Plozalizumab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Info Section: Key Facts About Plozalizumab
What is Plozalizumab?
Plozalizumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a key immune checkpoint in cancer cells. By inhibiting CD47, it enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack tumors.
What is the mechanism of action for Plozalizumab?
Plozalizumab works by binding to CD47, preventing it from sending a “don’t eat me” signal to immune cells, thereby promoting phagocytosis and enhancing the immune response against cancer cells.
What are the clinical applications of Plozalizumab?
Plozalizumab is being explored in clinical trials for its potential in treating various cancers, including hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. Ongoing research continues to assess its efficacy and safety in combination therapies.
1.) Understanding Plozalizumab
Plozalizumab is a monoclonal antibody currently being explored as a potential therapeutic agent in immuno-oncology. It targets CD47, a protein commonly overexpressed on the surface of many tumor cells. CD47 plays a crucial role in immune evasion, acting as a “don’t eat me” signal that prevents macrophages and other immune cells from attacking and engulfing cancer cells. By binding to CD47, Plozalizumab disrupts this signaling mechanism, allowing immune cells, particularly macrophages, to recognize and eliminate the cancer cells. This ability to overcome immune evasion makes Plozalizumab a promising approach to treating a wide variety of cancers, including both hematologic (blood-related) and solid tumors.
The significance of Plozalizumab lies in its ability to specifically target this immune checkpoint, which is a key factor in enabling cancer cells to evade the body’s natural immune response. Tumors that overexpress CD47 can avoid destruction by the immune system, allowing them to grow and metastasize unchecked. By blocking CD47’s interaction with its receptor SIRPα on macrophages, Plozalizumab essentially turns off this “don’t eat me” signal, thus reactivating the immune system to target and destroy the tumor cells.
Given the wide range of cancers that exploit the CD47-SIRPα pathway to evade immune surveillance, Plozalizumab has the potential to offer a new therapeutic avenue for patients with cancers that are resistant to traditional treatments. Early-phase clinical trials have already begun to assess its safety and efficacy, and the drug is being investigated in combination with other therapies, such as chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, to further enhance its effectiveness. Researchers are hopeful that Plozalizumab could be an important tool in the growing field of cancer immunotherapy, contributing to more effective treatment strategies for patients with advanced or refractory cancers.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Plozalizumab
Plozalizumab targets CD47, a cell surface protein that plays a significant role in immune evasion by tumors. Under normal circumstances, CD47 sends a “don’t eat me” signal to macrophages, preventing them from engulfing and destroying the tumor cells. This signaling pathway is critical for cancer cells to avoid immune detection and elimination. When Plozalizumab binds to CD47, it blocks the interaction between CD47 and its receptor, SIRPα, on macrophages. This blockage prevents the immune system from being tricked by the tumor cells, thus enabling macrophages to recognize and clear the cancerous cells.
By inhibiting the CD47-SIRPα interaction, Plozalizumab enhances macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, which is a key component of the immune system’s response to cancer. In addition to promoting macrophage activity, the disruption of this signaling pathway may lead to the activation of other immune cells that contribute to the immune response, such as dendritic cells and T-cells. This multi-faceted action makes Plozalizumab a promising immuno-oncology therapeutic, particularly for cancers that heavily rely on CD47 to evade immune detection.
Plozalizumab’s mechanism of action is distinct from traditional chemotherapy and radiation therapies, which work by directly killing tumor cells. Instead, Plozalizumab stimulates the body’s own immune system to target and eliminate tumor cells. This immunotherapeutic approach is particularly appealing for cancers that have become resistant to conventional treatments. Furthermore, by combining Plozalizumab with other therapies, researchers hope to enhance its efficacy and provide more durable treatment responses for patients with advanced or refractory cancers.
3.) Clinical Applications of Plozalizumab
Plozalizumab is currently being investigated in clinical trials for its potential to treat a wide range of cancers, both hematologic and solid tumors. Hematologic cancers, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes, often overexpress CD47, making them particularly vulnerable to immune evasion. In these cancers, Plozalizumab’s ability to block CD47 can restore the immune system’s ability to target and eliminate tumor cells. Early clinical trials have demonstrated encouraging results, suggesting that Plozalizumab can improve the efficacy of existing treatments, such as chemotherapy, in patients with hematologic malignancies.
In addition to hematologic cancers, Plozalizumab is also being studied for its potential in treating solid tumors, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and lung cancer. Solid tumors often use immune evasion mechanisms to suppress immune cell activity, which makes them resistant to many conventional therapies. By targeting CD47 and enhancing immune activity, Plozalizumab may offer a new treatment option for these hard-to-treat cancers. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring the safety and efficacy of Plozalizumab as a monotherapy and in combination with other treatments, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, targeted therapies, and chemotherapy.
The clinical applications of Plozalizumab are still being explored, but early results suggest that it has the potential to become an important tool in cancer immunotherapy. Researchers are continuing to evaluate its role in combination therapies and how it can be used to overcome resistance mechanisms in a variety of cancers. As research progresses, Plozalizumab may provide new hope for patients with cancers that are resistant to traditional treatments, offering a promising new approach to cancer therapy.
4.) Advancing Research on Plozalizumab with Biosimilars
While Plozalizumab is still under investigation, its biosimilar counterpart is providing valuable insights for ongoing research. A biosimilar product offers a highly similar version of the original monoclonal antibody, designed to replicate its function while offering cost-effective alternatives for research purposes. The Plozalizumab biosimilar provides researchers with an opportunity to explore this therapy in a more accessible form, supporting large-scale studies and preclinical research.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biological product that is highly similar to an already FDA-approved reference biologic, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, potency, and efficacy. In cancer research, biosimilars of monoclonal antibodies like Plozalizumab can be valuable tools for advancing scientific understanding, providing researchers with a cost-effective way to conduct experiments and clinical trials that may otherwise be cost-prohibitive.
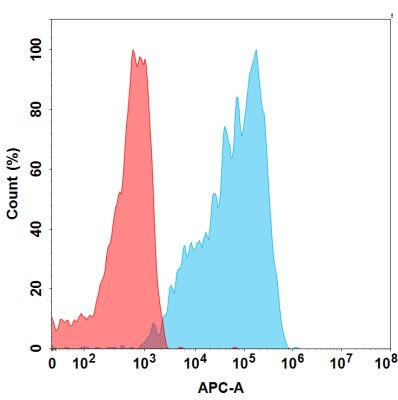
| Plozalizumab (Anti-CCR2) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CCR2 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison: Plozalizumab vs. Plozalizumab Biosimilar
Plozalizumab and its biosimilar are designed to bind to the same target, CD47, and function in a similar way to enhance immune responses against cancer cells. However, biosimilars are produced through a different manufacturing process that may lead to slight differences in composition. Despite these differences, biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to ensure they match the reference biologic in terms of safety and effectiveness. These similarities allow the biosimilar to be used as a powerful tool in research settings to further understand the potential of CD47-targeting therapies.
Benefits of Plozalizumab Biosimilar for Research
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Plozalizumab biosimilar is intended exclusively for research purposes and not for human clinical use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


