Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About Alemtuzumab
What is Alemtuzumab?
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD52, primarily used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) and certain cancers like chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
What is the mechanism of action for Alemtuzumab?
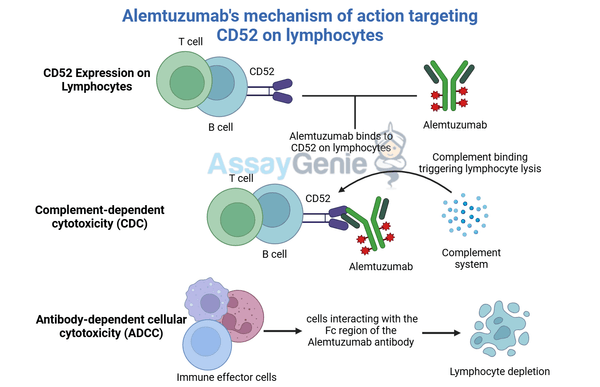
Alemtuzumab binds to CD52 on lymphocytes, leading to their depletion via immune-mediated cytotoxicity, resetting the immune system in diseases like MS.
What are the clinical applications of Alemtuzumab?
What are Alemtuzumab’s common side effects?
Side effects include infusion-related reactions, infections, and autoimmune complications such as thyroid disorders.
1.) Understanding Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab, also known by its brand names Lemtrada and Campath, is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against CD52, a surface antigen found on mature lymphocytes. Its ability to induce profound lymphocyte depletion has made it a cornerstone therapy for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The drug’s immunomodulatory effects allow for resetting the immune system, offering durable remission for many patients.
Initially approved in 2001 for the treatment of CLL, Alemtuzumab has since expanded its indications to include RRMS in 2014, offering an option for patients who have failed other treatments. In RRMS, Alemtuzumab’s ability to deplete both B and T lymphocytes reduces the autoimmune attack on the central nervous system, providing long-lasting relief and promoting durable remission for many patients. In CLL, it targets and eliminates malignant lymphocytes, significantly improving patient outcomes.
However, while Alemtuzumab’s immunomodulatory effects offer substantial therapeutic benefits, they also come with significant risks, including the potential for autoimmune disorders and serious infections. Consequently, its use requires careful patient monitoring, especially in the early stages of treatment. As research continues, Alemtuzumab may find new applications, extending its impact in both oncology and immunology. Its development represents a milestone in monoclonal antibody technology, offering valuable insights into how targeted therapies can shape the future of medicine.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab’s mechanism of action is based on its ability to specifically target CD52, a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of various immune cells, including mature lymphocytes, monocytes, and some dendritic cells. By binding to CD52, Alemtuzumab initiates both antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), resulting in the targeted depletion of these immune cells. This depletion profoundly alters the immune system, which is often followed by a period of immune reconstitution. The reconstituted immune system may show a modified response, potentially reducing the risk of autoreactivity and inflammation.
In multiple sclerosis (MS), Alemtuzumab targets and depletes autoreactive T and B lymphocytes, which are responsible for the autoimmune attack on the central nervous system. This depletion leads to a significant reduction in relapse rates and slows disease progression, making Alemtuzumab an effective therapy for patients with relapsing forms of MS who have failed other treatments.
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Alemtuzumab targets and depletes malignant lymphocytes, particularly those expressing CD52. This action aids in controlling the proliferation of cancerous cells and, when combined with other therapies, can improve overall survival rates and disease management.
While Alemtuzumab’s precision targeting offers significant therapeutic benefits, its potent immune-modulating effects require careful safety monitoring due to risks like infusion reactions, infections, and autoimmune disorders, which may manifest months or even years after treatment.
3.) Clinical Applications of Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab has transformative applications in treating autoimmune and hematologic diseases. Key areas include:
1. Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Alemtuzumab is FDA-approved for relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), significantly reducing relapse rates and delaying disability progression. This monoclonal antibody targets CD52-expressing lymphocytes, inducing prolonged immune modulation. It is particularly beneficial for patients who have shown an inadequate response to other disease-modifying therapies (DMTs). Clinical trials have highlighted its ability to induce durable remissions, making it a valuable option for managing aggressive forms of MS.
2. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Alemtuzumab was initially approved for treating CLL, where it works by depleting CD52-expressing malignant lymphocytes. It remains a valuable therapeutic option for patients with refractory or relapsed CLL, offering an alternative for cases where other treatments have failed. Recent advancements in combination therapies are further enhancing its efficacy, particularly in high-risk patients.
3. Off-Label Uses: Emerging research highlights Alemtuzumab’s potential in treating other autoimmune conditions, such as neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), a severe inflammatory condition of the central nervous system. Investigational studies are also exploring its role in combination regimens for hematologic malignancies and other immune-mediated disorders.
Despite its broad therapeutic potential, Alemtuzumab’s use necessitates careful patient selection and close monitoring. Adverse effects, such as autoimmune thyroid disease, infusion reactions, and increased infection risk, require proactive management strategies to mitigate these risks and optimize patient outcomes.
4.) Advancing Research on Alemtuzumab Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are highly similar to original biologic drugs, offering comparable efficacy and safety at a lower cost. These products undergo rigorous evaluation to ensure their equivalence to reference biologics.
| Alemtuzumab (Anti-CD52) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD52 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Alemtuzumab Biosimilars Compare:
Alemtuzumab biosimilars replicate the structure and function of the original drug, targeting CD52 with similar potency. They represent a cost-effective alternative for research and clinical applications, expanding access to cutting-edge therapies.
Benefits of Alemtuzumab Biosimilars:
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Alemtuzumab biosimilars are intended for research use only and should not be used for clinical applications without regulatory approval.
Biosimilars enhance the scientific community’s ability to explore therapeutic avenues, paving the way for next-generation immunotherapies.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025