Guselkumab: Advancing Psoriasis and Autoimmune Disease Research Through IL-23 Targeting
Quick Facts About Guselkumab
What is Guselkumab?
Guselkumab is a biologic therapy that selectively targets the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23), playing a critical role in inflammatory autoimmune conditions.
What is the mechanism of action for Guselkumab?
It inhibits IL-23 signaling by binding to the p19 subunit, disrupting downstream inflammatory pathways involved in diseases like psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Is Guselkumab safe?
Clinical trials have shown Guselkumab to have a favorable safety profile, with most side effects being mild to moderate, such as upper respiratory infections and injection-site reactions.
What conditions does Guselkumab treat?
Guselkumab is FDA-approved for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and active psoriatic arthritis, with emerging interest in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
What is the typical dosing schedule for Guselkumab?
Guselkumab is usually administered as a subcutaneous injection of 100 mg initially, followed by a dose at week 4, then every 8 weeks thereafter.
1.) Understanding Guselkumab
Guselkumab, marketed under the brand name Tremfya, is a groundbreaking, first-in-class biologic therapy developed by Janssen. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively targets the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23), a key cytokine involved in inflammatory pathways. Unlike earlier biologics that inhibit both IL-12 and IL-23 by targeting their shared p40 subunit, Guselkumab’s specificity for IL-23p19 allows for effective modulation of inflammation with a reduced impact on broader immune functions. This selective mechanism contributes to a more favorable safety profile and a tailored therapeutic approach for chronic inflammatory diseases.
Since its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, Guselkumab has transformed disease management by offering durable skin clearance and improved quality of life. It was later approved for active psoriatic arthritis, supported by robust data from the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 clinical trials, which demonstrated significant improvements in joint symptoms and physical function.
Emerging evidence from long-term extension studies and real-world data continues to affirm Guselkumab’s safety and sustained efficacy over time. With increasing monthly global searches—exceeding 4,400—interest in Guselkumab is steadily rising, reflecting its growing clinical importance and acceptance among healthcare providers and patients.
Ongoing research is now exploring its potential applications beyond dermatology, particularly in immune-mediated gastrointestinal conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These studies aim to determine whether Guselkumab’s targeted IL-23 inhibition can provide similar benefits in the complex inflammatory landscapes of these disorders.
2.) Guselkumab Mechanism of Action
Guselkumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody, exerts its therapeutic effects by selectively binding to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23)—a pivotal cytokine in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. IL-23 is instrumental in the differentiation, expansion, and survival of T-helper 17 (Th17) cells, which are major producers of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22. These cytokines contribute significantly to chronic inflammation and tissue damage in diseases like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and potentially other IL-23–driven conditions.
By inhibiting IL-23, Guselkumab disrupts the IL-23/IL-17 signaling axis, leading to decreased activation of Th17 cells and a subsequent reduction in inflammatory mediators. This highly targeted mechanism marks a significant evolution from earlier biologics, such as ustekinumab, that act on both IL-12 and IL-23 via their shared p40 subunit. Guselkumab’s selective action minimizes broader immune suppression, thereby preserving protective immune functions while still delivering potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Beyond acute cytokine inhibition, emerging data indicate that IL-23 blockade may influence tissue-resident memory T cells, which are believed to contribute to disease relapse and chronicity. By affecting these long-lived immune cells, Guselkumab may support the establishment of long-term immune tolerance, a critical factor in achieving sustained remission.
Additionally, with a half-life of approximately 15–18 days, Guselkumab supports a convenient dosing regimen—initial injections followed by maintenance every eight weeks. This extended interval not only enhances patient adherence but also contributes to consistent and durable clinical responses, ultimately improving long-term outcomes and quality of life.
3.) Clinical Applications of Guselkumab
Guselkumab has become a cornerstone therapy in the management of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and active psoriatic arthritis, where it demonstrates robust efficacy, durable response rates, and favorable tolerability. It is incorporated into clinical guidelines as a first-line biologic due to its ability to achieve high levels of skin clearance—frequently reaching PASI 90 and PASI 100 responses—as well as significant improvements in joint-related symptoms.
Key clinical trials underscore its therapeutic success. The VOYAGE 1 and 2 trials were instrumental in demonstrating Guselkumab’s superiority over adalimumab, a widely used TNF inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. These studies showed rapid onset and sustained skin clearance with a favorable safety profile. The ECLIPSE trial further validated its efficacy, comparing Guselkumab to secukinumab (an IL-17A inhibitor), and found greater sustained PASI responses at 48 weeks, highlighting its long-term benefit.
In psoriatic arthritis, the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 trials provided the clinical foundation for FDA approval. These studies demonstrated meaningful improvements in joint inflammation, dactylitis, enthesitis, and physical function, expanding Guselkumab’s utility beyond dermatologic manifestations.
Although not yet approved for gastrointestinal use, Guselkumab has shown early promise in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis through reductions in inflammatory biomarkers and improvements in endoscopic scores. Its highly targeted IL-23 inhibition and tolerability make it a compelling candidate for future therapeutic expansion.
As ongoing real-world studies and long-term trials continue to confirm its efficacy and safety, Guselkumab stands out as a reliable and versatile agent with growing potential in a range of immune-mediated conditions beyond dermatology.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Guselkumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product that is highly similar to an already approved biologic (the reference product), with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, purity, or potency. Unlike generics, biosimilars are produced from living systems and require rigorous analytical and clinical testing to confirm similarity.
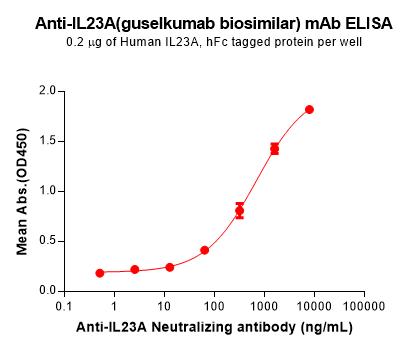
| Guselkumab (Anti-IL23A) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | IL-23A |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Guselkumab Biosimilar Compares to Guselkumab
Biosimilars of Guselkumab are developed to mimic the original molecule’s structure, mechanism, and pharmacokinetic profile. While they are not interchangeable in a clinical setting without regulatory approval, they serve as essential tools for preclinical and translational research where cost-effective alternatives are needed to advance discovery.
The biosimilar mirrors Guselkumab’s IL-23 inhibition mechanism, targeting the same p19 subunit, and can be used in cell-based assays, signal transduction studies, or drug screening platforms to simulate therapeutic environments.
Benefits for Research:
Guselkumab biosimilars offer several advantages for research:
These biosimilars are for research use only and not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. Their availability accelerates insights into disease mechanisms and facilitates the development of next-generation therapies targeting the IL-23/Th17 axis.
Advancing Research on Guselkumab
The emergence of Guselkumab biosimilars is reshaping how scientists approach autoimmune research. As pharmaceutical innovation accelerates, research-use-only biosimilars provide an ethical and scalable means to test hypotheses, identify new targets, and simulate treatment pathways without the regulatory and financial burden of clinical-grade biologics.
Whether exploring IL-23 blockade in new indications like ankylosing spondylitis, lupus, or hidradenitis suppurativa, or understanding resistance mechanisms in psoriasis, these biosimilars empower a broader spectrum of discovery.
With Guselkumab's growing relevance, biosimilars are not just mimics—they are enablers of innovation.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


