Tigatuzumab: Advancing Cancer Research with Targeted Therapies
Quick Facts About Tigatuzumab
What is Tigatuzumab?
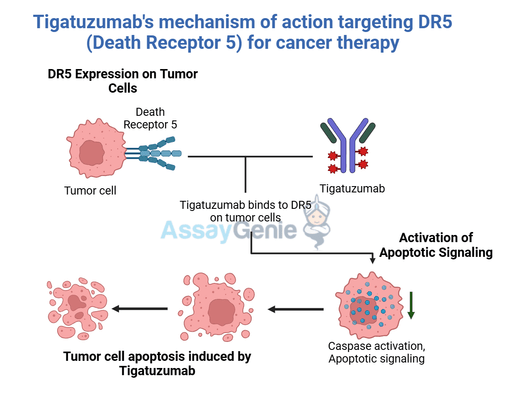
Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the death receptor 5 (DR5) pathway, inducing apoptosis in cancer cells.
What is the mechanism of action for Tigatuzumab?
Tigatuzumab binds to DR5, activating apoptotic pathways in cancer cells, making it a targeted therapy for solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
What are the clinical applications of Tigatuzumab?
Tigatuzumab has been investigated for treating various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer. Emerging research highlights its potential in combination therapies.
1.) Understanding Magrolimab
Tigatuzumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody targeting death receptor 5 (DR5), represents a pivotal advancement in the field of targeted cancer therapy. By specifically activating DR5, Tigatuzumab induces apoptosis in malignant cells while largely sparing healthy tissues, making it an attractive option for reducing the systemic toxicities typically associated with traditional chemotherapeutic approaches. Its mechanism leverages the tumor-selective expression of DR5, ensuring enhanced efficacy against cancer cells with minimal off-target effects.
Engineered with precision, Tigatuzumab has undergone extensive preclinical and clinical evaluations. In preclinical studies, it demonstrated the ability to potentiate apoptosis in a range of tumor models, including those resistant to conventional therapies. Its synergistic potential when combined with other anticancer agents, such as chemotherapeutics or immune checkpoint inhibitors, has also been highlighted, paving the way for novel combination strategies in cancer treatment. Early-phase clinical trials revealed encouraging outcomes, particularly in solid tumors like non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and pancreatic cancer, with acceptable safety profiles and evidence of efficacy in subsets of patients.
However, despite these promising findings, Tigatuzumab’s clinical development faced several obstacles, including variability in patient responses and challenges in defining biomarkers predictive of therapeutic success. Certain trials were discontinued due to insufficient efficacy in larger, unselected patient populations. Nevertheless, foundational studies involving Tigatuzumab remain highly influential, inspiring continued research into DR5-targeted therapies. These investigations have contributed to a deeper understanding of death receptor signaling and its implications in cancer biology, fostering the development of next-generation therapies aimed at improving patient outcomes.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Tigatuzumab
Tigatuzumab’s therapeutic potential lies in its precise targeting of death receptor 5 (DR5), a key player in the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) pathway. DR5 is selectively overexpressed on the surface of many cancer cells, making it an attractive target for pro-apoptotic therapies. By binding to DR5, Tigatuzumab triggers the receptor's activation and recruits intracellular signaling complexes that initiate the caspase cascade. Caspases, a family of proteolytic enzymes, act as central regulators of programmed cell death, culminating in the efficient apoptosis of tumor cells. This highly specific mechanism minimizes collateral damage to healthy tissues, a distinct advantage over traditional cancer therapies that often lack such selectivity.
Preclinical studies have showcased Tigatuzumab’s ability to enhance apoptosis when used in combination with chemotherapeutic agents. This synergistic effect is particularly valuable in overcoming drug resistance, a common challenge in cancer treatment. In experimental models, Tigatuzumab demonstrated robust efficacy in cancers with high DR5 expression, including pancreatic, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers. These findings emphasize its potential as part of combination therapy regimens aimed at treating aggressive or refractory malignancies.
Research into Tigatuzumab's interactions with DR5 continues to yield insights into the intricate biology of the TRAIL pathway. Such investigations have guided the design of next-generation antibodies with improved stability, binding affinity, and potency. By dissecting the complexities of apoptotic signaling, Tigatuzumab has not only advanced cancer therapy but also highlighted the importance of precision-targeted approaches in oncology, paving the way for innovative treatment paradigms.
3.) Clinical Applications of Tigatuzumab
Tigatuzumab has been extensively investigated in clinical settings for its potential to treat challenging cancers, including pancreatic adenocarcinoma, glioblastoma, and non-small cell lung cancer. Its integration into combination therapy strategies, particularly with chemotherapeutic agents such as gemcitabine or paclitaxel, has shown encouraging results. By leveraging Tigatuzumab's ability to selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells through DR5 activation, these combinations aim to maximize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic toxicity. Early clinical data suggested that Tigatuzumab could enhance treatment responses and improve overall survival rates in certain patient populations.
One pivotal study demonstrated the potential of Tigatuzumab in combination therapy to extend overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer. These findings spurred additional clinical trials aimed at optimizing dosing regimens, assessing the best treatment schedules, and identifying biomarkers predictive of patient responsiveness. The quest for predictive biomarkers is particularly crucial, as they could help stratify patients most likely to benefit from Tigatuzumab-based therapies, ensuring a more personalized approach to cancer treatment.
Despite these promising findings, some clinical trials were discontinued due to strategic shifts, variability in patient responses, or suboptimal results in broader patient populations. However, the data generated from these studies remain highly valuable, providing a foundation for the development of biosimilars and next-generation DR5-targeting antibodies. These advancements aim to improve upon Tigatuzumab’s pharmacological properties, efficacy, and safety profile. As a result, Tigatuzumab continues to hold relevance in oncology research, representing a cornerstone in the ongoing pursuit of innovative and effective cancer therapies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Tigatuzumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an original reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Biosimilars provide researchers with affordable and accessible alternatives, enabling broader investigations.
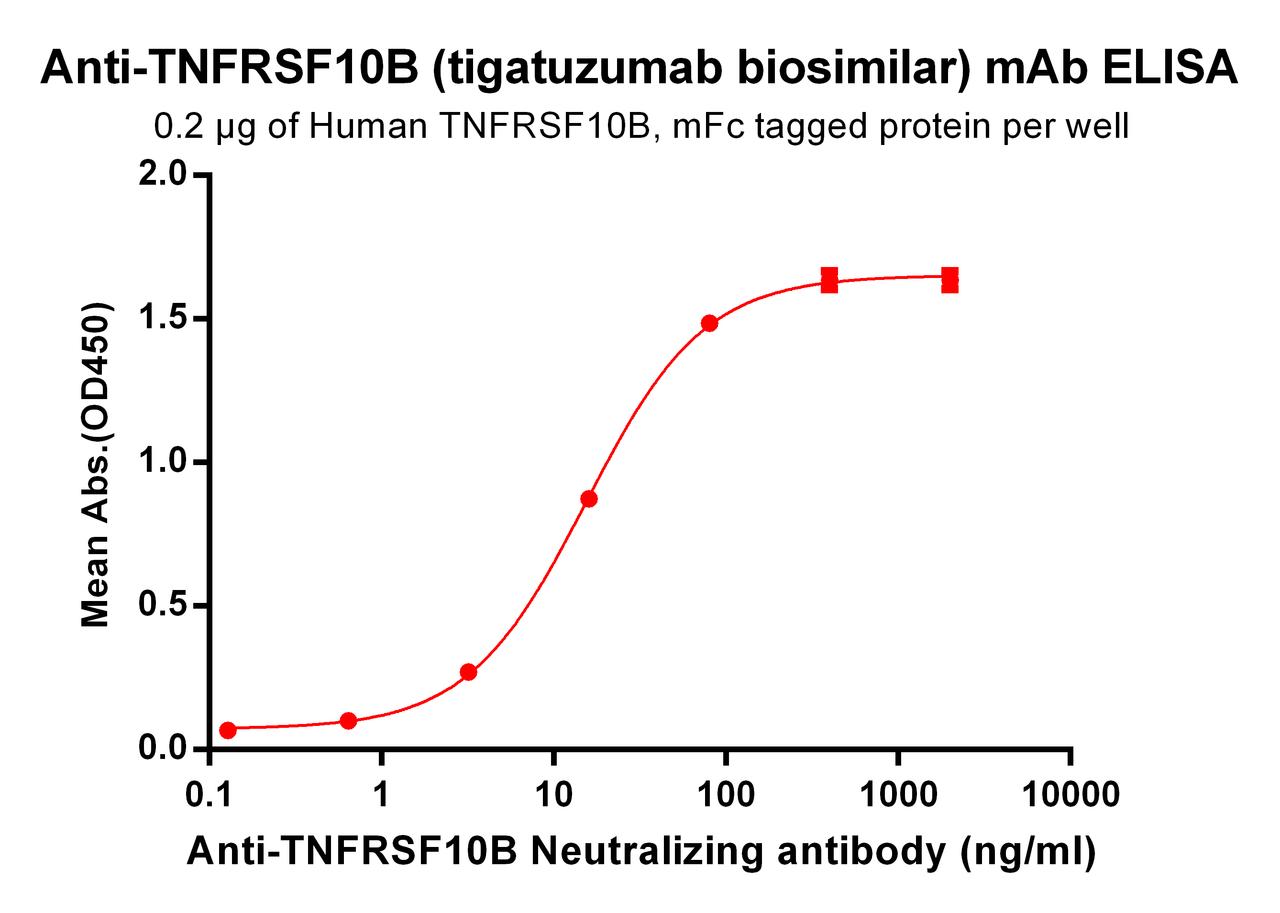
| Tigatuzumab (Anti-TNFRSF10B) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | TNFRSF10B |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does a Tigatuzumab Biosimilar Compare to Tigatuzumab?
Our Tigatuzumab biosimilar offers comparable functionality and specificity, making it a valuable tool for research. It maintains the ability to target DR5 and activate apoptotic pathways, ensuring consistent results in preclinical models.
Benefits of Using Tigatuzumab Biosimilars in Research
- Cost-Effective: Lower production costs make biosimilars accessible for extensive research applications.
- Research-Grade Quality: Optimized for in vitro and in vivo studies, our Tigatuzumab biosimilar supports robust experimental outcomes.
- Scalability: Reliable availability ensures consistent supply for long-term projects.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
This biosimilar is intended for research use only and not for human or clinical applications.
Advancing Research on Tigatuzumab
The development of Tigatuzumab biosimilars is bridging gaps in cancer research. By providing cost-effective, high-quality alternatives, these products empower researchers to explore novel therapeutic combinations and expand preclinical testing.
Future directions include studying biosimilar efficacy in emerging cancer models, assessing synergy with immunotherapies, and refining delivery mechanisms to enhance targeted therapy outcomes. By integrating biosimilars into research pipelines, scientists can accelerate discoveries and contribute to the growing body of knowledge in oncology.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025