Onvatilimab: Redefining the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Onvatilimab
What is Onvatilimab?
Onvatilimab is a monoclonal antibody targeting CD47, often referred to as the "don't eat me" signal, which is overexpressed on many cancer cells.
What role does Onvatilimab play in targeting CD47?
By blocking CD47, Onvatilimab enables macrophages and the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells effectively.
Is Onvatilimab safe?
Ongoing clinical trials indicate a promising safety profile, but research is still exploring long-term effects and combination therapies.
1.) Understanding Onvatilimab
Onvatilimab represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of immuno-oncology, offering a promising therapeutic strategy for combating cancer. It targets CD47, often referred to as the "don't eat me" signal, which cancer cells exploit to evade immune system attacks. By binding to CD47, Onvatilimab disrupts its interaction with SIRPα, a receptor on macrophages and dendritic cells, effectively lifting the inhibitory signal that prevents these immune cells from engulfing and destroying cancerous cells. This mechanism of action is particularly innovative because it restores the innate immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells, offering a novel approach to cancer therapy.
One of the most significant advantages of Onvatilimab is its potential to treat a wide range of malignancies, including both hematologic cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, and solid tumors, such as those in the lung, breast, and colon. Furthermore, Onvatilimab has demonstrated a remarkable capacity for synergy with other immunotherapies, particularly PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors. This combination has shown enhanced efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies, leading to improved tumor clearance and prolonged survival in patients.
Another key benefit of Onvatilimab is its ability to reduce immune evasion by cancer cells, a common challenge in oncology. By targeting this specific pathway, it addresses a critical need for more effective and durable treatments. As research progresses, Onvatilimab is poised to become a cornerstone of next-generation cancer therapies, offering new hope for patients facing some of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant forms of the disease.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Onvatilimab

Onvatilimab operates by targeting CD47, a protein often termed the "don't eat me" signal due to its role in protecting cells from phagocytosis by the immune system. Under normal physiological conditions, CD47 binds to the SIRPα receptor on macrophages, signaling them to refrain from engulfing the cell. While this mechanism is crucial for preventing the destruction of healthy cells, cancer cells exploit it by overexpressing CD47, effectively camouflaging themselves to evade immune detection.
By blocking the interaction between CD47 and SIRPα, Onvatilimab disrupts this deceptive strategy, restoring the immune system's innate ability to recognize and target malignant cells. This blockade yields two significant immunological outcomes. Firstly, it enhances phagocytosis, enabling macrophages to identify, engulf, and destroy cancer cells more efficiently. Secondly, it stimulates adaptive immune activation, where antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells process the remnants of destroyed cancer cells and present their antigens to T cells. This process triggers a robust, systemic immune response, recruiting and activating T cells to target and eliminate tumors throughout the body.
Preclinical models and clinical trials have underscored Onvatilimab’s potential to address critical challenges in cancer therapy. Notably, it has shown promise in overcoming resistance to conventional treatments, including other immune checkpoint inhibitors like PD-1/PD-L1 blockers. Its ability to synergize with these therapies amplifies its therapeutic efficacy, paving the way for combination regimens that harness multiple immune pathways. This dual mechanism of action positions Onvatilimab as a groundbreaking candidate in the realm of immuno-oncology, offering renewed hope for patients with resistant or aggressive cancers.
3.) Clinical Applications of Onvatilimab
Onvatilimab is undergoing extensive clinical evaluation for its application in treating a broad spectrum of cancers, including hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. The versatility of this anti-CD47 therapy lies in its ability to counter immune evasion, a common feature in various cancer types.
In hematologic malignancies, Onvatilimab demonstrates remarkable promise, particularly for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. These cancers often exploit CD47 overexpression to escape immune surveillance, allowing malignant cells to proliferate unchecked. By blocking the CD47-SIRPα interaction, Onvatilimab restores the immune system’s capacity to recognize and eliminate these cells, making it a powerful candidate for these challenging diseases. Furthermore, its ability to act as a macrophage checkpoint inhibitor creates opportunities for synergistic effects with existing treatments, such as chemotherapies or monoclonal antibodies like rituximab, enhancing overall therapeutic outcomes.
For solid tumors, including lung and breast cancers, Onvatilimab has shown encouraging results, particularly in combination with PD-L1 inhibitors. This combination strategy effectively amplifies anti-tumor activity by addressing multiple immune resistance pathways simultaneously. Solid tumors, which are traditionally resistant to immunotherapy, may benefit from this dual approach, as it enhances immune infiltration and reduces tumor burden.
Ongoing research continues to explore Onvatilimab's capacity to modify the tumor microenvironment by reducing immune suppression. Early data suggest its ability to reprogram the microenvironment to favor immune activation, potentially increasing the efficacy of other therapeutic agents. Foundational studies on CD47 blockade remain pivotal, offering valuable insights that guide the development of innovative treatments while solidifying Onvatilimab’s role in the next generation of cancer therapies.
4.) Advancing Research on Onvatilimab: The Role of Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product designed to be highly similar to an existing reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Biosimilars play a critical role in expanding access to groundbreaking treatments and accelerating research.
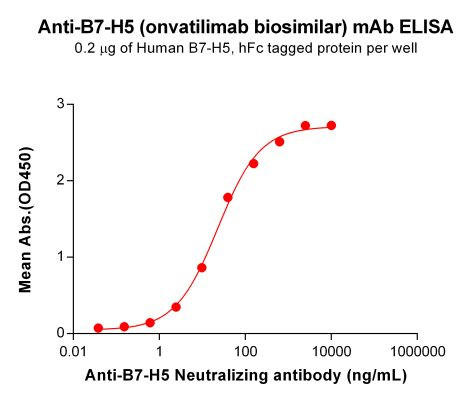
| Onvatilimab (Anti-B7-H5) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | B7-H5 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Onvatilimab Biosimilar Compares to Onvatilimab
Our Onvatilimab biosimilar provides researchers with a high-quality alternative for studying the mechanisms and applications of CD47 blockade. Key features include:
Structural Similarity: Matches the original Onvatilimab in its molecular composition.
Functional Consistency: Delivers identical pharmacodynamic effects, ensuring reliability in experimental setups.
Benefits of Onvatilimab Biosimilar in Research
By integrating the Onvatilimab biosimilar into experimental frameworks, researchers can accelerate their understanding of immune checkpoint inhibition and CD47-related pathways.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




