Naratuximab: Redefining Cancer Therapy with Precision Medicine
Quick Facts About Naratuximab
What is Naratuximab?
How does Naratuximab work?
It binds to the CD37 protein on the surface of B cells, delivering a cytotoxic payload to eliminate cancerous cells while sparing healthy ones.
What are the clinical uses of Naratuximab?
Naratuximab is primarily investigated for treating relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas, with promising results in clinical trials.
1.) Understanding Naratuximab
Naratuximab represents a groundbreaking advancement in antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapy, specifically designed to target CD37, a protein predominantly expressed on B cells. This high degree of specificity makes it particularly effective in treating B-cell malignancies, including aggressive subtypes such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma. By selectively binding to CD37, Naratuximab delivers a potent cytotoxic payload directly into malignant cells, ensuring maximum therapeutic impact while minimizing harm to healthy tissues.
Historically, cancer therapies have relied on broad-spectrum treatments, such as traditional chemotherapy and radiation, which often result in severe off-target effects, compromising patients’ quality of life. Naratuximab addresses these limitations by integrating precise antibody targeting with a powerful cytotoxic agent, significantly reducing systemic toxicity. This dual-action mechanism not only enhances treatment efficacy but also improves patient outcomes by reducing adverse effects commonly associated with conventional therapies.
By focusing on CD37, Naratuximab fills a critical gap in the treatment landscape, offering renewed hope to patients who have exhausted standard therapeutic options. Its novel approach makes it particularly valuable for individuals with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies, where treatment resistance is a major challenge. Additionally, emerging research suggests that Naratuximab’s applications may extend beyond lymphomas, potentially benefiting patients with autoimmune diseases and other malignancies where CD37 plays a crucial role.
As clinical trials progress, Naratuximab is poised to redefine cancer treatment, merging scientific innovation with tangible clinical benefits. Its potential to revolutionize precision oncology highlights its role as a cornerstone in next-generation cancer therapies.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Naratuximab
Naratuximab is a highly selective antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) designed to target the CD37 protein, a surface marker found on mature B cells and several B-cell malignancies, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). This targeted approach allows for precise delivery of its cytotoxic payload, significantly enhancing treatment efficacy while minimizing off-target effects. Upon binding to CD37, Naratuximab is internalized into the cancer cell, where the payload is released, disrupting essential cellular functions and ultimately triggering apoptosis.
The ADC’s mechanism of action integrates the specificity of monoclonal antibody therapy with the potent cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy. The antibody component ensures selective binding to malignant cells, while the attached chemotherapy agent eliminates them efficiently. This dual-action approach not only maximizes therapeutic efficacy but also reduces systemic toxicity, a common drawback of traditional chemotherapies.
Unlike conventional treatments that broadly suppress the immune system, Naratuximab’s targeted mechanism preserves healthy immune cells, reducing the severity of adverse effects. This selective nature makes it a valuable option for patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies, addressing an urgent need in oncology. Additionally, its ability to home in on CD37 offers a promising strategy for overcoming resistance to other treatments, particularly in aggressive forms of NHL such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated Naratuximab’s potent anti-tumor activity, even in cases resistant to standard therapies. By targeting CD37, it not only inhibits cancer cell proliferation but may also modulate immune responses, further expanding its therapeutic potential in hematologic malignancies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Naratuximab
Naratuximab is redefining the treatment paradigm for B-cell malignancies, providing a crucial therapeutic option for patients with limited treatment choices. As an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting CD37, it has demonstrated significant promise, particularly in relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including its aggressive subtype, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Given the high relapse rates and resistance associated with conventional therapies, Naratuximab offers renewed hope for patients facing poor prognoses.
In clinical trials, Naratuximab has exhibited remarkable efficacy, particularly when used in combination with established treatments such as rituximab. This synergistic approach has led to improved overall response rates, prolonged progression-free survival, and enhanced durability of remission. By specifically targeting CD37, Naratuximab provides a novel mechanism to eliminate resistant cancer cells while minimizing off-target effects, a crucial benefit for patients who have exhausted standard therapeutic options.
Beyond NHL, emerging preclinical and clinical data suggest that Naratuximab may have broader applications in treating other CD37-positive malignancies, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Its high specificity and favorable toxicity profile make it an attractive candidate for combination regimens, potentially optimizing treatment outcomes while reducing adverse effects.
Looking ahead, ongoing research is investigating the potential of Naratuximab in autoimmune disorders and various hematologic malignancies. As clinical studies progress, this innovative ADC could revolutionize the management of B-cell-driven diseases, paving the way for more personalized and effective treatment strategies. With its expanding therapeutic applications, Naratuximab holds immense promise in transforming patient care on a global scale.
4.) Advancing Research on Naratuximab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are highly similar alternatives to biologic drugs, offering comparable efficacy and safety while reducing research costs.
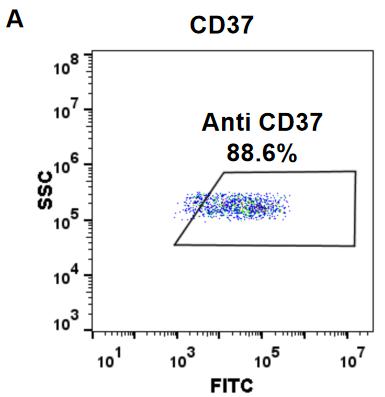
| Naratuximab (Anti-CD37) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD37 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How do Naratuximab and its biosimilar compare?
The biosimilar closely mimics Naratuximab in structure and function, enabling researchers to study its properties in preclinical and translational models.
Benefits of Naratuximab Biosimilars
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Naratuximab biosimilars are for research purposes only and not intended for clinical use. They enable critical advancements in drug discovery and development, ensuring continued innovation in cancer care.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



