Human FGF18 Recombinant Protein (His tag)
- SKU:
- RPES5664
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Product Name: | Human FGF18 Recombinant Protein (His tag) |
| Product Code: | RPES5664 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Expression Host: | E.coli |
| Synonyms: | FGFI, zFGF5 |
| Mol Mass: | 19.36 kDa |
| AP Mol Mass: | 23 kDa |
| Tag: | C-His |
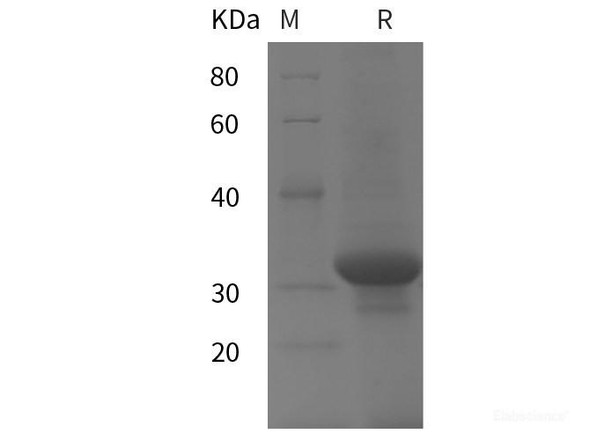
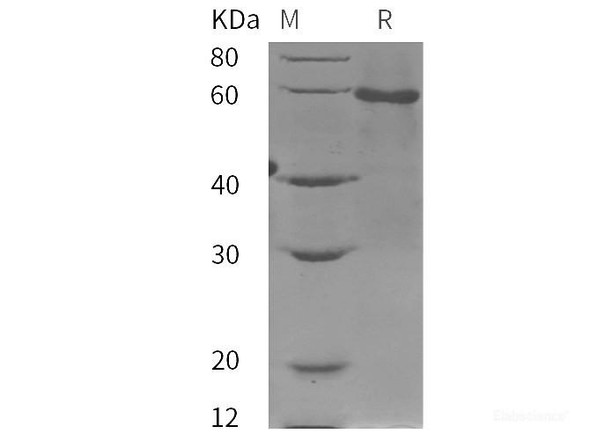
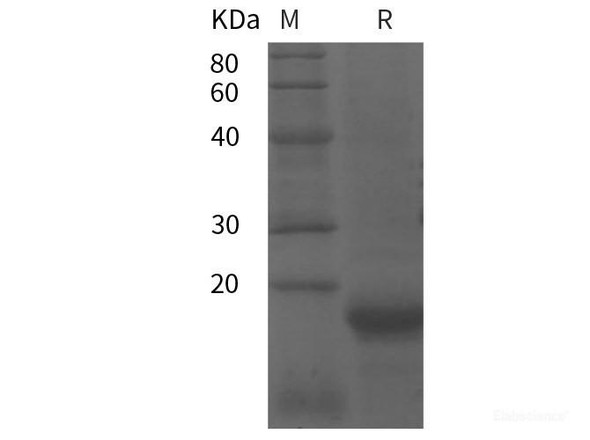
| Purity: | > 95 % as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE. |
| Endotoxin Level: | Please contact us for more information. |
| Bio Activity: | Testing in progress |
| Sequence: | Val 31-Ala 207 |
| Accession: | O76093 |
| Storage: | Generally, lyophilized proteins are stable for up to 12 months when stored at -20 to -80°C. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 4-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at < -20°C for 3 months. |
| Shipping: | This product is provided as lyophilized powder which is shipped with ice packs. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Please refer to the specific buffer information in the printed manual. |
| Reconstitution: | Please refer to the printed manual for detailed information. |
| Background: | Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 (FGF-18) is a 20 kDa protein that plays an important role in skeletal development and bone homeostasis . Mature human FGF-18 shares 99% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat FGF-18 . It is expressed in embryonic somites and the neural fold , adult lung , cerebellar and hippocampal neurons , hair follicle root sheath cells , and osteogenic mesenchymal cells . FGF-18 binds to FGF R2c, FGF R3c as well as the Golgi protein GLG1 and induces the proliferation of astrocytes and microglia, vascular endothelial cells, dermal fibroblasts, papilla cells, and keratinocytes . FGF-18 is required for normal skeletal development . It recruits osteoclasts and osteoblasts to the growth plate, promotes osteoclast formation and function, inhibits osteoblast differentiation, promotes skeletal vascularization, and induces chondrocyte hypertrophy and cartilage matrix formation. |