Varlilumab: Unlocking CD27’s Potential in Cancer Research
What You Need to Know About Varlilumab
What is Varlilumab?
What is the mechanism of action for Varlilumab?
What are the clinical applications of Varlilumab?
1.) Understanding Varlilumab
Varlilumab (CDX-1127) is a human monoclonal antibody developed by Celldex Therapeutics, targeting CD27, a critical member of the TNF receptor superfamily. CD27 is predominantly expressed on T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, playing a pivotal role in immune cell activation, survival, and proliferation. Its interaction with the ligand CD70 triggers downstream signaling that supports immune effector function, making it a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
Varlilumab is designed to exploit CD27’s role in immune activation to enhance anti-tumor responses. This antibody provides dual benefits: stimulating T-cell activation and effector responses while mitigating immune-suppressive elements within the tumor microenvironment. In preclinical and clinical studies, Varlilumab has been shown to increase the proliferation of cytotoxic T cells and inhibit the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which are often elevated in tumors and contribute to immune evasion.
A significant aspect of Varlilumab’s therapeutic application is its compatibility with other immune-modulating agents, particularly checkpoint inhibitors like nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody. Combining Varlilumab with nivolumab leverages complementary mechanisms, where Varlilumab activates immune cells, and nivolumab prevents tumor-driven immune suppression. This synergistic approach enhances the overall anti-tumor response, offering promising results in clinical trials for multiple cancer types, including melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
By targeting CD27, Varlilumab represents an innovative strategy to reshape the tumor microenvironment and potentiate immune-mediated destruction of cancer cells, exemplifying the growing emphasis on combination immunotherapies in oncology.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Varlilumab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Varlilumab
Varlilumab is an immunomodulatory monoclonal antibody that targets CD27, a co-stimulatory receptor expressed primarily on T-cells. CD27 plays a critical role in enhancing T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production, essential components of a robust and sustained immune response. By binding to CD27, Varlilumab amplifies T-cell activation, enabling a more effective immune response against tumors. This effect is particularly advantageous in the context of combination therapies involving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Checkpoint inhibitors relieve the suppression of T-cell activity mediated by inhibitory pathways such as PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4, while Varlilumab ensures sustained T-cell activation and proliferation, creating a synergistic mechanism that enhances the anti-tumor immune response.
Beyond its role in immune activation, Varlilumab exerts direct anti-tumor effects through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). This mechanism involves the recruitment of immune effector cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, to target and destroy CD27-expressing cancer cells. The engagement of Fc receptors on NK cells by the Fc region of Varlilumab facilitates this process, leading to the targeted lysis of tumor cells. By combining immune system activation with ADCC-mediated direct cytotoxicity, Varlilumab demonstrates a multifaceted therapeutic approach.
Additionally, preclinical studies suggest that Varlilumab may influence the tumor microenvironment by reducing regulatory T-cell (Treg) populations, which are often associated with immune suppression in tumors. This shift not only enhances effector T-cell function but also helps to reverse immune evasion strategies employed by cancer cells. The ability to modulate both systemic and localized immune responses positions Varlilumab as a promising agent in cancer immunotherapy, with potential applications across a range of tumor types when used as a monotherapy or in combination with other immune-activating agents.

3.) Clinical Applications of Varlilumab
Varlilumab, an anti-CD27 monoclonal antibody, has demonstrated significant potential in various clinical trials, especially when combined with other immunotherapeutic agents. One of its most notable combinations is with nivolumab, a PD-1 inhibitor. This pairing has been extensively studied for its ability to synergistically enhance immune responses in advanced cancers, including melanoma, glioblastoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma. By targeting different immune pathways, this combination aims to overcome the immune resistance mechanisms that cancer cells often exploit.
In glioblastoma, an aggressive and notoriously treatment-resistant brain tumor, varlilumab has shown potential in modulating the immune microenvironment. Glioblastoma is characterized by a highly immunosuppressive milieu, which hinders the efficacy of conventional and immunotherapeutic approaches. Preliminary studies suggest that varlilumab may reinvigorate T-cell activity, making it a valuable adjunct to checkpoint inhibitors like nivolumab in this context.
For melanoma and Hodgkin lymphoma, varlilumab has exhibited promise in refractory or relapsed cases. Through its activation of CD27, a co-stimulatory receptor on T cells, it enhances the immune system's ability to identify and attack cancer cells, potentially leading to improved outcomes in patients who have not responded to traditional therapies.
Although some clinical trials involving varlilumab have been discontinued, the insights derived from these studies remain critical. They continue to inform research into optimizing immunotherapeutic combinations and refining treatment strategies for challenging malignancies, highlighting varlilumab's ongoing relevance in the field of cancer immunotherapy.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Varlilumab
Advancing Research on Varlilumab
Our biosimilar product, Varlilumab biosimilar, offers researchers a cost-effective and high-quality alternative to study CD27-targeted therapies. Designed for research use only, it provides a reliable tool for advancing discoveries in immuno-oncology.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product designed to be highly similar to an original reference product, matching its structure, function, and activity. Biosimilars provide researchers with accessible options for preclinical and exploratory studies without the high costs associated with original biologics.
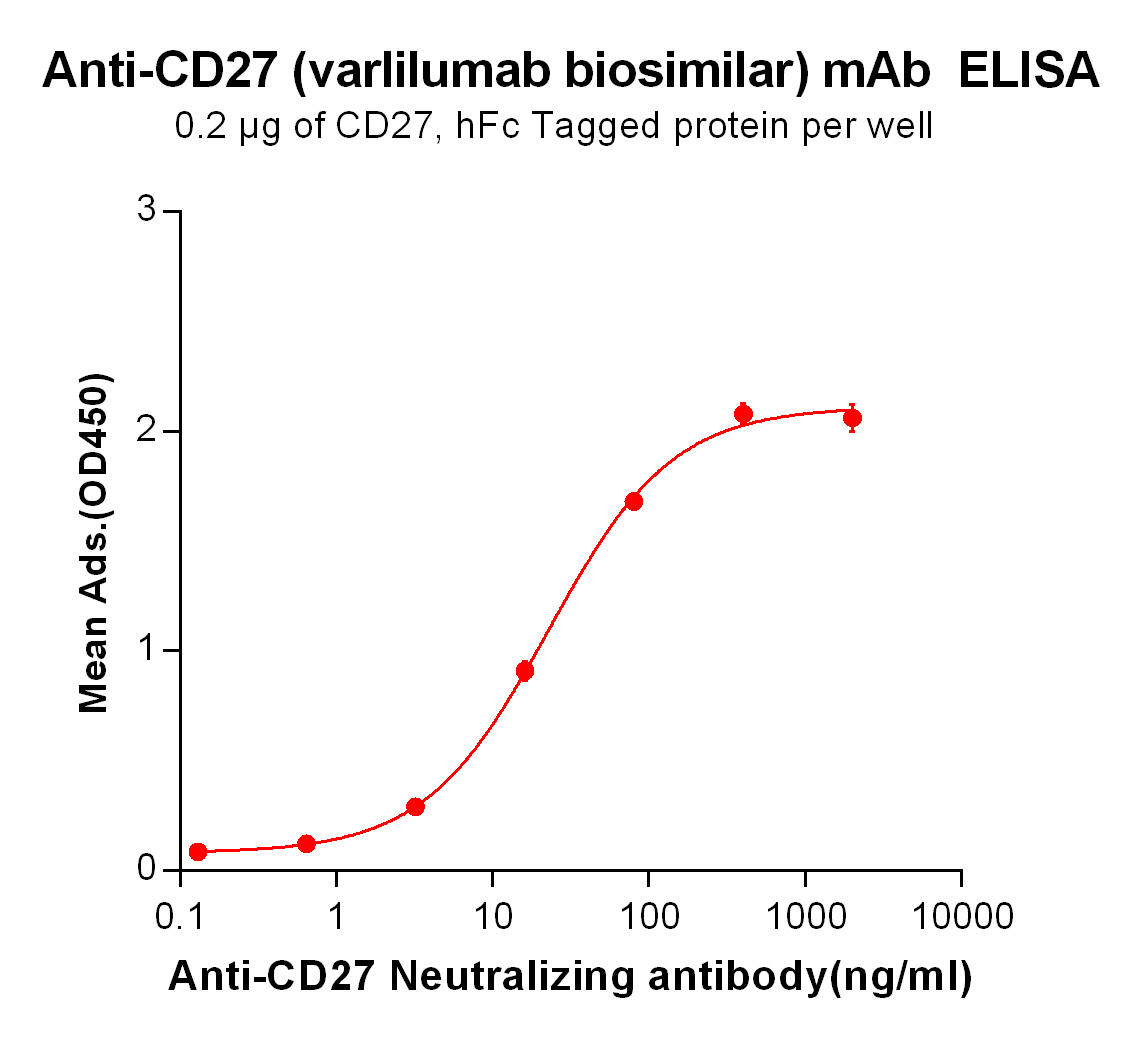
| Varlilumab (Anti-CD27) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD27 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison with Varlilumab
While maintaining structural and functional integrity, the Varlilumab biosimilar is optimized for laboratory applications. It enables scientists to explore CD27-related pathways and evaluate potential combination therapies.
Benefits of Varlilumab Biosimilar
- Cost-Effective:Facilitates more extensive research budgets.
- Reliable: Ensures consistent quality and performance in experimental setups.
- Accessible: Offers global researchers access to advanced tools for immuno-oncology studies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer
The Varlilumab biosimilar is intended exclusively for research purposes and is not approved for clinical or therapeutic use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025