Vibostolimab: Mechanism, Clinical Applications, and Research Potential in Oncology
Key Facts About Vibostolimab
What is Vibostolimab?
Vibostolimab is an anti-TIGIT monoclonal antibody developed by Merck, targeting immune checkpoint pathways to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
What is the mechanism of action for Vibostolimab?
Vibostolimab inhibits TIGIT, a receptor that suppresses T-cell activity, promoting a robust immune response against cancer cells.
What are the clinical applications of Vibostolimab?
It is investigated for various cancers, including melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), often in combination with pembrolizumab.
Is Vibostolimab safe?
Studies have demonstrated a manageable safety profile, with side effects similar to other immune checkpoint inhibitors.
1.) Understanding Vibostolimab
Vibostolimab represents a groundbreaking advancement in oncology, targeting TIGIT (T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains), a key receptor implicated in the immune escape mechanisms utilized by tumors to evade detection and destruction by the immune system. TIGIT is primarily expressed on T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, where it functions as a negative regulator of immune responses. By engaging with its ligands, such as CD155 on tumor cells and antigen-presenting cells, TIGIT suppresses T cell activity and inhibits NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. This suppression creates an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, allowing cancer cells to proliferate unchecked. Vibostolimab, as a potent TIGIT inhibitor, interrupts this interaction, effectively reactivating suppressed immune cells. This reactivation empowers T cells and NK cells to regain their ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells, offering a novel approach to overcoming immune evasion and enhancing anti-tumor immunity.
Merck, a global leader in oncology research, is spearheading the development of Vibostolimab, recognizing its potential to transform immune checkpoint inhibition strategies. A primary focus of its development is in combination therapies, particularly with pembrolizumab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody. While pembrolizumab blocks PD-1 to enhance T cell activity, Vibostolimab complements this by targeting TIGIT, addressing multiple immune escape pathways simultaneously. This dual blockade creates synergistic effects, intensifying immune activation and reducing resistance observed in monotherapy treatments. Clinical trials have shown promising results, with the combination demonstrating efficacy in diverse cancer types, including solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. As development progresses, Vibostolimab stands out as a key innovation, addressing critical gaps in cancer therapy, improving response rates, and ultimately enhancing patient outcomes. Through its unique mechanism of action and potential for combination therapies, Vibostolimab is poised to play a transformative role in the future of oncology.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Vibostolimab
Vibostolimab exerts its therapeutic effect by antagonizing TIGIT, an inhibitory receptor found on immune effector cells such as CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. TIGIT plays a pivotal role in immune suppression by competing with CD226 (DNAM-1), a co-stimulatory receptor, for binding to shared ligands like PVR (CD155) and PVRL2 (CD112). This competition creates an immunosuppressive environment as TIGIT binding to these ligands sends inhibitory signals that dampen the activity of T cells and NK cells. This suppression allows tumors to evade immune surveillance and proliferate unchecked. Vibostolimab disrupts this interaction by specifically binding to TIGIT, thereby blocking its ability to transmit inhibitory signals and tipping the balance towards immune activation.
By targeting TIGIT, Vibostolimab reactivates T cells and NK cells, restoring their cytotoxic functions and enabling them to recognize and destroy tumor cells more effectively. This mechanism of action is especially significant because it addresses a critical immune checkpoint that operates independently of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. The dual blockade of TIGIT and PD-1 pathways offers a synergistic approach to cancer therapy. While PD-1 inhibitors like pembrolizumab enhance T cell responses by preventing immune exhaustion, Vibostolimab complements this by addressing the TIGIT/CD226 axis, removing another layer of immune suppression.
This synergy between Vibostolimab and pembrolizumab has shown promise in expanding treatment options, particularly for cancers that exhibit resistance to monotherapy. By simultaneously targeting distinct but interconnected immune regulatory pathways, this combination strategy offers a more comprehensive reactivation of the immune system, potentially improving outcomes for patients with advanced or refractory tumors.
3.) Clinical Applications of Vibostolimab
Vibostolimab has shown significant potential in various cancer types, particularly melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), by reversing immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment and promoting robust anti-tumor responses.
Melanoma: In combination with pembrolizumab, Vibostolimab has demonstrated enhanced efficacy in advanced melanoma, especially among patients with high tumor PD-L1 expression. This combination offers a promising therapeutic strategy by leveraging complementary mechanisms of immune reactivation.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Preliminary clinical results indicate that Vibostolimab may play a critical role in overcoming resistance in patients refractory to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. By targeting the TIGIT/CD226 axis, Vibostolimab addresses immune escape mechanisms unique to this patient population, potentially improving outcomes.
Emerging Applications: Beyond melanoma and NSCLC, ongoing studies are investigating the efficacy of Vibostolimab in other solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. This research underscores its versatility and highlights its potential to be integrated into a broader range of cancer treatment paradigms.
Despite its promise, Vibostolimab remains in the early stages of clinical evaluation. Long-term data regarding its safety and sustained efficacy are still being collected, making it a compelling subject for continued investigation. As these studies progress, Vibostolimab holds the potential to reshape immune-oncology treatment strategies, offering hope for patients with limited options.
4.) Advancing Research on Vibostolimab Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an already approved biologic (the reference product), with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Biosimilars offer cost-effective solutions for research and clinical applications.
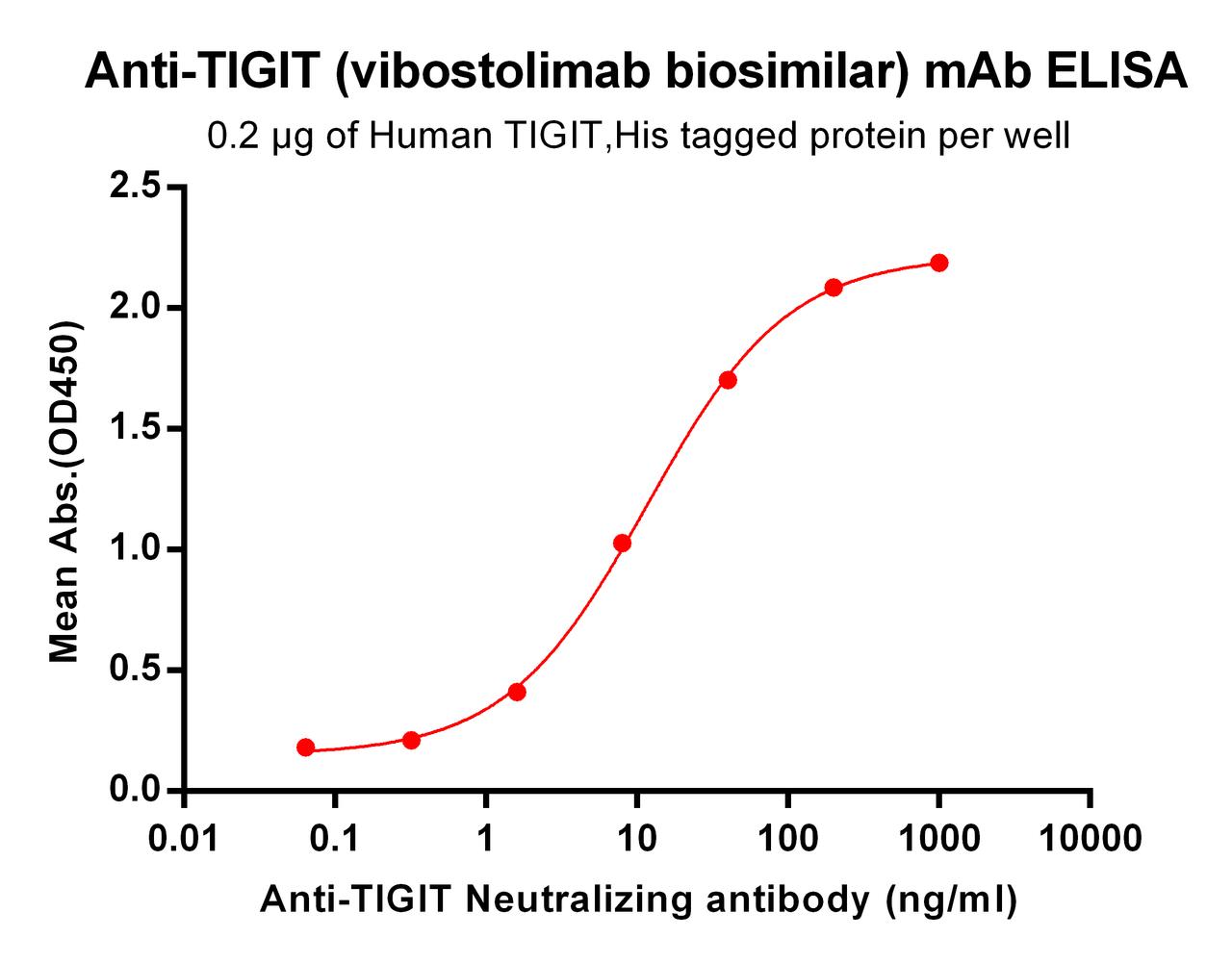
| Vibostolimab (Anti-TIGIT) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | TIGIT |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Vibostolimab Biosimilars Drive Research Innovation
Biosimilars of Vibostolimab are pivotal in advancing oncology research. They provide researchers with affordable tools to explore TIGIT-targeting mechanisms and develop novel combination therapies. These biosimilars replicate the functional properties of Vibostolimab, ensuring accurate results in preclinical and translational studies.
Benefits of Vibostolimab Biosimilars
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced financial barriers for academic and commercial research.
- Accessibility: Broader availability enables diversified studies across research centers.
- Research Use Only: Biosimilars are designated for laboratory use, ensuring ethical compliance and alignment with regulatory guidelines.
By facilitating studies on immune checkpoint pathways, Vibostolimab biosimilars pave the way for next-generation cancer therapies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Our Vibostolimab Biosimilar Antibody is intended exclusively for research use and is not approved for clinical or therapeutic applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025



