Tesnatilimab: Unveiling the Potential of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Tesnatilimab
What is Tesnatilimab?
Tesnatilimab is an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody designed to block the "don’t eat me" signal used by cancer cells to evade immune responses.
What is the mechanism of action for Tesnatilimab?
Tesnatilimab binds to the CD47 receptor on cancer cells, enhancing their phagocytosis by macrophages and other immune cells.
What are the clinical applications of Tesnatilimab?
It is being explored for its efficacy in treating various cancers, including hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
Is Tesnatilimab safe?
Studies highlight its potential with a manageable safety profile, though some patients may experience mild-to-moderate immune-related side effects.
1.) Understanding Tesnatilimab
Tesnatilimab represents a cutting-edge advancement in cancer immunotherapy by targeting CD47, a protein frequently overexpressed on cancer cells to evade immune destruction. CD47 serves as a "don’t eat me" signal by interacting with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, thereby suppressing the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy malignant cells. By disrupting this interaction, tesnatilimab reactivates the innate immune system, allowing macrophages to phagocytose and eliminate cancer cells.
What sets tesnatilimab apart is its dual role in enhancing both innate and adaptive immunity. The clearance of cancer cells by macrophages stimulates antigen presentation, further activating T cells and fostering a robust adaptive immune response. This broad immune activation positions tesnatilimab as a highly versatile therapeutic agent.
Tesnatilimab's ability to synergize with other therapies is another significant advantage. When combined with checkpoint inhibitors, it complements their mechanism by enhancing T-cell activity. Similarly, its integration with chemotherapeutic agents has shown potential to amplify cytotoxic effects and improve outcomes in resistant cancers.
With ongoing clinical trials exploring its application across multiple malignancies, tesnatilimab is poised to address significant unmet needs, offering hope to patients with cancers unresponsive to traditional therapies. Its innovative mechanism underscores its potential to redefine cancer treatment paradigms.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Tesnatilimab
Tesnatilimab operates through a sophisticated mechanism that centers on disrupting the CD47-SIRPα interaction, a critical pathway cancer cells exploit to evade immune detection. CD47, often overexpressed on cancer cells, acts as a “don’t eat me” signal by binding to SIRPα receptors on macrophages, effectively silencing their phagocytic activity. Tesnatilimab blocks this interaction, restoring the innate immune system's ability to target and destroy malignant cells through multiple mechanisms:
Phagocytosis Activation;
By inhibiting CD47 from binding to SIRPα, tesnatilimab allows macrophages to recognize cancer cells as threats. This facilitates the engulfment and subsequent destruction of these cells via phagocytosis, marking a crucial step in eliminating tumor burdens.
Synergistic Immune Activation;
Tesnatilimab also plays a pivotal role in amplifying the adaptive immune response. The removal of cancer cells by macrophages leads to the release of tumor antigens, which are presented to T cells. When used in conjunction with T-cell activation therapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, tesnatilimab significantly enhances the overall immune attack on tumors.
Tumor Microenvironment Modulation;
Tesnatilimab reprograms the tumor microenvironment by reducing immunosuppressive signals and fostering an environment conducive to anti-tumor immunity. This includes altering cytokine profiles and recruiting additional immune cells to sustain the immune assault.
3.) Clinical Applications of Tesnatilimab
Tesnatilimab is emerging as a versatile immunotherapy agent with significant potential in both hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. By targeting CD47, a protein commonly overexpressed on cancer cells, Tesnatilimab restores the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate malignant cells, offering a novel approach to cancer treatment.
Early clinical trials have demonstrated Tesnatilimab’s promise in treating hematologic cancers such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). These malignancies often evade immune detection through CD47 overexpression, making them ideal candidates for CD47-targeted therapies. Tesnatilimab enhances the immune clearance of malignant cells, showing potential for improving outcomes in these challenging diseases.
Tesnatilimab is also being actively investigated for its efficacy in solid tumors, including ovarian, colorectal, and lung cancers—types where CD47 is frequently overexpressed. Its ability to re-engage the immune system in these cancers highlights its potential as a broadly applicable therapeutic option across multiple tumor types.
Combination Therapies: When paired with checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies, Tesnatilimab amplifies immune responses, offering a multi-pronged attack on tumors.By pairing with these agents, Tesnatilimab amplifies immune responses, enabling a multi-pronged attack on tumors and addressing resistance mechanisms that often limit the effectiveness of monotherapies.
While clinical trials continue to evaluate its long-term efficacy and safety, Tesnatilimab has already shown encouraging results, paving the way for its integration into modern cancer treatment protocols. Its potential to enhance immune responses across a range of cancers underscores its transformative role in oncology.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Tesnatilimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an existing approved reference product, offering comparable safety, potency, and efficacy. Biosimilars are invaluable in research, enabling cost-effective and accessible study models for understanding complex therapeutics like Tesnatilimab.
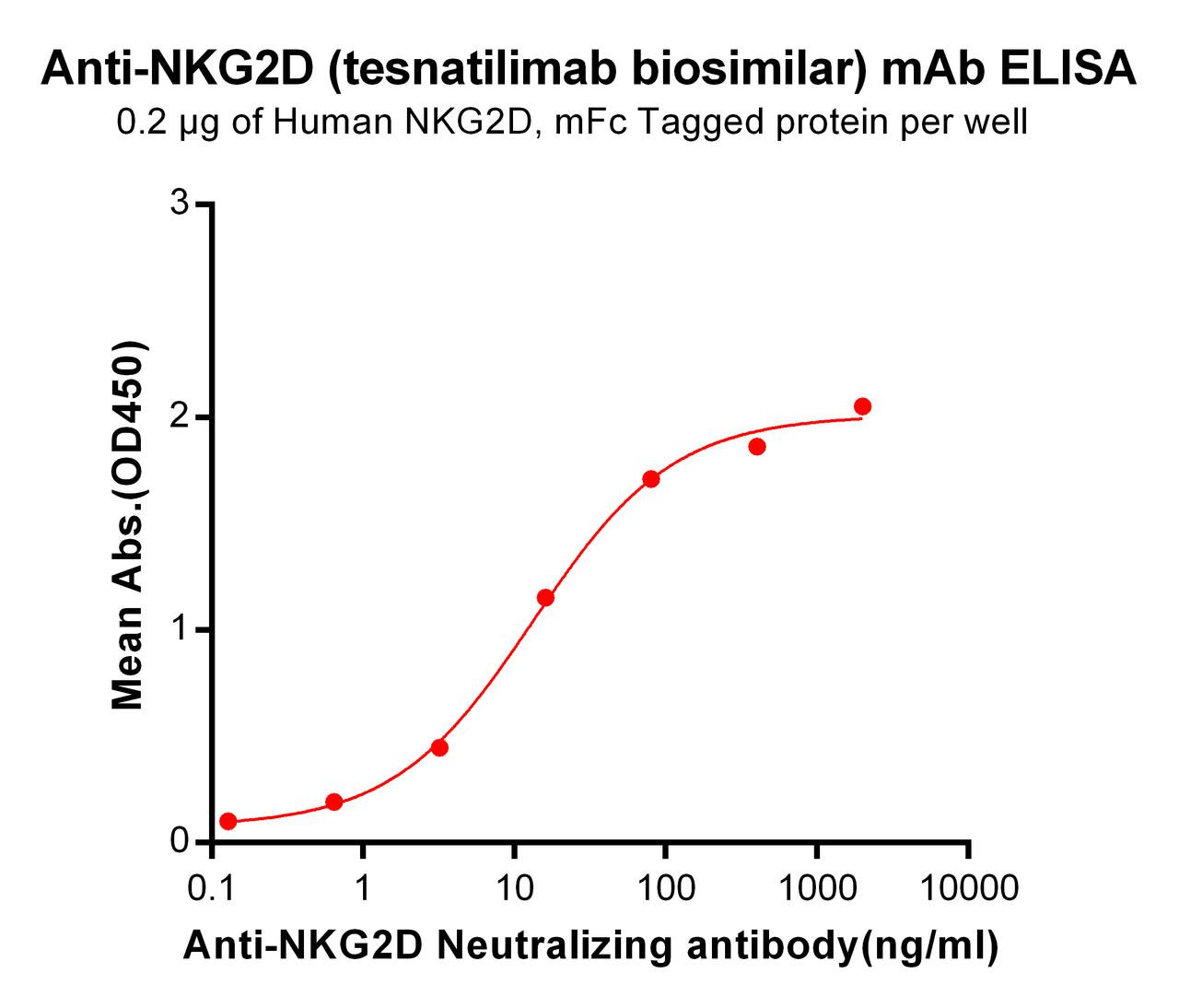
| Tesnatilimab (Anti-NKG2D) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | NKG2D |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Tesnatilimab Biosimilar Compares to Tesnatilimab
The Tesnatilimab biosimilar replicates the structure and function of the original antibody, making it an excellent tool for preclinical and exploratory research. While it is not approved for clinical use, its availability enhances the scope of studies by:
Facilitating Comparative Research: Researchers can study differences in immune responses across various cancer models.
Reducing Costs: Biosimilars offer a more affordable option for conducting expansive experiments.
Expanding Accessibility: They make high-quality research feasible even for resource-constrained institutions.
Advancing Research on Tesnatilimab
Tesnatilimab biosimilars accelerate discovery in immuno-oncology. By providing researchers with affordable and reliable tools, they support investigations into:
New combination therapies involving CD47 inhibition.
Mechanistic studies on immune cell interactions in the tumor microenvironment.
Preclinical assessments of potential adverse effects and mitigation strategies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Tesnatilimab biosimilars are intended exclusively for research purposes and are not approved for therapeutic or diagnostic use in humans.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




