Tisotumab Vedotin: A Breakthrough in Targeted Cancer Therapy
Quick Facts About Tisotumab Vedotin
What is Tisotumab Vedotin?
Tisotumab Vedotin (Tivdak™) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) designed to target tissue factor (TF) and is FDA-approved for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.
How does Tisotumab Vedotin work?
It binds to TF-expressing cancer cells, delivering a cytotoxic payload that disrupts microtubules, leading to cancer cell death.
What are the clinical applications of Tisotumab Vedotin?
Primarily used for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, it is also being studied for use in other solid tumors.
What are the key side effects of Tisotumab Vedotin?
Common side effects include ocular toxicity, peripheral neuropathy, and fatigue, necessitating careful patient monitoring.
1.) Understanding Tisotumab Vedotin
Tisotumab Vedotin is a next-generation antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed by Genmab and Seagen, and it has emerged as a cutting-edge treatment in the oncology landscape. It targets tissue factor (TF), a protein overexpressed in several malignancies, making it a critical therapeutic target. Tissue factor is not only involved in promoting tumor growth and metastasis but also plays a significant role in immune evasion, which enables cancer cells to escape the body’s natural defense mechanisms. The overexpression of TF is frequently observed in various cancers, such as cervical, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. This provides a unique opportunity to selectively target these cells using Tisotumab Vedotin, which binds specifically to TF, thereby allowing for a more precise and effective treatment option.
FDA-approved in 2021, Tisotumab Vedotin has garnered significant attention as a major advancement in targeted therapy, particularly for patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer who have exhausted other treatment options. Cervical cancer, once thought to be difficult to treat with conventional therapies, has shown remarkable responses to Tisotumab Vedotin. This therapy presents an alternative to chemotherapy, which often carries high levels of systemic toxicity. Traditional chemotherapy affects both malignant and healthy cells, leading to a wide range of side effects.
Tisotumab Vedotin, on the other hand, offers a more targeted approach, specifically delivering the cytotoxic drug to cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This ability to target TF-expressing tumor cells while sparing healthy cells highlights Tisotumab Vedotin’s potential in revolutionizing cancer treatment, especially for patients with limited therapeutic options. The increasing clinical evidence of its efficacy is contributing to its growing reputation as a promising agent in the fight against cancer.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Tisotumab Vedotin
Tisotumab Vedotin works through a sophisticated and highly targeted mechanism of action involving three key steps that ensure its potency and precision in killing cancer cells. The first step is target recognition. The monoclonal antibody in Tisotumab Vedotin specifically binds to tissue factor (TF) expressed on the surface of tumor cells. TF is often overexpressed in various malignancies, and by targeting it, Tisotumab Vedotin can selectively identify and bind to cancer cells while minimizing the impact on healthy cells.
Once the antibody binds to the TF on the cancer cell surface, the second step, payload delivery, occurs. After binding to the tumor cell, Tisotumab Vedotin is internalized into the cancer cell. Once inside, the cytotoxic drug payload—monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE)—is released. MMAE is a powerful microtubule inhibitor that prevents the formation of microtubules, which are essential for cell division and survival. By disrupting this critical process, MMAE effectively halts the cancer cell’s ability to divide and proliferate.
The final step, cancer cell death, is triggered as MMAE interferes with the cell’s internal machinery. Without functioning microtubules, the cancer cell undergoes apoptosis, or programmed cell death. This selective targeting of cancer cells, coupled with the potent microtubule inhibitor MMAE, ensures that Tisotumab Vedotin is highly effective in killing tumor cells. The ability to deliver the cytotoxic payload directly to cancer cells minimizes the systemic toxicity often associated with conventional chemotherapy. This results in a more targeted and less harmful treatment approach, which is a significant advantage for patients undergoing therapy. The precision of this therapy offers a promising future for cancer treatments, particularly in cases where other therapies have failed.
3.) Clinical Applications of Tisotumab Vedotin
Tisotumab Vedotin has primarily been approved for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, offering hope for patients with limited treatment options. Cervical cancer, particularly in its advanced stages, has long been difficult to treat effectively. Patients with this type of cancer often have limited choices once first-line treatments, such as chemotherapy, fail. The approval of Tisotumab Vedotin in 2021 marked a major milestone in cervical cancer treatment, providing a more targeted and effective option that has demonstrated significant clinical benefits. In clinical trials, Tisotumab Vedotin has shown promising results, including substantial improvements in progression-free survival and overall response rates in patients who have already undergone multiple rounds of treatment. This has made it a valuable addition to the oncology arsenal, especially for patients who have few other therapeutic options available.
Beyond cervical cancer, Tisotumab Vedotin is being investigated for its potential efficacy in treating other cancers that exhibit high expression of tissue factor, such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and other solid tumors. The drug’s ability to selectively target cancer cells while minimizing systemic toxicity has sparked interest in its broader application across various malignancies. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring the use of Tisotumab Vedotin in combination with other therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, to potentially enhance its therapeutic effect. Early studies suggest that these combination approaches may further improve patient outcomes, particularly in cancers that are resistant to traditional treatments.
As research continues, there is great optimism that Tisotumab Vedotin will expand its indications and provide a powerful tool for treating various types of cancers with high tissue factor expression. The precision of Tisotumab Vedotin in targeting cancer cells, combined with its ability to deliver potent cytotoxic payloads directly to tumor cells, makes it a promising candidate in precision oncology. Its application in combination therapies could lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects, offering patients a safer and more efficient option for cancer treatment. As clinical trials continue to evolve, Tisotumab Vedotin’s role in the fight against cancer may grow, positioning it as a key component of future cancer therapies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Tisotumab Vedotin
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic that closely matches an approved reference product in safety, purity, and efficacy, offering a cost-effective alternative for research and drug development.
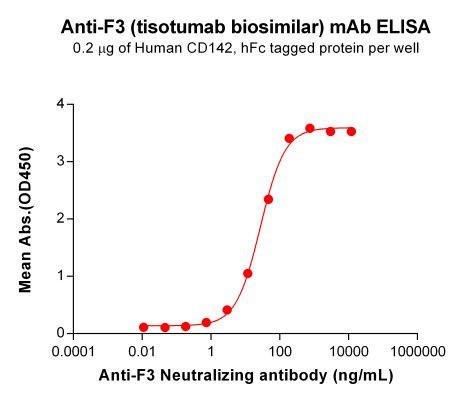
| Tisotumab (Anti-F3) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD142 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Biosimilar vs. Reference Product
Tisotumab Vedotin
- Target: Tissue Factor (TF)
- Mechanism: MMAE payload conjugated to monoclonal antibody; binds TF, leading to internalization and cell death
- Use: Clinical and research applications in treating cancers like cervical, ovarian, and lung cancer
- Target: Tissue Factor (TF)
- Mechanism: Similar to Tisotumab Vedotin, using MMAE payload
- Use: Research use only; potential cost-effective alternative to the original Tisotumab Vedotin
Benefits of Tisotumab Vedotin Biosimilars in Research
- Cost-Effective Research: Provides a lower-cost alternative for preclinical and translational studies.
- Reliable Mechanism: Mimics the action of the reference product for experimental consistency.
- Scalability: Supports high-throughput screening and drug discovery efforts.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Tisotumab Vedotin biosimilar is for research use only and is not approved for clinical applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



