Vesencumab: Unlocking the Potential of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Vesencumab
What is Vesencumab?
Vesencumab is an experimental monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a key regulator of immune evasion in cancer cells.
How Does Vesencumab Work?
By blocking CD47, Vesencumab enhances macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, enabling the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells more effectively.
What Are the Clinical Applications of Vesencumab?
Vesencumab is being explored for its role in treating various malignancies, including hematologic cancers and solid tumors.
Is Vesencumab Safe?
Preliminary studies suggest that Vesencumab is well-tolerated, though research continues to optimize its safety profile and minimize off-target effects.
1.) Understanding Vesencumab
Vesencumab is an innovative immunotherapy designed to harness the body’s immune system to combat cancer. It belongs to a class of therapies targeting CD47, a surface protein commonly referred to as the “don’t eat me” signal. CD47 is overexpressed in numerous cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, and solid tumors, allowing malignant cells to evade immune detection by inhibiting macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. By blocking CD47, Vesencumab removes this protective shield, restoring the ability of macrophages and other innate immune cells to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
Recent studies highlight Vesencumab’s synergistic potential when combined with other immunotherapies, such as PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors, which target adaptive immune evasion mechanisms. While Vesencumab primarily enhances the innate immune response, checkpoint inhibitors work by reactivating exhausted T cells, leading to a more robust and sustained anti-tumor effect. This combination strategy may be particularly effective in tumors resistant to traditional immunotherapies, broadening treatment options for patients with aggressive or refractory cancers.
Beyond macrophage activation, emerging research suggests that Vesencumab might influence dendritic cell function, improving antigen presentation and fostering a stronger adaptive immune response. Additionally, preclinical models indicate that Vesencumab may enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation by sensitizing tumors to immune-mediated destruction.
As clinical trials progress, Vesencumab continues to gain recognition as a promising candidate in oncology. Future research will determine its full therapeutic potential, optimal combination strategies, and efficacy across various cancer types, paving the way for more effective, immune-based cancer treatments.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Vesencumab
Vesencumab exerts its therapeutic effects by targeting CD47, a key immune checkpoint that cancer cells exploit to evade immune surveillance. Under normal physiological conditions, CD47 interacts with its ligand, signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα), on macrophages, sending an inhibitory signal that prevents the immune system from mistakenly attacking healthy cells. However, many cancers—including hematologic malignancies, solid tumors, and metastatic cancers—overexpress CD47, effectively cloaking themselves from immune destruction.
By blocking CD47-SIRPα interactions, Vesencumab disrupts this immune evasion strategy, restoring the innate immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. This occurs through several key mechanisms:
1. Restoring Macrophage Activity
Vesencumab reinvigorates macrophages, allowing them to efficiently phagocytose cancer cells. By neutralizing CD47, macrophages regain their ability to detect and eliminate malignant cells, reducing tumor burden.
2. Promoting Adaptive Immunity
Beyond macrophages, Vesencumab indirectly influences the adaptive immune response by enhancing antigen presentation. When macrophages engulf tumor cells, they process and present tumor antigens to dendritic cells and T cells, leading to a sustained anti-tumor immune response. This may contribute to the development of long-term immune memory, reducing the risk of cancer recurrence.
3. Improving Treatment Synergy
Vesencumab shows enhanced efficacy when combined with chemotherapy, radiation, and other immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors). These combination therapies can amplify anti-tumor immune responses, making them particularly promising for cancers that are resistant to standard treatments.
While initial clinical trials have demonstrated Vesencumab’s potential to revolutionize cancer immunotherapy, further research is needed to optimize dosage, patient selection, and combination strategies for maximal therapeutic benefit.
3.) Clinical Applications of Vesencumab

Vesencumab is currently being explored for its therapeutic potential across a range of hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, where CD47 overexpression serves as a major mechanism of immune evasion. By neutralizing CD47-SIRPα interactions, Vesencumab enhances macrophage-mediated tumor clearance and promotes a broader immune response, making it a promising candidate in cancer immunotherapy.
Hematologic Malignancies
Preclinical and early-phase clinical trials have demonstrated significant efficacy of Vesencumab in hematologic cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), and multiple myeloma. In these malignancies, cancerous cells frequently upregulate CD47, allowing them to escape immune-mediated destruction. Vesencumab has shown the ability to restore immune surveillance, leading to improved tumor cell clearance. Additionally, early data suggest that combining Vesencumab with traditional treatments such as monoclonal antibodies (e.g., rituximab) or chemotherapy may further enhance its therapeutic impact.
Solid Tumors
Beyond blood cancers, Vesencumab is also being investigated for its role in solid tumors, particularly in pancreatic, breast, colorectal, and ovarian cancers. These malignancies often exhibit aggressive progression and resistance to conventional therapies, making the need for novel immunotherapeutic strategies essential. By reprogramming the tumor microenvironment, Vesencumab has shown promise in increasing tumor susceptibility to immune attack.
Combination Therapies
Emerging research suggests that Vesencumab’s efficacy is amplified when combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies, or standard treatments like chemotherapy and radiation. These combination approaches may help overcome tumor immune resistance, leading to longer-lasting responses and improved patient survival.
As ongoing clinical trials refine the optimal dosing, safety profile, and efficacy of Vesencumab, researchers remain optimistic about its potential to reshape the landscape of cancer immunotherapy, particularly for treatment-resistant malignancies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Vesencumab
Biosimilars play a critical role in expanding access to advanced therapies while supporting ongoing scientific research. Vesencumab biosimilar provides an opportunity for researchers to further investigate CD47-targeting strategies without the cost and accessibility barriers associated with the original biologic.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar, but non-identical, version of a biologic drug, designed to match its structure and function. Unlike generics, biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to ensure comparable efficacy and safety.
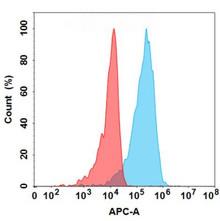
| Vesencumab (Anti-NRP1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD304 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does the Vesencumab Biosimilar Compare?
The biosimilar version retains key characteristics of Vesencumab, including:
- Similar binding affinity to CD47
- Comparable immune activation effects
- Equivalent safety and pharmacokinetic profiles
Benefits of Vesencumab Biosimilar in Research
- Cost-effective alternative for preclinical studies
- Supports drug combination testing
- Expands accessibility for global research institutions
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Note: Vesencumab biosimilar is for research use only and not intended for human therapeutic applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




