface of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. It belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF), which plays critical roles in regulating immune responses. Activation of TNFRSF9 boosts the activity and survival of T cells and NK cells, making it a powerful target in cancer immunotherapy where enhanced anti-tumor immunity is essential for effective treatment.When TNFRSF9 binds to its ligand, 4-1BBL, expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), it delivers a robust co-stimulatory signal that promote
…
29th Oct 2024
Dual PD-1/PD-L2 Blockade: Expanding the Horizons of Cancer Immunotherapy
Introduction to PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Cancer ImmunotherapyThe PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway has been instrumental in cancer immunotherapy, with PD-1 (programmed death-1) inhibitors showing success across various cancers by restoring T cell function and enhancing immune responses. PD-1, a receptor on T cells, interacts with its ligand PD-L1, which is commonly expressed on tumor cells and tumor-associated immune cells. This binding suppresses T cell activity, allowing tumors to evade immune destruction. However, PD-L1 is not the only ligand for PD-1—PD-L2 also binds to PD-1 and can significantly contribute to immune evasion in certain tumors.While most current therapies
…
29th Oct 2024
CD86: Enhancing T Cell Activation in Immunotherapy
Introduction to CD86 and Its Role in Immune Activation CD86 is a crucial co-stimulatory molecule that plays an essential role in T cell activation, driving the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy infected or cancerous cells. Expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, CD86 binds to receptors on T cells to regulate their activity. CD86 interacts with CD28 to provide a critical co-stimulatory signal necessary for full T cell activation, promoting proliferation, cytokine production, and effector functions in immune responses.In the context of cancer immunotherapy, harnessing CD86's co-stimulatory functi
…
23rd Oct 2024
CD80: Amplifying Immune Activation Through Co-Stimulatory Pathways
Introduction to CD80 and Its Role in Immune Activation CD80 is a critical immune checkpoint molecule that plays an essential role in T cell activation through co-stimulatory pathways. Expressed primarily on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages, CD80 interacts with receptors on T cells to regulate immune responses. Specifically, CD80 engages CD28 to provide a crucial co-stimulatory signal necessary for full T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. This co-stimulation amplifies the immune system's ability to recognize and attack pathogens, as well as cancer cells.In addition to its role in immune activation, CD80 can
…
23rd Oct 2024
TLR4: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in Cancer Progression
Introduction to TLR4 and Cancer Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a key component of the innate immune system, primarily responsible for detecting infections and initiating inflammatory responses. This receptor recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from bacteria, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from injured or stressed cells. Once activated, TLR4 triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are crucial for defending the body against infections.However, the role of TLR4 in cancer is more complex. While TLR4-mediated inflammation is essential for immune protection, chronic inflammation driven by
…
22nd Oct 2024
CD73: Combating Tumor Immunosuppression by Targeting Adenosine
Introduction to CD73 and Tumor Immunosuppression CD73, also known as ecto-5'-nucleotidase, is an enzyme found on the surface of various cells, including tumor cells and immune cells. It plays a central role in producing adenosine, a molecule with potent immunosuppressive effects, particularly in the tumor microenvironment. By breaking down extracellular ATP (a danger signal) into adenosine, CD73 contributes to creating an environment that dampens immune responses, allowing tumors to evade immune surveillance and grow unchecked.The adenosine pathway has emerged as a critical target in cancer immunotherapy, as elevated adenosine levels within tumors lead to the suppression of
…
21st Oct 2024
CD39: A Novel Target to Overcome Immunosuppression in Cancer
Introduction to CD39 and Cancer Immunosuppression CD39 is an ectonucleotidase enzyme that plays a crucial role in generating adenosine, a powerful immunosuppressive molecule within the tumor microenvironment. By converting extracellular ATP (a danger signal that activates the immune system) into AMP, CD39 initiates the adenosine production pathway, which is completed by CD73. Adenosine, in turn, suppresses immune cell activity, particularly that of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells, thus protecting tumor cells from immune destruction.Targeting CD39 with therapies like BU69, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits CD39 activity, is a promising strategy to r
…
21st Oct 2024
SLAMF7: Activating Natural Killer Cells for Potent Anti-Cancer Responses
Introduction to SLAMF7 in Cancer Immunotherapy SLAMF7, also known as Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule F7, is a surface receptor found on natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, plasma cells, and certain immune-regulatory cells. This receptor plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses, particularly by enhancing the cytotoxic activity of NK cells, which are a critical part of the body’s first line of defense against tumors. The SLAMF7 receptor, also referred to as CD319, has garnered significant attention as a target for cancer immunotherapy due to its ability to activate NK cells and facilitate tumor destruction.In cancers such as multiple myeloma and solid tum
…
16th Oct 2024