Talacotuzumab: Exploring CD123-Targeting Therapies in AML and MDS Research
Key Facts About Talacotuzumab
What is Talacotuzumab?
Talacotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target CD123, a protein commonly found on the surface of certain blood cancer cells.
How does Talacotuzumab work?
It binds to CD123, recruiting the body’s immune cells to destroy cancer cells, making it a targeted and innovative approach in cancer therapy.
What are Talacotuzumab’s potential uses?
Talacotuzumab has been studied for treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), offering hope for patients with these challenging conditions.
1.) Understanding Talacotuzumab
Talacotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody developed to target CD123, a key marker present on leukemia stem cells and some other malignant cells. CD123, or the alpha chain of the interleukin-3 receptor, is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), making it a promising therapeutic target. By specifically targeting CD123, Talacotuzumab aims to disrupt the survival and proliferation of cancerous cells, offering a novel approach to treatment.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Talacotuzumab Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Talacotuzumab
The mechanism of action of Talacotuzumab centers on its ability to bind to CD123 with high specificity. This binding recruits immune effector cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). By engaging the immune system, Talacotuzumab helps eliminate cancer cells that express CD123, while sparing normal cells with low or no CD123 expression. This targeted approach minimizes off-target effects and enhances its therapeutic potential.

3.) Clinical Applications of Talacotuzumab
Talacotuzumab has primarily been explored for its role in treating AML and MDS. Studies have indicated that it may be particularly effective in combination with other therapies, such as decitabine. Although some clinical trials investigating Talacotuzumab were discontinued due to safety and efficacy concerns, its CD123-targeting mechanism remains a significant focus in cancer research and provides a foundation for the development of future therapies.
4.) Advancing Research on Talacotuzumab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic products designed to be highly similar to an original reference biologic drug. They match the reference drug in terms of structure, safety, and efficacy but are developed independently. Biosimilars are critical tools for advancing research by providing affordable and accessible options for scientists.
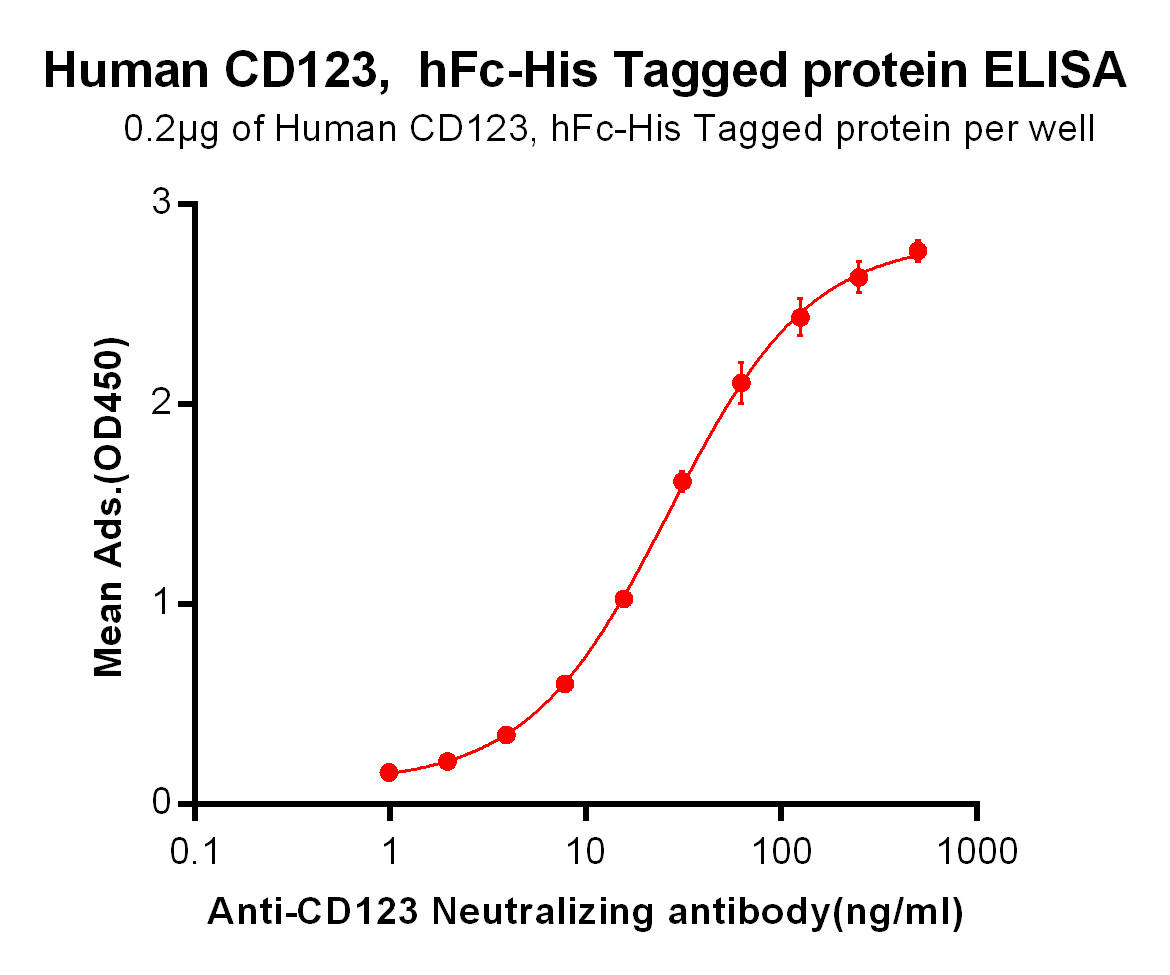
| Talacotuzumab (Anti-CD123) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD123 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Talacotuzumab Biosimilar
Our Talacotuzumab biosimilar, Talacotuzumab biosimilar, offers researchers a reliable option for studying CD123-targeting therapies. While not intended for clinical use, this biosimilar serves as a valuable resource for preclinical studies and investigative projects.
Benefits of Using Talacotuzumab Biosimilar in Research
- Accessibility : Biosimilars provide a cost-effective alternative to proprietary biologics, facilitating broader access for researchers.
- Reliability: With high structural and functional similarity to the original drug, our biosimilar ensures consistent and reproducible results.
- Applications: Ideal for studying mechanisms of action, testing drug combinations, and exploring resistance pathways in AML and MDS research.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Talacotuzumab biosimilar is for research use only and is not intended for clinical or diagnostic applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025



