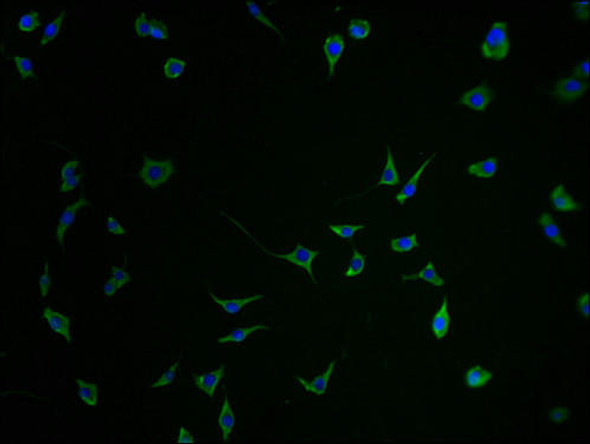
DUSP13 Antibody (PACO14389)
- SKU:
- PACO14389
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- IHC
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Description
DUSP13 Antibody (PACO14389)
The DUSP13 Polyclonal Antibody (PACO14389) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the function of DUSP13, a dual-specificity phosphatase involved in cellular signaling pathways. This antibody, generated in rabbits, exhibits high specificity towards human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications. By binding to the DUSP13 protein, this antibody enables precise detection and analysis in a variety of cell types, making it an essential component for studies in molecular biology and signaling research.DUSP13, a member of the dual-specificity phosphatase family, plays a crucial role in the regulation of key signaling molecules involved in cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation.
Its function in cellular signaling pathways makes it an attractive target for investigations into various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders. By understanding the activity of DUSP13, researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of disease pathology and potentially identify novel therapeutic targets for intervention.
| Antibody Name: | DUSP13 Antibody (PACO14389) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO14389 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, IHC:1:50-1:200 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Fusion protein of human DUSP13 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
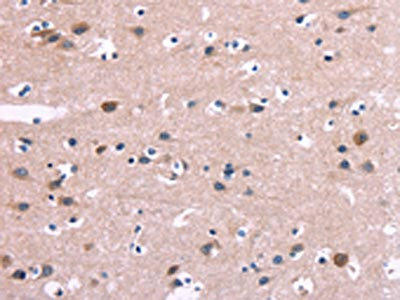 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human brain tissue using PACO14389(DUSP13 Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200). |
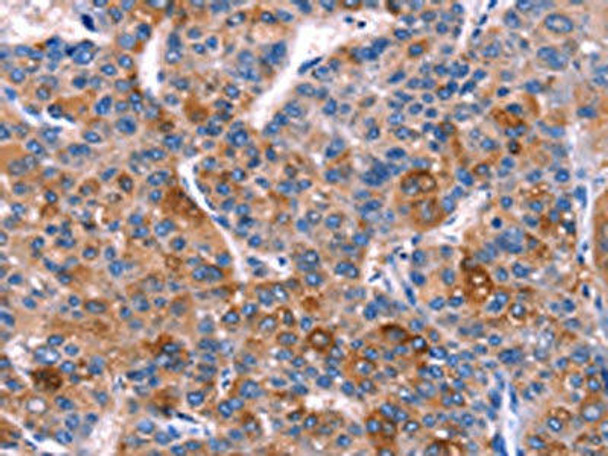
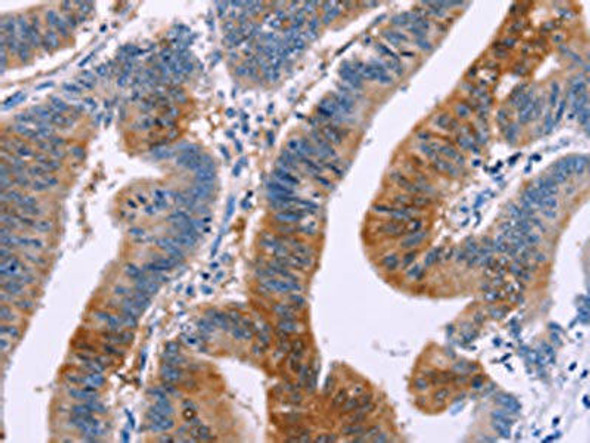
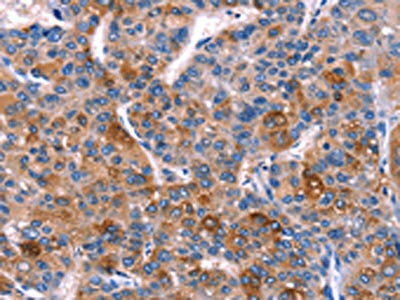 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using PACO14389(DUSP13 Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | Members of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase superfamily cooperate with protein kinases to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. This superfamily is separated into two families based on the substrate that is dephosphorylated. One family, the dual specificity phosphatases (DSPs) acts on both phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine/threonine residues. This gene encodes different but related DSP proteins through the use of non-overlapping open reading frames, alternate splicing, and presumed different transcription promoters. Expression of the distinct proteins from this gene has been found to be tissue specific and the proteins may be involved in postnatal development of specific tissues. |
| Synonyms: | dual specificity phosphatase 13 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | DUSP13: May be involved in the regulation of meiosis and/or differentiation of testicular germ cells during spermatogenesis. Exhibits intrinsic phosphatase activity towards both phospho- seryl/threonyl and -tyrosyl residues of myelin basic protein, with similar specific activities in vitro. Belongs to the protein-tyrosine phosphatase family. Non-receptor class dual specificity subfamily. 5 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative promoter. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.1.3.16; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Protein phosphatase, dual-specificity; Cell cycle regulation; EC 3.1.3.48 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q22.2 Cellular Component: cytoplasm Molecular Function:protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity Biological Process: meiosis; spermatogenesis; protein amino acid dephosphorylation |
| NCBI Summary: | Members of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase superfamily cooperate with protein kinases to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. This superfamily is separated into two families based on the substrate that is dephosphorylated. One family, the dual specificity phosphatases (DSPs) acts on both phosphotyrosine and phosphoserine/threonine residues. This gene encodes different but related DSP proteins through the use of non-overlapping open reading frames, alternate splicing, and presumed different transcription promoters. Expression of the distinct proteins from this gene has been found to be tissue specific and the proteins may be involved in postnatal development of specific tissues. A protein encoded by the upstream ORF was found in skeletal muscle, whereas the encoded protein from the downstream ORF was found only in testis. In mouse, a similar pattern of expression was found. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants were described, but the full-length sequence of only some were determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9UII6 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 257051044 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 51207 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9UII6.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9UII6,Q5JSC6, Q6IAR0, Q96GC2, A8K776, A8K782, B3KPY1 B3KXT0, B4DUK0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q6B8I1,Q9UII6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 198 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Dual specificity protein phosphatase 13 isoform B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | dual specificity phosphatase 13 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DUSP13 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BEDP; MDSP; TMDP; SKRP4; DUSP13A; DUSP13B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | dual specificity protein phosphatase 13; muscle-restricted DSP; branching-enzyme interacting DSP; testis- and skeletal-muscle-specific DSP; branching-enzyme interacting dual-specificity protein phosphatase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Dual specificity protein phosphatase 13 isoform B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Dual specificity phosphatase SKRP4; Testis- and skeletal-muscle-specific DSP |
| Protein Family: | Dual specificity protein phosphatase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DUSP13 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DS13B_HUMAN |