Utomilumab: Advancing Immuno-Oncology Research
Quick Facts About Utomilumab
What is Utomilumab?
Utomilumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting 4-1BB (CD137), a co-stimulatory receptor on T-cells, designed to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
What is the mechanism of action for Utomilumab?
What are the clinical applications of Utomilumab?
It has been investigated in combination therapies for cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and melanoma, aiming to improve immune checkpoint therapy outcomes.
1.) Understanding Utomilumab
Utomilumab represents a pivotal development in immuno-oncology as a second-generation immune checkpoint agonist. Unlike traditional immune checkpoint inhibitors that block suppressive pathways, Utomilumab activates the immune system by targeting 4-1BB, a co-stimulatory receptor expressed on activated T-cells and natural killer (NK) cells. This receptor is critical for the proliferation and survival of T-cells and the enhancement of their cytotoxic activity.
By engaging 4-1BB, Utomilumab amplifies the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells. Its unique mechanism makes it a valuable tool in addressing tumors that evade traditional therapies, offering hope for improved outcomes in challenging oncologic cases. Research has highlighted Utomilumab’s potential synergy with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, broadening its application in combination therapies.
Recent advancements in immunotherapy have underscored the importance of targeting co-stimulatory pathways. Utomilumab serves as a cornerstone for developing innovative strategies to combat immune resistance in cancer. Despite challenges in clinical translation, such as optimal dosing and patient selection, its foundational role in immuno-oncology research continues to inspire future therapeutic breakthroughs. This biologic provides a lens into how immune activation can be harnessed for lasting anti-tumor responses.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Utomilumab
The mechanism of action of Utomilumab centers on its role as an agonist of 4-1BB (CD137), a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily. Upon binding to 4-1BB, Utomilumab stimulates a cascade of immune-enhancing effects:
1. T-Cell Activation: Utomilumab’s engagement with 4-1BB promotes robust T-cell activation, leading to increased proliferation and survival. This ensures a sustained immune response capable of targeting tumor cells.
2. Cytotoxic Function Enhancement: Activated T-cells and NK cells exhibit heightened cytotoxic activity, improving the clearance of malignant cells.
3. Immune Memory Formation: Utomilumab supports the development of immunological memory, enhancing long-term surveillance against cancer recurrence.
These immune-enhancing properties are vital for combating tumors that suppress or evade immune detection. By binding selectively to 4-1BB, Utomilumab minimizes off-target effects, ensuring that the therapeutic impact is concentrated on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. This targeted approach reduces systemic toxicity, which is a common concern in immuno-oncology treatments.
Emerging evidence suggests that Utomilumab’s mechanism synergizes well with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as PD-1/PD-L1 antagonists. This combination not only amplifies the immune response but also addresses immune resistance, a major hurdle in cancer therapy. Utomilumab’s distinct mechanism and selective activity make it a versatile candidate in the evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy.

3.) Clinical Applications of Utomilumab
Utomilumab has been evaluated in several clinical contexts to determine its efficacy as a monotherapy and in combination with other immunotherapies. Key areas of focus include:
Combination with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Utomilumab has shown promise when combined with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors like pembrolizumab or avelumab. This combination aims to enhance anti-tumor immunity by simultaneously stimulating T-cell activation and blocking immune suppression.
Solid Tumors: Trials have explored its use in various cancers, including NSCLC, melanoma, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Early-phase studies indicate that Utomilumab can improve response rates, particularly in tumors with low immunogenicity. Its ability to activate both T-cells and NK cells provides a dual mechanism of action that is particularly advantageous in difficult-to-treat malignancies.
Hematologic Malignancies: Although less extensively studied, Utomilumab’s role in blood cancers such as lymphoma highlights its potential to stimulate NK cells, providing a complementary mechanism to T-cell activation. This makes it an intriguing candidate for dual-targeting strategies in hematologic settings.
Despite promising preclinical and early clinical results, Utomilumab’s development has faced challenges. These include optimizing dosing regimens and navigating competition from other 4-1BB agonists. However, its foundational contributions to immuno-oncology research highlight its significance. By paving the way for next-generation therapies, Utomilumab continues to inform innovative approaches for enhancing anti-tumor immunity.
4.) Advancing Research with Utomilumab Biosimilar
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar version of a biologic drug, developed to match the original product in terms of safety, purity, and efficacy. Biosimilars play a crucial role in making advanced therapeutics more accessible and cost-effective for research and development.
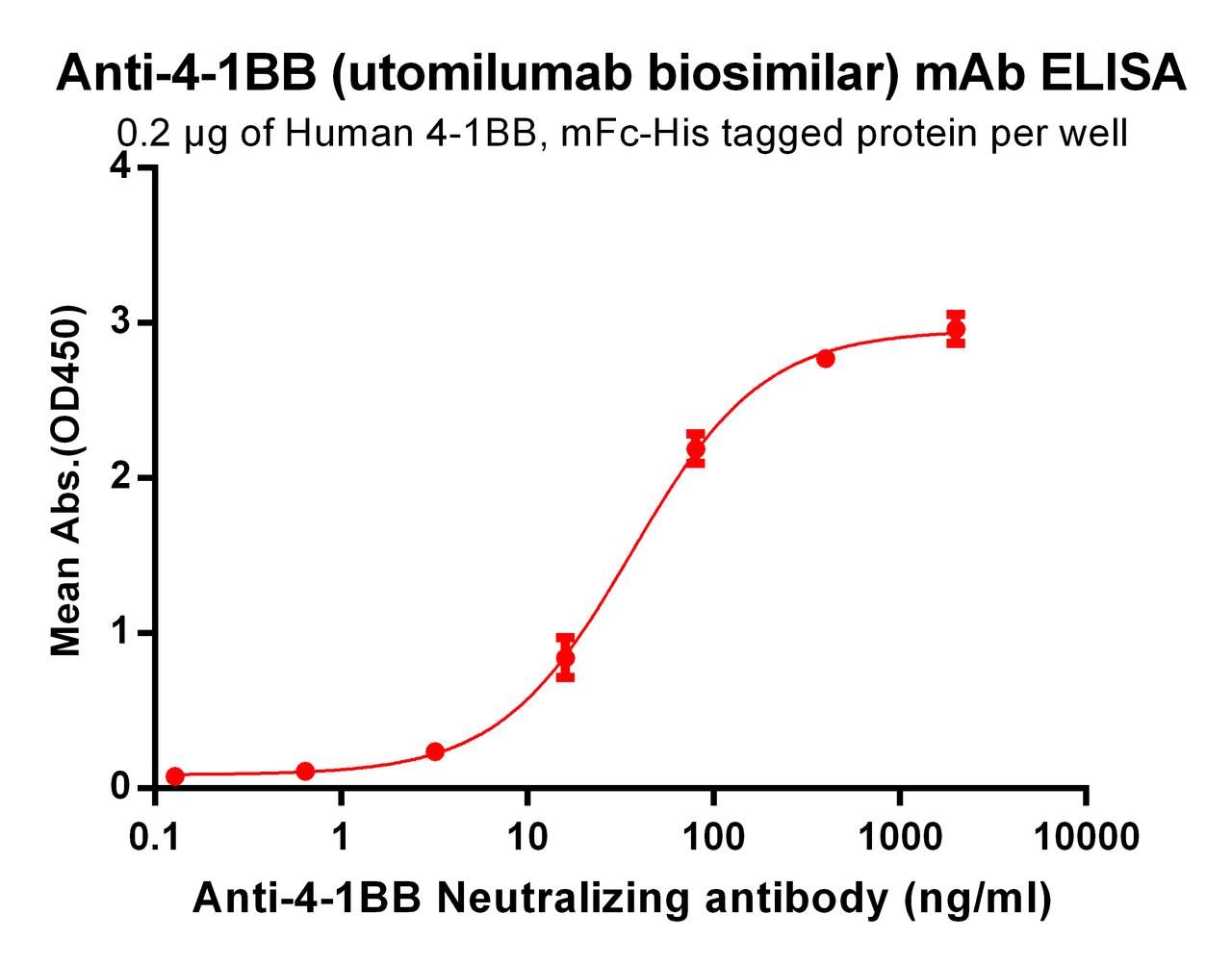
| Utomilumab (Anti-4-1BB) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | 4-1BB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison to Utomilumab:
While identical in function, biosimilars are designated for “research use only,” emphasizing their role in preclinical and early-phase investigations rather than direct clinical application. This distinction allows researchers to explore innovative uses, optimize combination regimens, and refine dosing strategies.
Benefits of the Utomilumab Biosimilar:
Our Utomilumab biosimilar offers researchers an invaluable tool to further investigate the 4-1BB pathway. By mimicking the original drug’s properties, this biosimilar provides:
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Lower costs facilitate broader research initiatives.
- High Consistency: Rigorous manufacturing standards ensure reliability in experimental outcomes.
- Accessibility: Availability for preclinical and translational studies accelerates discovery efforts.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
This product is intended exclusively for research purposes and not for human use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




