Ruplizumab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Ruplizumab
What is Ruplizumab?
Ruplizumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a protein that helps cancer cells evade immune detection.
What is the mechanism of action for Ruplizumab?
Ruplizumab works by inhibiting the interaction between CD47 and its receptor, SIRPα, thereby enabling immune cells to recognize and attack tumor cells more effectively.
What are the clinical applications of Ruplizumab?
Ruplizumab is being studied primarily for its role in treating various cancers, including hematologic and solid tumors, through its immune-modulating effects.
1.) Understanding Ruplizumab
Ruplizumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody engineered to target CD47, a protein present on the surface of many cells, including cancer cells. CD47 functions as a "don’t eat me" signal by interacting with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, suppressing their phagocytic activity. Cancer cells exploit this mechanism by overexpressing CD47, effectively cloaking themselves from the immune system and evading detection. Ruplizumab plays a crucial role in cancer therapy by blocking the CD47-SIRPα interaction, thereby neutralizing this immune escape strategy. By doing so, Ruplizumab enables macrophages and other immune cells to recognize and eliminate tumor cells, restoring effective immune surveillance.
The therapeutic potential of Ruplizumab in cancer treatment is remarkable, particularly for tumors resistant to traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Unlike conventional approaches that focus on directly targeting tumor cells or broadly stimulating immune responses, Ruplizumab functions as a precise immune modulator. It enhances the body’s natural immune defenses, making it a promising option for various malignancies, including both hematological cancers and solid tumors.
Moreover, Ruplizumab’s mechanism of action is not limited to activating macrophages. It also has the potential to improve the efficacy of other treatments, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, by creating a more permissive tumor microenvironment. Current research is focused on refining its therapeutic application, optimizing dosing regimens, and minimizing off-target effects to enhance patient outcomes. As an innovative strategy harnessing the innate immune system, Ruplizumab represents a significant advancement in the development of targeted cancer immunotherapies, offering new hope for patients with challenging malignancies.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Ruplizumab
Ruplizumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a protein commonly expressed on the surface of both healthy and cancer cells. CD47 functions as a "don't eat me" signal by interacting with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, thereby inhibiting the phagocytic activity of these immune cells. Cancer cells exploit this pathway by overexpressing CD47, effectively cloaking themselves from immune system detection and avoiding destruction. Ruplizumab’s mechanism of action in cancer therapy is centered on its ability to block the CD47-SIRPα interaction, lifting this inhibitory signal and enabling macrophages and other components of the immune system to identify and eliminate tumor cells.
The potential of Ruplizumab in oncology is significant, as it targets a fundamental mechanism of immune evasion employed by tumors. Unlike traditional cancer therapies that directly kill tumor cells or broadly stimulate the immune system, Ruplizumab acts as an immune modulator, fine-tuning the immune response to specifically target malignant cells. This precision makes it particularly promising for treating cancers that are resistant to conventional therapies, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Early research suggests that Ruplizumab could be effective across a wide range of cancers, including hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Its ability to synergize with other treatments, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy, further enhances its therapeutic potential. Current clinical trials are focused on optimizing its dosage, minimizing potential side effects, and identifying patient populations that would benefit most. By harnessing the power of the innate immune system, Ruplizumab represents a novel and potentially transformative approach to cancer therapy, offering new hope for patients with difficult-to-treat malignancies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Ruplizumab
Ruplizumab is emerging as a groundbreaking therapeutic agent with diverse clinical applications, particularly in oncology, where its mechanism of targeting CD47 presents a novel approach to cancer treatment. CD47 is frequently overexpressed in both solid and hematologic malignancies, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer, allowing tumor cells to evade immune detection and destruction. By blocking the CD47-SIRPα interaction, Ruplizumab restores the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. This makes it a promising option for treating cancers that have proven resistant to conventional therapies.
Ongoing clinical trials are exploring Ruplizumab’s efficacy as a monotherapy and in combination with other treatment modalities. Combining Ruplizumab with chemotherapy has shown potential to synergistically enhance tumor elimination by simultaneously promoting immune activation and directly damaging cancer cells. Additionally, pairing Ruplizumab with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-1 or anti-CTLA-4 therapies, could create a more comprehensive immune response by targeting multiple pathways involved in immune evasion. Early-phase trials have yielded encouraging results, demonstrating improved tumor clearance and prolonged survival in patients with refractory cancers.
Beyond oncology, Ruplizumab is being investigated for its potential in non-cancer conditions where modulating immune activity is beneficial. Researchers are studying its role in diseases characterized by immune dysregulation, further broadening its clinical relevance.
The future of Ruplizumab lies in its potential to integrate into personalized medicine approaches, offering tailored solutions based on the patient’s specific tumor biology and immune profile. Its versatility and effectiveness position it as a pivotal addition to the landscape of cancer immunotherapy.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Ruplizumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product that is highly similar to an already-approved reference product but may have minor differences in clinically inactive components. Biosimilars offer an affordable alternative to original therapies while maintaining the same level of safety and efficacy.
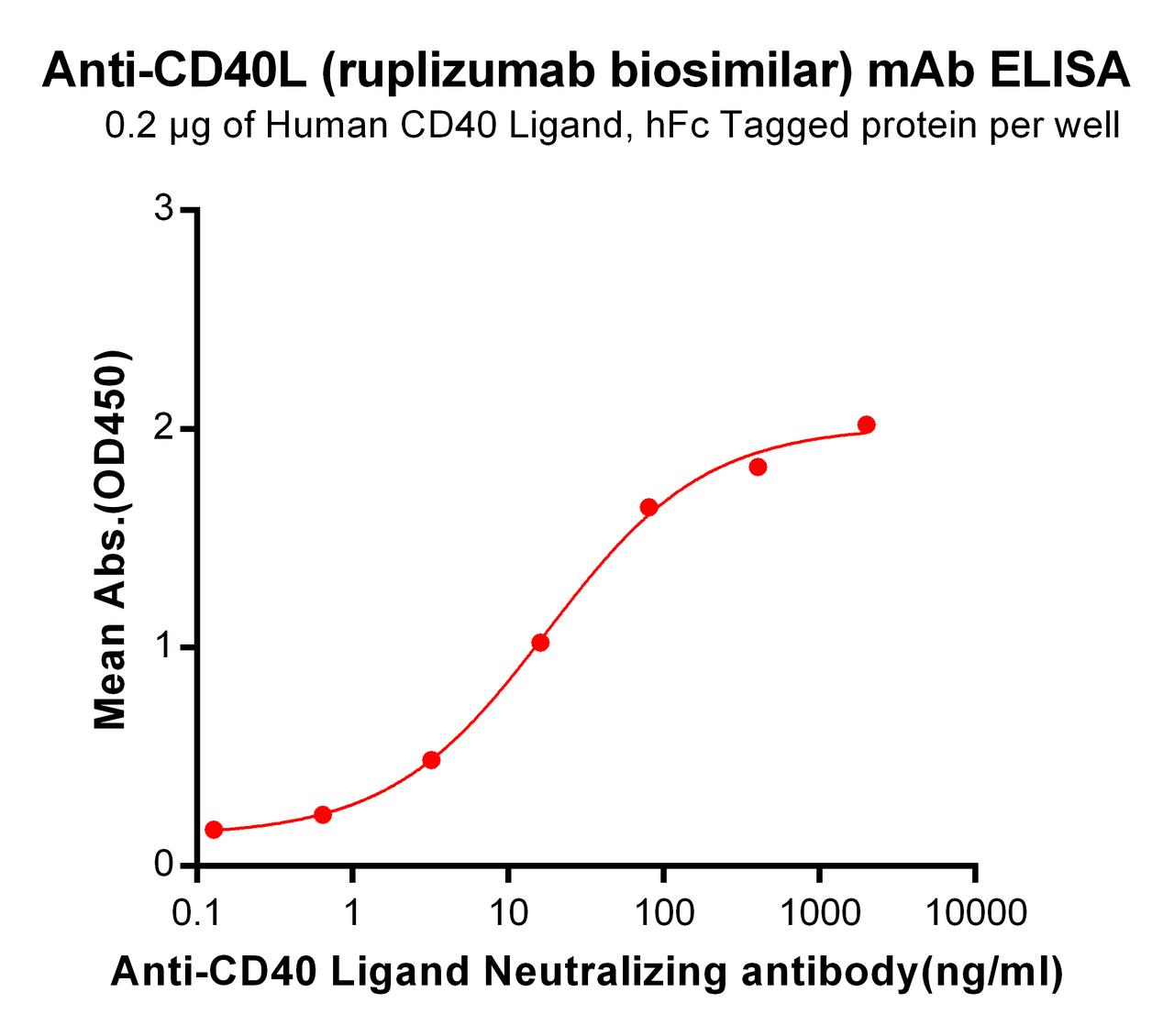
| Ruplizumab (Anti-CD40L) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD40L |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Ruplizumab Biosimilar Compares to Ruplizumab
Ruplizumab biosimilar is developed to be structurally similar to the reference Ruplizumab, offering similar pharmacological effects in treating cancers. The main distinction lies in the production process, where minor differences in manufacturing can lead to slight variations in the final product. Despite these differences, biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the same quality standards and therapeutic efficacy as the original drug.
Advancing Research on Ruplizumab
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Ruplizumab biosimilar is for research use only and is not yet approved for clinical use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



