Pembrolizumab: Unveiling Its Mechanism and Research Applications with Biosimilars
Key Facts: Pembrolizumab
Is Pembrolizumab Safe?
Pembrolizumab is widely recognized as safe for most patients, with side effects ranging from mild to severe. Commonly reported side effects include fatigue, rash, and immune-related complications such as colitis or pneumonitis.
What is the Mechanism of Action for Pembrolizumab?
Pembrolizumab functions by inhibiting the PD-1 pathway, a mechanism that tumors often exploit to evade immune detection. By blocking this pathway, Pembrolizumab enhances the immune system’s ability to identify and destroy cancer cells.
Does Pembrolizumab Lower IgG4 Levels?
Research has shown that Pembrolizumab can reduce IgG4 levels, which may influence immune modulation and its effectiveness in cancer therapy.
1.) Understanding Pembrolizumab: A Breakthrough in Immunotherapy
Pembrolizumab, commercially known as Keytruda, is a monoclonal antibody utilized in immunotherapy. It targets the programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptor, an immune checkpoint, enabling the body’s immune system to combat cancer cells more effectively.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Pembrolizumab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab binds to the PD-1 receptor on T-cells, preventing its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2—proteins frequently overexpressed by tumor cells. This inhibition revitalizes T-cell activity, empowering the immune system to attack cancer cells more aggressively. This mechanism has been validated in treating various cancers, including melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and urothelial carcinoma.
3.) Clinical Applications of Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab has proven effective across a spectrum of cancers, often serving as a first-line treatment for advanced stages. Notable applications include:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Particularly in patients exhibiting high PD-L1 expression.
- Melanoma: As an adjuvant therapy or for treating metastatic conditions.
- Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): Especially in recurrent or metastatic scenarios.
- Bladder cancer: Promising results in combination therapies for advanced urothelial cancers.
- Ongoing research aims to expand Pembrolizumab’s applications, including novel combination therapies and targeted treatments.
4.) Advancing Pembrolizumab Research with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic products that closely replicate an existing FDA-approved reference product. They deliver comparable safety, efficacy, and quality, serving as cost-effective alternatives for research and clinical exploration.
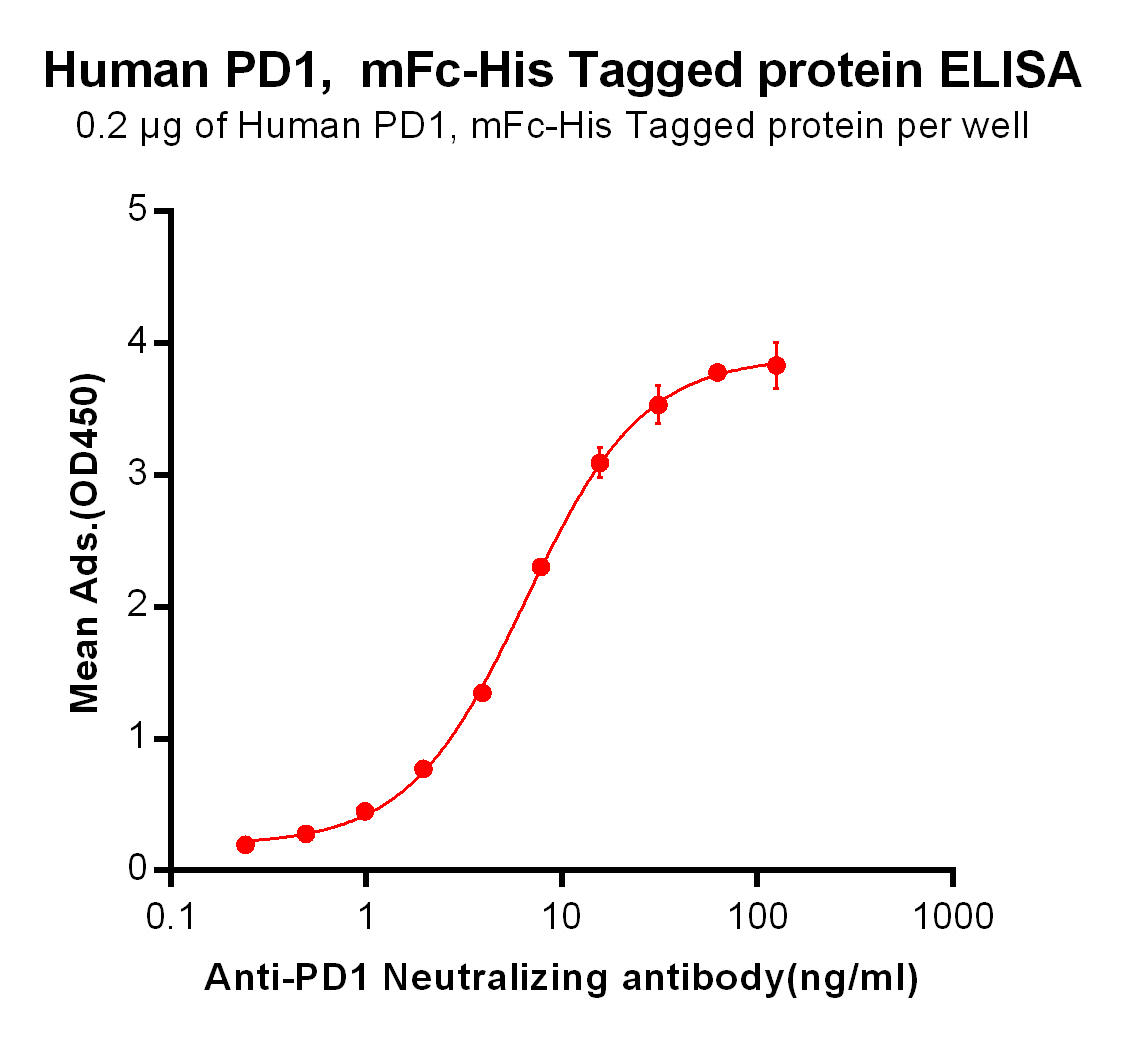
| Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | PD-1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does the Pembrolizumab Biosimilar Compare?
Our Pembrolizumab biosimilar replicates the original monoclonal antibody in both structure and function. It provides researchers with a reliable tool for preclinical studies, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Benefits of the Pembrolizumab Biosimilar for Research
- Cost Efficiency: Facilitates comprehensive research within budget constraints.
- Accessibility: Offers a practical alternative when the reference product is limited or unavailable.
- Research Use Only: Suited for in vitro and in vivo studies, aiding in PD-1/PD-L1 pathway analysis, immunotherapy mechanism exploration, and drug development efforts.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
This product is intended for research purposes only and is not suitable for diagnostic or therapeutic use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Tigatuzumab: Advancing Cancer Research with Targeted Therapies
Quick Facts About TigatuzumabWhat is Tigatuzumab?Tigatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025




