Ponsegromab: A Breakthrough in Heart Failure and Cachexia Research
Quick Facts About Ponsegromab
What is Ponsegromab?
Ponsegromab is an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by Pfizer, primarily studied for its potential in treating heart failure and cancer-associated cachexia.
What is the Mechanism of Action of Ponsegromab?
Ponsegromab targets Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), a cytokine linked to inflammation, appetite regulation, and muscle wasting. By inhibiting GDF-15, Ponsegromab aims to counteract cachexia and improve patient outcomes in cardiovascular and cancer-related conditions.
What Are the Clinical Applications of Ponsegromab?
Ponsegromab is being evaluated for its potential to mitigate muscle wasting in heart failure and cancer cachexia, with ongoing and emerging studies highlighting its therapeutic promise.
1.) Understanding Ponsegromab
Ponsegromab is a fully human monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), a stress-induced cytokine that plays a significant role in disease progression, particularly in heart failure and cancer cachexia. GDF-15 is known to modulate appetite, energy balance, and muscle homeostasis, and its elevated levels are associated with severe weight loss, muscle wasting, and overall poor prognosis in chronic illnesses. By targeting and neutralizing GDF-15, Ponsegromab aims to counteract these detrimental effects, offering a potential breakthrough in managing cachexia-related complications.
Cachexia is a multifactorial syndrome characterized by unintentional weight loss, muscle atrophy, and systemic inflammation, significantly contributing to morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic conditions such as cancer, heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Current treatment options for cachexia are limited, and there is a pressing need for targeted therapies that can address the underlying biological mechanisms driving muscle deterioration.
Pfizer’s research on Ponsegromab is focused on its ability to improve muscle strength, restore energy balance, and ultimately enhance survival outcomes for affected individuals. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated promising results, suggesting that inhibiting GDF-15 may help mitigate muscle wasting and weight loss while improving patients' quality of life. Given its mechanism of action, Ponsegromab holds potential as a novel therapeutic approach to address the unmet medical needs in cachexia management. Further clinical trials are underway to evaluate its efficacy and safety in larger patient populations, potentially paving the way for a groundbreaking treatment option in chronic disease care.
2.) Ponsegromab Mechanism of Action
Ponsegromab exerts its therapeutic effects by specifically targeting and inhibiting Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), a stress-induced cytokine that plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of cachexia and cardiovascular diseases. GDF-15 is upregulated in response to various pathological conditions, including chronic inflammation, heart failure, cancer, and metabolic disorders. Elevated levels of GDF-15 contribute to a cascade of adverse physiological effects, including appetite suppression, increased energy expenditure, and significant muscle atrophy, ultimately leading to frailty and a decline in overall health.
The primary mechanism of Ponsegromab involves blocking GDF-15 signaling, thereby disrupting its ability to activate the GDF-15 receptor complex, which is linked to anorexia and metabolic dysregulation. GDF-15 is known to interact with the GDNF family receptor α-like (GFRAL) in the brainstem, specifically within the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius, regions that regulate appetite and energy homeostasis. When GDF-15 binds to GFRAL, it triggers pathways that lead to reduced food intake, altered metabolism, and muscle degradation. By neutralizing GDF-15, Ponsegromab effectively prevents this signaling cascade, helping to restore metabolic balance.
This inhibition results in multiple beneficial effects, including improved appetite, enhanced nutrient absorption, and better muscle maintenance. By mitigating the effects of cachexia, Ponsegromab has the potential to improve quality of life and survival outcomes in patients with chronic illnesses. Ongoing research continues to explore its full therapeutic potential, with early clinical data suggesting that targeting the GDF-15 pathway could revolutionize the management of muscle-wasting diseases and associated metabolic dysfunctions.
3.) Clinical Applications of Ponsegromab

Ponsegromab has emerged as a promising therapeutic candidate for managing conditions characterized by severe muscle wasting and metabolic dysregulation, particularly heart failure and cancer cachexia. Cachexia, a debilitating syndrome associated with chronic illnesses, leads to progressive weight loss, muscle atrophy, fatigue, and poor treatment outcomes. Current treatment options are limited, with no FDA-approved therapies specifically targeting the underlying mechanisms of cachexia. Ponsegromab’s ability to inhibit Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15) positions it as a novel intervention aimed at improving metabolic balance, preserving muscle mass, and enhancing overall quality of life in affected individuals.
Clinical investigations into Ponsegromab have primarily focused on its efficacy in Phase 2 trials, where it has demonstrated potential benefits in reducing the negative impact of elevated GDF-15 levels. In patients with heart failure, excessive GDF-15 activity is linked to cardiac cachexia, systemic inflammation, and poor cardiovascular outcomes. By neutralizing GDF-15, Ponsegromab may help mitigate muscle loss, improve energy levels, and support better functional capacity in these patients. Similarly, in cancer cachexia, where rapid muscle wasting significantly affects prognosis and treatment tolerance, Ponsegromab’s mechanism offers a potential strategy to counteract the metabolic imbalances driven by the disease.
Additionally, emerging data suggest that Ponsegromab could play a role in palliative care by helping to manage weight loss and frailty in advanced-stage patients. Further research is required to fully establish its long-term efficacy, safety, and broader clinical applications, but early findings indicate a significant advancement in disease management for cachexia-related conditions.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Ponsegromab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference drug, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety or efficacy. Biosimilars play a crucial role in research by providing cost-effective alternatives for studying biologic pathways.
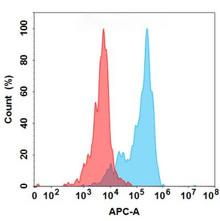
| Ponsegromab (Anti-GDF15) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GDF15 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Ponsegromab Biosimilar Compares to Ponsegromab
Biosimilar versions of Ponsegromab are developed to replicate its effects while offering accessibility for research. While not intended for clinical use, these biosimilars facilitate preclinical studies, drug development, and mechanistic research.
Benefits of Ponsegromab Biosimilars in Research
Cost-effective tool: Enables broader research accessibility.
Facilitates new drug discovery: Supports novel therapeutic investigations.
Accelerates scientific progress: Helps validate biological mechanisms and potential clinical applications.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Ponsegromab biosimilar products are intended for research use only and not for clinical applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




