Unveiling Prezalumab: Targeting the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Immunotherapy
What You Need to Know About Prezalumab
What is Prezalumab?
Prezalumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a protein often overexpressed in cancer cells to evade immune detection. It is being investigated for its potential in cancer immunotherapy.
What is the mechanism of action for Prezalumab?
Prezalumab works by blocking the CD47 pathway, which helps tumors evade immune attack. By inhibiting CD47, Prezalumab enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
What are the clinical applications of Prezalumab?
Prezalumab is being explored in the treatment of various cancers, including hematological malignancies and solid tumors, to harness the immune system’s potential to fight cancer.
1.) Understanding Prezalumab
Prezalumab is a promising monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a critical protein often referred to as the "don't eat me" signal. This protein is overexpressed on many cancer cells, allowing them to evade immune detection and destruction. CD47 interacts with SIRPα, a receptor found on immune cells, including macrophages. This interaction inhibits immune cell activation and prevents the immune system from attacking cancer cells. By blocking this interaction, Prezalumab enables macrophages and other immune cells to recognize and attack tumor cells, effectively enhancing the body’s immune response.
Prezalumab’s mechanism of action positions it as a valuable tool in cancer immunotherapy, specifically in the field of immuno-oncology. Its ability to boost the body’s natural immune response to cancer offers new hope for patients with advanced or refractory cancers. Traditional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, often have limited effectiveness, particularly in later-stage or aggressive cancers. Prezalumab, by targeting immune evasion mechanisms, has the potential to overcome these barriers, providing a more targeted and less toxic treatment option for patients.
The drug has gained significant attention due to its broad therapeutic potential. It is being investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer, including hematologic malignancies like leukemia and lymphoma, as well as solid tumors such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and breast cancer. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the safety and efficacy of Prezalumab, with early findings suggesting it could be an important addition to cancer treatment regimens, especially for patients whose cancers have proven resistant to conventional therapies.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Prezalumab
Prezalumab works by targeting the CD47 receptor, a protein that plays a critical role in immune evasion by tumor cells. CD47 is commonly overexpressed in a wide variety of cancers, sending a "don't eat me" signal to immune cells, particularly macrophages, which are responsible for detecting and eliminating cancer cells. Under normal circumstances, the interaction between CD47 and the SIRPα receptor on macrophages suppresses immune cell activation and prevents the macrophages from engulfing the tumor cells. This immune evasion mechanism allows the cancer cells to proliferate unchecked and metastasize to other parts of the body.
By binding to CD47, Prezalumab blocks this inhibitory signal, allowing macrophages and other immune cells to recognize and attack the cancer cells. This results in an enhanced immune response against the tumor, as immune cells are no longer prevented from recognizing and destroying cancerous cells. Additionally, the blockage of the CD47-SIRPα interaction helps recruit other immune components to the tumor site, amplifying the body’s overall anti-cancer immune response.
This novel approach to cancer therapy has significant potential, as it taps into the body’s innate immune system to target and destroy malignant cells. Prezalumab’s ability to reverse immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment is a promising development in cancer immunotherapy. Researchers are continuing to study its effectiveness and safety, and early-phase clinical trials suggest that Prezalumab could be an important addition to the arsenal of immunotherapies, potentially providing better outcomes for patients with cancers that are resistant to traditional treatments.
3.) Clinical Applications of Prezalumab
Prezalumab is currently under investigation in clinical trials for its potential to treat a wide range of cancers. The drug has shown particular promise in hematologic malignancies, such as leukemia and lymphoma, where CD47 is often overexpressed. In these cancers, the immune evasion mechanism mediated by CD47 plays a crucial role in tumor progression. By targeting CD47, Prezalumab aims to disrupt this immune suppression, enabling the immune system to better target and destroy the tumor cells.
In addition to hematologic malignancies, Prezalumab is also being evaluated in early-phase studies for solid tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and breast cancer. These cancers are often more difficult to treat and have a higher propensity for resistance to conventional therapies. Early trial data suggests that Prezalumab can enhance immune responses in these solid tumors, potentially improving patient outcomes and survival rates. One of the key advantages of Prezalumab is its ability to target tumors that are resistant to traditional chemotherapy and radiation treatments, offering a novel treatment approach for patients with limited options.
Moreover, Prezalumab is being explored in combination with other cancer therapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors. The combination of Prezalumab with drugs that target other immune checkpoint proteins, such as PD-1 or CTLA-4, may provide a synergistic effect, overcoming the tumor’s resistance mechanisms and further boosting the anti-cancer immune response. As clinical trials continue to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Prezalumab, its potential to become an essential component of cancer treatment regimens grows, providing new hope for patients with difficult-to-treat cancers.
4.) Advancing Research on Prezalumab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
As research into Prezalumab continues, the development of its biosimilar presents an exciting opportunity to expand its accessibility and lower the cost of treatment in clinical settings. A biosimilar is a biologic product that is highly similar to an already approved reference product but may have slight differences in inactive ingredients or manufacturing processes. Biosimilars play a crucial role in enhancing research by providing a more cost-effective alternative while maintaining comparable efficacy.
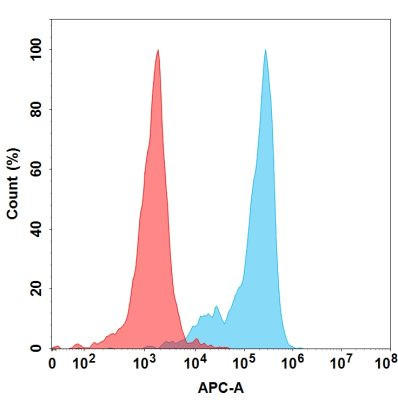
| Prezalumab (Anti-B7-H2) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | B7-H2 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does the Prezalumab Biosimilar Compare?
Our Prezalumab biosimilar (link to product) offers researchers an alternative to the original Prezalumab with the same mechanism of action targeting CD47. The biosimilar enables scientists to explore new combinations, dosages, and treatment regimens in preclinical and clinical trials. These advancements are key to enhancing the understanding of Prezalumab’s full therapeutic potential, especially in areas like patient-specific treatments and combination therapies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Prezalumab biosimilar is intended for research purposes only and is not approved for clinical use. It offers unique advantages in experimental settings, helping to drive innovations in cancer immunotherapy.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



