Human PTGDS Recombinant Protein (RPPB2219)
- SKU:
- RPPB2219
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P41222
- Research Area:
- Enzymes
Description
| Product Name: | Human PTGDS Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB2219 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | PTGDS |
| Synonyms: | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase, Beta-trace protein, Cerebrin-28, Glutathione-independent PGD synthase, Lipocalin-type prostaglandin-D synthase, Prostaglandin-D2 synthase, PGD2 synthase, PGDS, PGDS2, PTGDS, PDS, PGD2, LPGDS, L-PGDS. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | PTGDS solution (1mg/ml) containing 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0), 1mM DTT, 30% glycerol, 1mM EDTA and 0.1M NaCl. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
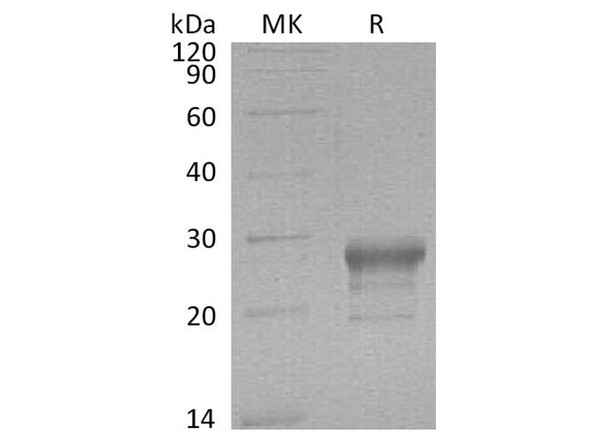
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MAPEAQVSVQ PNFQQDKFLG RWFSAGLASN SSWLREKKAA LSMCKSVVAP ATDGGLNLTS TFLRKNQCET RTMLLQPAGS LGSYSYRSPH WGSTYSVSVV ETDYDQYALL YSQGSKGPGE DFRMATLYSR TQTPRAELKE KFTAFCKAQG FTEDTIVFLP QTDKCMTEQ |
Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase (PTGDS) is a glutathione-independent prostaglandin D synthase which catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) to postaglandin D2 (PGD2). PTGDS is may have vital roles in both maturation and maintenance of the central nervous system and male reproductive system. PTGDS is the most abundant protein in the cerebral spinal fluid and recent evidence suggests that PTGDS acts as a beta-amyloid chaperone and may play a role in the deposition of Ab plaques in Alzheimer�s disease.
PTGDS produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 189 amino acids (23-190 a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 20.9kDa.PTGDS is fused to a 21 amino acid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | PTGDS: Catalyzes the conversion of PGH2 to PGD2, a prostaglandin involved in smooth muscle contraction/relaxation and a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Involved in a variety of CNS functions, such as sedation, NREM sleep and PGE2-induced allodynia, and may have an anti-apoptotic role in oligodendrocytes. Binds small non-substrate lipophilic molecules, including biliverdin, bilirubin, retinal, retinoic acid and thyroid hormone, and may act as a scavenger for harmful hydrophopic molecules and as a secretory retinoid and thyroid hormone transporter. Possibly involved in development and maintenance of the blood-brain, blood-retina, blood-aqueous humor and blood-testis barrier. It is likely to play important roles in both maturation and maintenance of the central nervous system and male reproductive system. Belongs to the calycin superfamily. Lipocalin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 5.3.99.2; Secreted; Endoplasmic reticulum; Lipid Metabolism - arachidonic acid; Secreted, signal peptide; Isomerase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q34.2-q34.3 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; extracellular space; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; nuclear membrane; rough endoplasmic reticulum; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; extracellular region Molecular Function:retinoid binding; prostaglandin-D synthase activity; transporter activity; fatty acid binding Biological Process: transport; cyclooxygenase pathway; response to glucocorticoid stimulus; arachidonic acid metabolic process; prostaglandin biosynthetic process; regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a glutathione-independent prostaglandin D synthase that catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) to postaglandin D2 (PGD2). PGD2 functions as a neuromodulator as well as a trophic factor in the central nervous system. PGD2 is also involved in smooth muscle contraction/relaxation and is a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. This gene is preferentially expressed in brain. Studies with transgenic mice overexpressing this gene suggest that this gene may be also involved in the regulation of non-rapid eye movement sleep. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P41222 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 730305 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5730 |
| NCBI Accession: | P41222.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P41222,Q5SQ10, Q7M4P3, Q9UC22, Q9UCC9, Q9UCD9, B2R727 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P41222 |
| Molecular Weight: | 21kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | prostaglandin D2 synthase 21kDa (brain) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PTGDS�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PDS; PGD2; PGDS; LPGDS; PGDS2; L-PGDS�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase; cerebrin-28; PGD2 synthase; beta-trace protein; prostaglandin D synthase; prostaglandin-D2 synthase; glutathione-independent PGD synthase; glutathione-independent PGD synthetase; lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase; lipocalin-type prostaglandin-D synthase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-trace protein; Cerebrin-28; Glutathione-independent PGD synthase; Lipocalin-type prostaglandin-D synthase; Prostaglandin-D2 synthase; PGD2 synthase; PGDS; PGDS2 |
| Protein Family: | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PTGDS�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PTGDS_HUMAN |