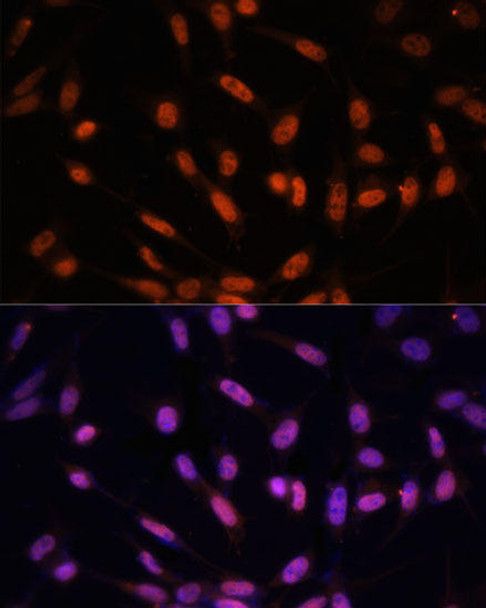
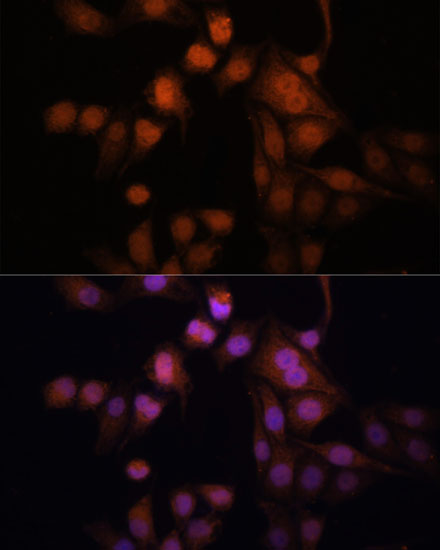
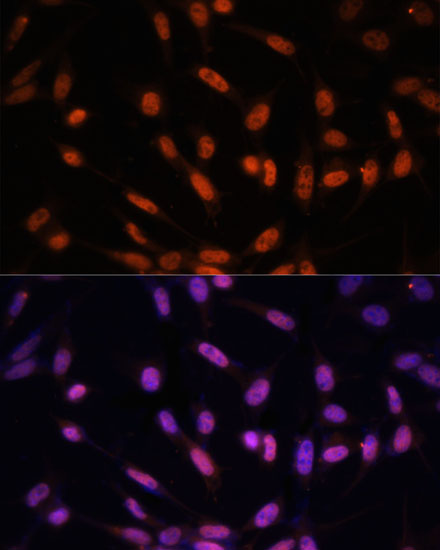
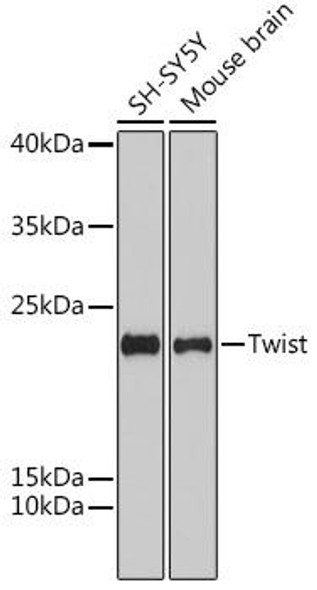
Anti-Twist Antibody (CAB7314)
- SKU:
- CAB7314
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
Anti-Twist Antibody (CAB7314)
The Twist1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB7314) is a vital tool for researchers studying the Twist1 protein, a key regulator of cell differentiation and development. Raised in rabbits, this antibody has high reactivity with human samples and is validated for use in various applications, including Western blot and immunohistochemistry.Twist1 is a transcription factor involved in embryonic development, wound healing, and cancer progression. Dysregulation of Twist1 has been linked to tumor metastasis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and poor prognosis in various cancers.
By targeting Twist1 with this antibody, researchers can track its expression and activity in different cell types, providing valuable insights into its role in tumorigenesis and metastasis.With its specificity and sensitivity, the Twist1 Polyclonal Antibody is an essential tool for research in oncology, developmental biology, and regenerative medicine. It enables precise detection and analysis of Twist1 protein levels, facilitating a better understanding of its function and potential therapeutic targets in cancer and other diseases.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Twist Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7314 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 103-202 of human Twist (NP_000465.1). |
| Application: | IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 103-202 of human Twist (NP_000465.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | YEEL QTQR VMAN VRER QRTQ SLNE AFAA LRKI IPTL PSDK LSKI QTLK LAAR YIDF LYQV LQSD ELDS KMAS CSYV AHER LSYA FSVW RMEG AWSM SASH |
| Gene ID: | 7291 |
| Uniprot: | Q15672 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 20kDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
| Synonyms: | TWIST1, ACS3, BPES2, BPES3, CRS, CRS1, CSO, SCS, TWIST, bHLHa38 |
| Background: | Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors have been implicated in cell lineage determination and differentiation. The protein encoded by this gene is a bHLH transcription factor and shares similarity with another bHLH transcription factor, Dermo1. The strongest expression of this mRNA is in placental tissue; in adults, mesodermally derived tissues express this mRNA preferentially. Mutations in this gene have been found in patients with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | TWIST1: Acts as a transcriptional regulator. Inhibits myogenesis by sequestrating E proteins, inhibiting trans-activation by MEF2, and inhibiting DNA-binding by MYOD1 through physical interaction. This interaction probably involves the basic domains of both proteins. Also represses expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFA and IL1B. Regulates cranial suture patterning and fusion. Activates transcription as a heterodimer with E proteins. Regulates gene expression differentially, depending on dimer composition. Homodimers induce expression of FGFR2 and POSTN while heterodimers repress FGFR2 and POSTN expression and induce THBS1 expression. Heterodimerization is also required for osteoblast differentiation. Efficient DNA binding requires dimerization with another bHLH protein. Homodimer or heterodimer with E proteins such as TCF3. ID1 binds preferentially to TCF3 but does not interact efficiently with TWIST1 so ID1 levels control the amount of TCF3 available to dimerize with TWIST1 and thus determine the type of dimer formed. Subset of mesodermal cells. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription regulation; Inhibitor; Cell development/differentiation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7p21.2 Cellular Component: nucleus Molecular Function:protein domain specific binding; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; protein heterodimerization activity; bHLH transcription factor binding; transcription factor binding Biological Process: transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis; negative regulation of skeletal muscle development; muscle development; rhythmic process; neuron migration; palate development; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; negative regulation of histone phosphorylation; negative regulation of histone acetylation; odontogenesis; negative regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation; ossification; in utero embryonic development; negative regulation of transcription factor activity; outer ear morphogenesis; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation; osteoblast differentiation; positive regulation of angiogenesis; neural tube closure; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic digit morphogenesis; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of bone mineralization; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade Disease: Robinow-sorauf Syndrome; Craniosynostosis 1; Saethre-chotzen Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors have been implicated in cell lineage determination and differentiation. The protein encoded by this gene is a bHLH transcription factor and shares similarity with another bHLH transcription factor, Dermo1. The strongest expression of this mRNA is in placental tissue; in adults, mesodermally derived tissues express this mRNA preferentially. Mutations in this gene have been found in patients with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15672 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2498009 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7291 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15672.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15672,Q92487, Q99804, A4D128, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15672 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated: 20 kdaObserved: 34 kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Twist-related protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | twist family bHLH transcription factor 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TWIST1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CRS; CSO; SCS; ACS3; CRS1; BPES2; BPES3; TWIST; bHLHa38 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | twist-related protein 1; H-twist; twist homolog 1; B-HLH DNA binding protein; TWIST homolog of drosophila; class A basic helix-loop-helix protein 38; twist basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Twist-related protein 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Class A basic helix-loop-helix protein 38; bHLHa38; H-twist |
| Protein Family: | Twist-related protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TWIST1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TWST1_HUMAN |