Belantamab: A Game-Changer in Multiple Myeloma Therapy
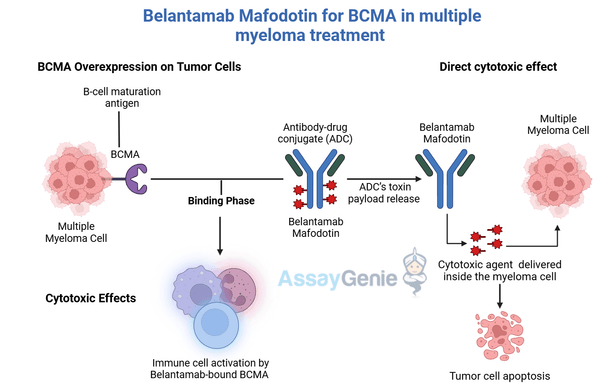
Belantamab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a protein highly expressed on malignant plasma cells in multiple myeloma (MM). By delivering a potent cytotoxic agent directly to BCMA-positive cells, Belantamab offers a precision approach to treating relapsed or refractory MM. The biosimilar provides an affordable, accessible alternative, broadening the reach of BCMA-targeted therapies.
This article explores the mechanism of action, clinical applications, and advantages of Belantamab biosimilar in oncology.
1. Understanding BCMA and Its Role in Multiple Myeloma
What is BCMA?
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is a receptor expressed on:
- Plasma Cells: Essential for plasma cell survival and function.
- Malignant Plasma Cells: Overexpressed in MM, making it an ideal therapeutic target.
Why Target BCMA?
- Tumor-Specific Expression: Highly expressed in MM cells with minimal expression in other tissues.
- Survival Signaling: BCMA contributes to MM cell proliferation and drug resistance.
2. Belantamab Biosimilar: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Features of the Biosimilar
The Belantamab biosimilar mirrors the safety, efficacy, and quality of the original ADC while significantly reducing costs.
- Target: BCMA on MM cells.
- Mechanism: Combines BCMA targeting with cytotoxic payload delivery.
- Affordability: Reduces financial barriers to advanced MM therapies.
3. Mechanism of Action
Step | Details |
|---|---|
BCMA Binding | The biosimilar binds to BCMA on the surface of MM cells. |
ADC Internalization | The antibody-drug complex is internalized into the malignant cell. |
MMAF Release | The cytotoxic payload monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF) is released, disrupting microtubule assembly. |
Tumor Cell Death | MMAF induces apoptosis, selectively destroying BCMA-positive cells. |
4. Clinical Applications
Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM)
Monotherapy
- Effective in heavily pretreated patients with relapsed or refractory MM.
- Offers an alternative for patients resistant to proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs), or anti-CD38 antibodies.
Combination Therapy
- Investigated in combination with immunomodulatory drugs (e.g., lenalidomide) and proteasome inhibitors (e.g., bortezomib) to enhance efficacy.
Emerging Applications
Minimal Residual Disease (MRD)
- Potential use in eradicating MRD to improve long-term outcomes in MM.
CAR-T Synergy
- May be integrated with BCMA-directed CAR-T cell therapies for comprehensive BCMA targeting.
5. Benefits of Belantamab Biosimilar
Targeted Cytotoxicity
Delivers a potent cytotoxic payload directly to BCMA-positive cells, minimizing off-target effects.
Cost-Effective Access
The biosimilar reduces treatment costs, enabling broader access to innovative therapies.
Versatile Applications
Demonstrates efficacy as monotherapy or in combination regimens, addressing diverse patient needs.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Adverse Effects
- Ocular Toxicity: Corneal events such as keratopathy are common; regular monitoring and dose adjustments are required.
- Hematologic Toxicity: Includes thrombocytopenia and neutropenia, manageable with supportive care.
Resistance Development
- Tumors may develop resistance by downregulating BCMA expression. Combination therapies can mitigate this risk.
7. Comparison: Belantamab vs. Biosimilar
Feature | Belantamab Mafodotin | Biosimilar |
|---|---|---|
Target | BCMA on malignant plasma cells. | BCMA on malignant plasma cells. |
Mechanism | ADC delivering MMAF to induce apoptosis. | ADC delivering MMAF to induce apoptosis. |
Indications | Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. | Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. |
Efficacy | Proven in clinical trials. | Equivalent in preclinical and clinical studies. |
Cost | High | Reduced, improving accessibility. |
8. Future Directions
Expanded Indications
- Exploring efficacy in earlier lines of treatment for newly diagnosed MM.
- Investigating use in BCMA-positive hematologic malignancies beyond MM.
Combination Strategies
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Combining with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors to enhance immune responses.
- Radiotherapy: Using Belantamab alongside radiation for localized tumor control.
9. Summary Table
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Target | BCMA, overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. |
Primary Use | Treating relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. |
Mechanism of Action | ADC delivering MMAF to induce apoptosis in BCMA-positive cells. |
Biosimilar Benefits | Affordable, accessible, and clinically equivalent to Belantamab mafodotin. |
Conclusion
The Belantamab biosimilar offers a transformative approach to treating multiple myeloma. By targeting BCMA, it delivers potent anti-cancer effects while sparing healthy tissues. As a cost-effective alternative, the biosimilar expands access to advanced ADC therapies, improving outcomes for patients worldwide.
References
- Trudel, S., et al., 2019. Targeting BCMA in multiple myeloma with Belantamab mafodotin. Blood, 134(22), pp.2335-2345.
- ClinicalTrials.gov, 2023. Studies on Belantamab mafodotin and biosimilar therapies. Available at www.clinicaltrials.gov.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA), 2023. Guidelines for ADC biosimilar development in oncology. Available at www.ema.europa.eu.
- Cohen, A.D., et al., 2021. BCMA as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 14(1), pp.1-15.
- Lonial, S., et al., 2020. Ocular toxicity management in Belantamab mafodotin therapy. The Oncologist, 25(8), pp.583-590.
Recent Posts
-
Tigatuzumab Biosimilar: Harnessing DR5 for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting death receptor 5 (DR5), a member of the …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing CD52-Targeted Therapy
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, a glycoprotein highly expressed on …17th Dec 2025 -
Enavatuzumab Biosimilar: Advancing TWEAKR-Targeted Therapy in Cancer
Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting TWEAK receptor (TWEAKR, also known as F …17th Dec 2025