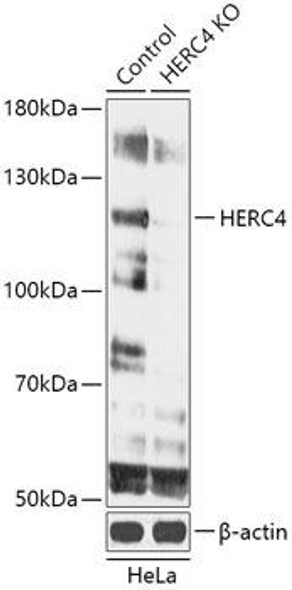
Anti-DDX58 Antibody (CAB18003)[KO Validated]
- SKU:
- CAB18003
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
Anti-DDX58 Antibody (CAB18003)[KO Validated]
The DDX58 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB18003) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the DDX58 protein, also known as RIG-I, which plays a crucial role in innate immunity and antiviral responses. This rabbit polyclonal antibody is highly specific to human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications.DDX58 is a key sensor of viral RNA and is involved in triggering the immune response to viral infections. By binding to DDX58, this antibody allows for the detection and analysis of this important protein in various cell types, making it ideal for studies in virology, immunology, and infectious diseases research.
The role of DDX58 in antiviral immunity makes it a promising target for the development of new antiviral therapies and vaccines. Understanding the mechanisms by which DDX58 functions can lead to important insights for the treatment and prevention of viral infections. This antibody is a valuable tool for researchers looking to advance our understanding of the immune response to viral pathogens.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DDX58 Antibody [KO Validated] |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB18003 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 830 to the C-terminus of human DDX58 (NP_055129.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:20 - 1:100 IP 1:20 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | A-549 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 830 to the C-terminus of human DDX58 (NP_055129.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | HYTV LGDA FKEC FVSR PHPK PKQF SSFE KRAK IFCA RQNC SHDW GIHV KYKT FEIP VIKI ESFV VEDI ATGV QTLY SKWK DFHF EKIP FDPA EMSK |
| Gene ID: | 23586 |
| Uniprot: | O95786 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell projection, Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, ruffle membrane, tight junction |
| Calculated MW: | 101kDa/106kDa |
| Observed MW: | 102kDa |
| Synonyms: | DDX58, RIG-I, RIGI, RLR-1, SGMRT2 |
| Background: | DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases which are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving RNA binding and alteration of RNA secondary structure. This gene encodes a protein containing RNA helicase-DEAD box protein motifs and a caspase recruitment domain (CARD). It is involved in viral double-stranded (ds) RNA recognition and the regulation of immune response. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | DDX58: an innate immune receptor which acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral nucleic acids and plays a major role in sensing viral infection and in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Its ligands include: 5'- triphosphorylated ssRNA and dsRNA and short dsRNA (<1 kb in length). In addition to the 5'-triphosphate moiety, blunt-end base pairing at the 5'-end of the RNA is very essential. Overhangs at the non-triphosphorylated end of the dsRNA RNA have no major impact on its activity. A 3'overhang at the 5'triphosphate end decreases and any 5'overhang at the 5' triphosphate end abolishes its activity. Upon ligand binding it associates with mitochondria antiviral signaling protein MAVS which activates the IKK- related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE which phosphorylate interferon regulatory factors IRF3 and IRF7, in turn activating transcription of antiviral immunological genes, including IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. Detects both positive and negative strand RNA viruses including members of the families Paramyxoviridae: Human respiratory synctial virus and measles virus (MeV), Rhabdoviridae: vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), Orthomyxoviridae: influenza A and B virus, Flaviviridae: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), dengue virus (DENV) and west Nile virus (WNV). It also detects rotavirus and reovirus. Also involved in antiviral signaling in response to viruses containing a dsDNA genome such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Detects dsRNA produced from non-self dsDNA by RNA polymerase III, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs). May play important roles in granulocyte production and differentiation, bacterial phagocytosis and in the regulation of cell migration. Maintained as a monomer in an autoinhibited state. Upon viral dsRNA binding and conformation shift, homomultimerizes and interacts with MAVS. Interacts with DHX58, IKBKE, TBK1 and STING. Interacts (via CARD domain) with TRIM25 (via SPRY domain). Interacts with RNF135. Interacts with CYLD. Interacts with NLRC5; blocks the interaction of MAVS to DDX58. Interacts with SRC. Interacts with protein Z of Guanarito virus, Machupo virus, Junin arenavirus and Sabia virus. This interaction disrupts its interaction with MAVS, impeding downstream IRF3 and NF-kappa-B activation and resulting in decreased IFN-beta induction. Interacts (via CARD domain) with Human respiratory syncytial virus A non-structural protein 2 (NS2) and this interaction disrupts its interaction with MAVS, impeding downstream IRF3 activation. Present in vascular smooth cells. Belongs to the helicase family. RLR subfamily. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.6.4.13; Hydrolase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9p12 Cellular Component: actin cytoskeleton; cytoplasm; cytosol; tight junction Molecular Function:double-stranded RNA binding; identical protein binding; protein binding; single-stranded RNA binding; zinc ion binding Biological Process: detection of virus; innate immune response; negative regulation of interferon type I production; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production; positive regulation of interferon-beta production; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; positive regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of cell migration; response to virus Disease: Singleton-merten Syndrome 2 |
| NCBI Summary: | DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases which are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving RNA binding and alteration of RNA secondary structure. This gene encodes a protein containing RNA helicase-DEAD box protein motifs and a caspase recruitment domain (CARD). It is involved in viral double-stranded (ds) RNA recognition and the regulation of immune response. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O95786 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 81170421 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 23586 |
| NCBI Accession: | O95786.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O95786,Q5HYE1, Q5VYT1, Q9NT04, A2RU81, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O95786 |
| Molecular Weight: | 101,377 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | DEXD/H-box helicase 58 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DDX58 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RIGI; RIG-I; RLR-1; SGMRT2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | DEAD box protein 58; RIG-I-like receptor 1; RLR-1; Retinoic acid-inducible gene 1 protein; RIG-1; Retinoic acid-inducible gene I protein; RIG-I |
| Protein Family: | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DDX58 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DDX58_HUMAN |


![Anti-DDX58 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB18003)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-h68l9z2lnx/product_images/j/341/A18003_1__13148.jpg)