Talquetamab: Exploring its Role in Cancer Therapy and Ongoing Research
Quick Info Section: Key Facts About Talquetamab
What is Talquetamab?
Talquetamab is a novel monoclonal antibody being developed for the treatment of multiple myeloma and other cancers. It targets GPRC5D, a protein expressed on the surface of myeloma cells, aiming to stimulate the body's immune system to attack and destroy the tumor cells.
What is the mechanism of action of Talquetamab?
What are the clinical applications of Talquetamab?
Talquetamab is primarily being studied for its potential in treating multiple myeloma, particularly in patients who have not responded well to traditional therapies. Emerging studies are exploring its efficacy in various stages of the disease.
Is Talquetamab FDA-approved?
Talquetamab is not yet FDA-approved, but clinical trials are progressing, with promising results in treating hematologic cancers like multiple myeloma.
What are the side effects of Talquetamab?
Common side effects may include cytokine release syndrome (CRS), fatigue, and fever, though the safety profile is under continuous review in clinical trials.
1.) Understanding Talquetamab
Talquetamab represents a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment of hematologic malignancies, particularly multiple myeloma. This innovative bispecific monoclonal antibody specifically targets GPRC5D, a protein that is overexpressed on myeloma cells but largely absent in healthy tissues. This precise targeting mechanism offers a significant advantage, allowing Talquetamab to selectively engage the immune system without affecting normal cells. By binding to GPRC5D, Talquetamab activates T-cells to directly recognize and eliminate cancerous myeloma cells, offering a more targeted and less toxic alternative to traditional therapies, which often involve broad cytotoxic effects.
The specificity of Talquetamab’s action has drawn considerable attention in ongoing clinical research, particularly as it pertains to its potential role in reducing the side effects commonly associated with chemotherapy. By focusing immune responses on the tumor cells, Talquetamab minimizes collateral damage to healthy tissues, making it a promising candidate for more personalized treatment regimens. Researchers are currently exploring its use both as a monotherapy and in combination with other immunotherapies to enhance its efficacy and broaden its therapeutic potential.
Beyond multiple myeloma, Talquetamab’s unique mechanism of action could extend to other cancers where GPRC5D is similarly overexpressed. As research progresses, Talquetamab holds the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment by offering more effective, targeted therapies with fewer side effects. Its success could pave the way for a new generation of precision immuno-oncology treatments, tailored to the individual immune profiles of patients, marking a significant shift in how cancer therapies are developed and administered.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Talquetamab
The mechanism of action of Talquetamab revolves around its dual specificity, a hallmark of bispecific antibodies, making it a powerful tool in treating multiple myeloma. Talquetamab is engineered to bind to two distinct targets: GPRC5D, a tumor-specific protein overexpressed on multiple myeloma cells, and CD3, a receptor found on T-cells. This dual-targeting approach allows Talquetamab to act as a bridge, simultaneously engaging T-cells and tumor cells. By binding to both GPRC5D and CD3, it activates T-cells to recognize and destroy myeloma cells through cytotoxic mechanisms, enhancing the immune response against the tumor.
What sets Talquetamab apart from conventional monoclonal antibodies is its ability to engage both the cancer cells and the immune system at the same time. Most traditional monoclonal antibodies are designed to recognize and bind to a single target antigen on cancer cells, which can limit their effectiveness. In contrast, Talquetamab’s bispecific action leverages the body’s immune system more efficiently, driving a stronger immune response. In addition to directly targeting the myeloma cells, Talquetamab stimulates T-cell proliferation, increasing the overall cytotoxic activity against the tumor.
This approach is especially beneficial for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, where traditional therapies often fall short. Early clinical trials have shown promising results, with Talquetamab significantly improving patient outcomes. Its ability to precisely target tumor cells while activating the immune system offers a new therapeutic avenue for patients with limited treatment options. As research progresses, Talquetamab has the potential to become a cornerstone in immuno-oncology, offering hope for improved survival and quality of life.
3.) Clinical Applications of Talquetamab
Talquetamab is primarily being investigated for its role in treating multiple myeloma, particularly in patients who have not responded to traditional therapies such as chemotherapy, proteasome inhibitors, or immunomodulatory drugs. This patient group often faces limited treatment options, and Talquetamab’s novel mechanism of action offers new hope for improving outcomes in these difficult cases. Clinical trials are currently assessing its use across various stages of multiple myeloma, from relapsed and refractory settings to earlier stages of the disease, aiming to determine its potential to extend progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates.
Emerging research suggests that Talquetamab could be effective not only as a monotherapy but also in combination with other therapeutic agents, such as immunomodulatory drugs or proteasome inhibitors. This combination strategy could amplify its anti-tumor effects, positioning Talquetamab as a crucial component in future treatment regimens for multiple myeloma. Clinical studies are investigating its potential as a frontline therapy, evaluating whether it can be used in earlier lines of treatment to prevent disease relapse and improve long-term outcomes.
Additionally, Talquetamab is being explored in combination with innovative immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, which may further enhance its clinical benefits. While still in the investigational phase, early results are promising, with indications that Talquetamab could significantly impact the treatment landscape for hematologic cancers. If ongoing trials confirm its efficacy and safety, Talquetamab has the potential to redefine how multiple myeloma is treated, offering new options for patients with limited therapeutic alternatives.
4.) Introducing the Biosimilar Product
How Talquetamab without CD3 Biosimilar Compares to Talquetamab
In the pursuit of more affordable and accessible treatments, the Talquetamab biosimilar without CD3 is being developed to offer researchers an alternative that mirrors the original Talquetamab’s therapeutic properties, excluding the CD3 arm. This biosimilar allows for focused research on the GPRC5D-targeting aspect of Talquetamab, providing scientists with a valuable tool to better understand the compound’s efficacy and potential for broader applications. This research-focused product does not carry the full clinical implications of the original therapy but opens avenues for detailed investigation into the mechanics of cancer immunotherapy.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, efficacy, and potency. For researchers, biosimilars like Talquetamab without CD3 serve as critical tools to advance understanding of drug targets and mechanisms of action while offering cost-effective alternatives for early-stage studies.
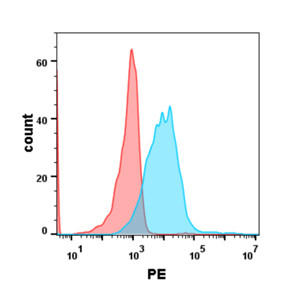
| Talquetamab (Anti-GPRC5D) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GPRC5D |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison: Talquetamab vs. Talquetamab Biosimilar
The Talquetamab biosimilar without CD3 shares the same GPRC5D-targeting properties as the original but excludes the CD3-binding feature. This makes it an ideal research tool for exploring the potential of GPRC5D as a therapeutic target, without the added complexity of immune cell activation via CD3. Researchers can study the isolated effects of GPRC5D targeting, helping to refine strategies for optimal therapeutic combinations.
Benefits of the Talquetamab Biosimilar
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Please note that Talquetamab without CD3 biosimilar is intended for research use only and is not approved for clinical use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
3D Organoid Cell Viability Assay: Assessing Environmental Stress on BENOs for Live Delivery
Ibatici, D. (1), Westhoff, A. (1)Assessing Environmental Stress on BENOs for Live Deli …21st Feb 2025


