TUNEL staining : The method of choice for measuring cell death
TUNEL Staining : The method of choice for measuring cell death
In this article we will discuss everything you need to know about the TUNEL staining assay. We'll start by explaining what TUNEL staining is and how it works.
Next, we'll discuss the different types of TUNEL stains available. Then, we'll take a look at the advantages of TUNEL staining over other apoptosis assays.
Finally, we'll provide some tips for performing TUNEL staining correctly.
Key Takeaways
- TUNEL assay detects apoptotic cells through DNA strand cleavage and labeling with fluorescent dye.
- Proper cell fixation and permeabilization are crucial for accurate results.
- Two types of TUNEL stains: FITC-dUTP (sensitive) and PI-dUTP (photobleaching-resistant).
- Counterstaining with DAPI helps distinguish apoptotic nuclei.
- TUNEL staining is highly sensitive, works with fixed cells, and can be combined with other stains for comprehensive analysis.
- Fresh cells and reagents, diluted stain, and optimized conditions are essential for reliable results.
Principles of TUNEL assay
The TUNEL assay is based on the principle of apoptosis, or cell death. Apoptosis is a process by which cells self-destruct in order to remove themselves from a situation in which they are no longer able to function. In order for apoptosis to occur, cells must first undergo DNA damage. Once DNA damage has occurred, the cell will activate enzymes known as caspases. Caspases are a family of enzymes that cleave DNA at specific sites. The TUNEL cell death assay takes advantage of this fact by using an enzyme known as terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT).
TdT is able to recognize and bind to the ends of DNA strands that have been cleaved by caspases. Once TdT has bound to the DNA, it will catalyze the addition of a nucleotide to the end of the DNA strand. This process is known as nick translation. The addition of a nucleotide creates a new end for the DNA strand, which can then be detected using a fluorescent dye. This is the principle behind TUNEL staining.
TUNEL 1-Step Kits
Related Kits
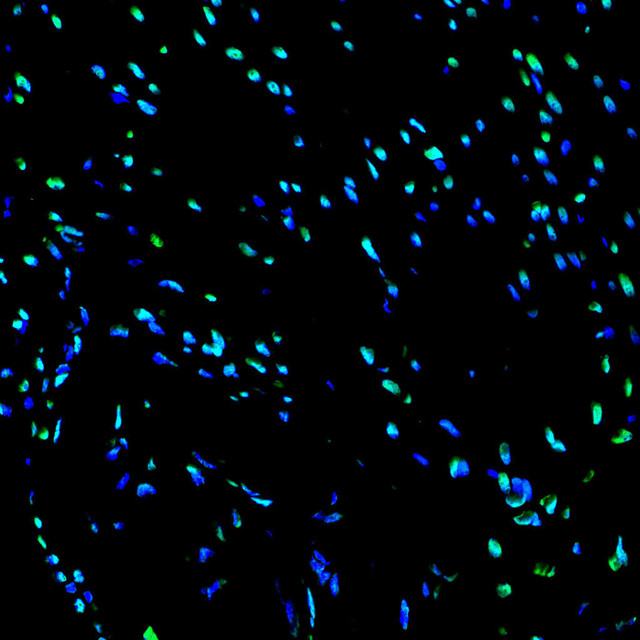
| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FITC) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | 490/520 |
| Detection Method | Fluorometric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |
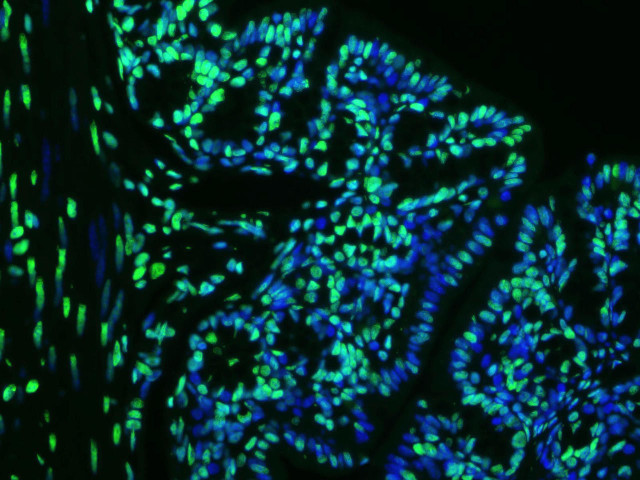
| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FL488) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | 495/519 |
| Detection Method | Fluorometric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |
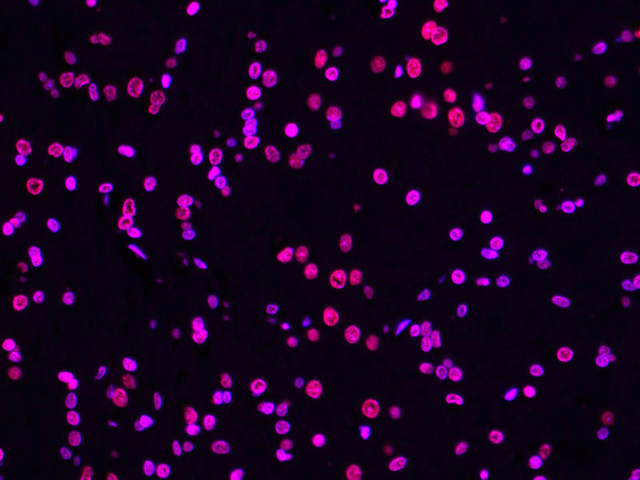
| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FL594) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | 590/617 |
| Detection Method | Fluorometric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |
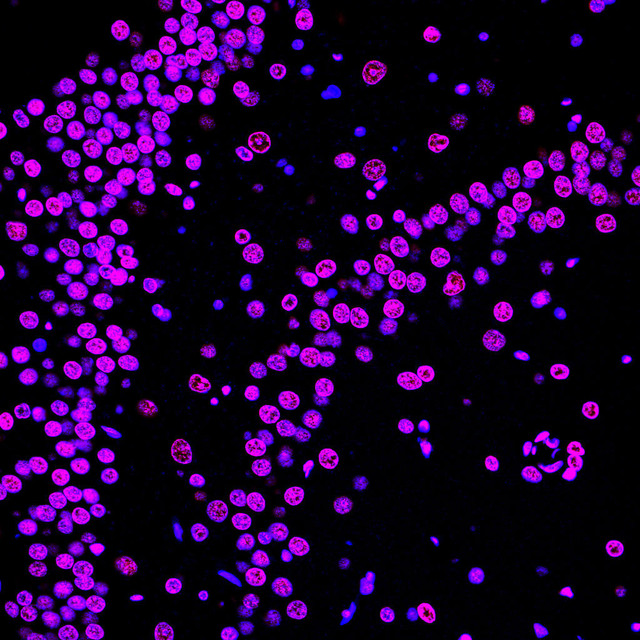
| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FL647) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | 650/665 |
| Detection Method | Fluorometric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |
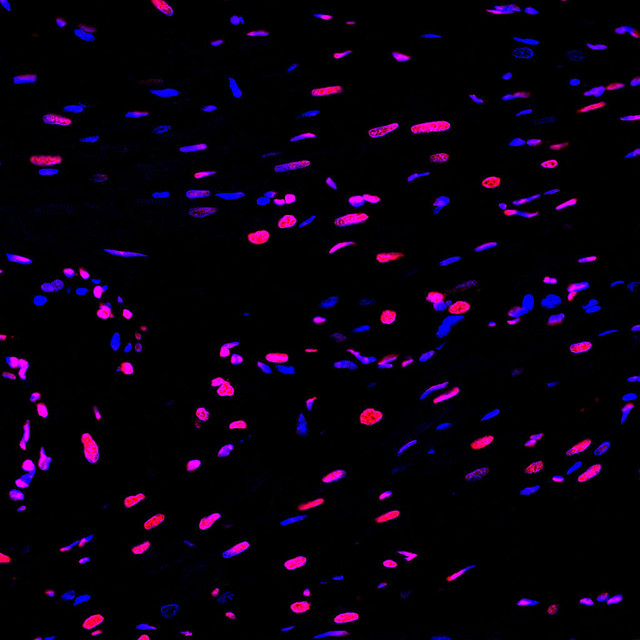
| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FL555) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | 555/565 |
| Detection Method | Fluorometric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |

| TUNEL 1-Step In Situ Apoptosis Kit (FL555) | |
|---|---|
| Ex/EM (nm) | - |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric Method |
| Product Type: | Cellular Assay |
TUNEL Staining Protocol
When performing TUNEL staining, it is important to ensure that the cells are properly fixed and permeabilized. This can be done by incubating the cells in a fixative solution, such as paraformaldehyde, for at least 30 minutes. The cells should then be permeabilized with a detergent, such as Triton X-100, prior to staining. Below are the steps to follow to detect apoptotic cells using the TUNEL assay:
- Fix the cells in paraformaldehyde for 30 minutes
- Permeabilize with Triton X-100
- Incubate in the TUNEL reaction mixture for 60 minutes
- Rinse with PBS and mount on slides using a mounting medium such as Prolong Gold Antifade Reagent.
- View under a fluorescence microscope using an excitation wavelength of 405 nm and an emission wavelength of 525 nm
Types of TUNEL Stains
There are two types of TUNEL stains available. FITC-dUTP is the most commonly used stain as it is highly sensitive and easy to use. PI-dUTP is less sensitive, but it is resistant to photobleaching.
When performing TUNEL staining, it is important to use a negative stain such as DAPI to counterstain apoptotic nuclei. This will help to ensure that only apoptotic cells are detected. It is important to remember that the TUNEL assay is not specific for apoptosis and will also detect necrotic cells. In order to avoid false positives, it is important to use a positive control such as staurosporine-treated cells.
Streptavidin-biotin conjugates can also be used in place of dUTP to detect apoptotic cells. In this method, biotin-tagged nucleotides are used in the TUNEL reaction mixture. The streptavidin-biotin conjugate is then used to bind to the biotin tags. Biotin-tagged nucleotides are more resistant to degradation and will produce a stronger signal. This method is more sensitive than using FITC-dUTP or PI-dUTP, but it is also more expensive and not as widely available.
Advantages of TUNEL Assay
There are several advantages to using TUNEL staining over other apoptosis assays. The first advantage is that TUNEL staining is highly sensitive, specific, and easy to use, when compared to other methods, such as flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. This means that TUNEL staining can be used to detect apoptosis at earlier stages, before the cell has undergone extensive DNA damage.
Another advantage of TUNEL staining is that it can be used on fixed cells, meaning that there is no need to perform live-cell imaging. This is a significant advantage, as live-cell imaging can be difficult to perform and often requires expensive equipment. This is an important advantage over other apoptosis assays, such as the Annexin V assay, which can only be used on live cells. In addition, TUNEL staining is resistant to photobleaching and can be used on a variety of cell types.
Finally, TUNEL staining can be used in combination with other stains, such as dapi or propidium iodide, to create a more complete picture of the cell. This is especially useful when investigating the early stages of apoptosis, as it can be difficult to detect DNA damage using dapi or propidium iodide alone.
Tips for Optimizing TUNEL Staining
There are a few important tips to keep in mind when performing TUNEL staining.
First, it is important to use freshly isolated cells. This is because apoptotic cells degrade quickly and can be difficult to detect if the cells are not fresh. It is also important to use fresh reagents when performing TUNEL staining. Reagents that have been stored for long periods of time may not be effective, and this can lead to false negative results.
Second, it is important to use a diluted TUNEL stain. This will help to ensure that the cells are correctly stained and that false positives are not detected. Third, it is important to keep the staining reaction going for a minimum of 15 minutes. Finally, it is important to wash the cells thoroughly after staining in order to remove any unbound TUNEL stain.
Staining conditions have to be optimized in order to achieve the best possible results. This may require some experimentation and trial and error. By following the tips mentioned in this blog, you can ensure that the TUNEL assay provides accurate and reliable results. This concludes our comprehensive guide to TUNEL staining. We hope you found it informative and helpful!
Written by Jahnavi Konduru
Jahnavi Konduru completed her undergraduate degree in Biotechnology before completing her masters in Immunotherapeutics at Trinity College Dublin. She now works as an Assay Development Scientist at Epona Biotech.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


