Nadecnemab: Advancing Cancer Research Through Anti-CD47 Targeting
Quick Facts About Nadecnemab
What is Nadecnemab?
Nadecnemab is an investigational monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a key immune checkpoint protein involved in cancer evasion.
How Does Nadecnemab Work?
By blocking CD47, Nadecnemab removes the "don’t eat me" signal that cancer cells use to escape immune surveillance, allowing macrophages and other immune cells to recognize and eliminate them.
What Are the Clinical Applications of Nadecnemab?
Nadecnemab is being studied for its potential in treating hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, particularly in combination with other immunotherapies.
1.) Understanding Nadecnemab
Nadecnemab represents a new frontier in immuno-oncology, offering a promising approach to enhancing the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. This novel therapeutic agent targets CD47, a transmembrane protein broadly expressed on malignant cells. Under normal physiological conditions, CD47 functions as a "don't eat me" signal, preventing macrophages and other immune cells from attacking healthy tissue. However, cancer cells exploit this mechanism to evade immune surveillance, allowing unchecked proliferation and tumor progression.
By specifically inhibiting CD47, Nadecnemab disrupts this immune evasion strategy, thereby restoring the ability of the innate immune system to detect and eliminate tumor cells. This targeted approach has positioned Nadecnemab as a significant candidate in cancer treatment, particularly for malignancies that demonstrate high CD47 expression.
Recent preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated Nadecnemab’s potential efficacy across multiple cancer types, particularly in hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma. Its ability to enhance immune-mediated tumor clearance has led researchers to investigate its use as both a monotherapy and in combination with other immune-based treatments, such as PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and conventional chemotherapeutic agents.
Early-phase trials have shown promising results, with indications that CD47 blockade can improve overall survival rates and reduce tumor burden in patients with relapsed or refractory disease. As ongoing research continues to refine dosage regimens, administration strategies, and combination therapies, Nadecnemab remains at the forefront of innovative cancer treatment strategies, offering hope for improved outcomes in patients with challenging malignancies.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Nadecnemab
Nadecnemab exerts its therapeutic effect by binding to CD47, a key immune checkpoint protein that plays a fundamental role in regulating macrophage activity. Under normal physiological conditions, CD47 interacts with the signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, transmitting an inhibitory signal that prevents phagocytosis of healthy cells. However, cancer cells overexpress CD47 to hijack this mechanism, effectively evading immune detection and destruction.
By blocking CD47, Nadecnemab disrupts the interaction between CD47 and SIRPα, thereby removing the inhibitory signal that protects cancer cells. This allows macrophages to recognize, engulf, and destroy malignant cells in a process known as antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP). This mechanism of action enables the immune system to mount a more effective response against tumors, potentially improving long-term disease control.
One of the key advantages of Nadecnemab over traditional chemotherapy is its ability to selectively target cancer cells without causing widespread damage to healthy tissues. Conventional chemotherapeutic agents indiscriminately target rapidly dividing cells, often leading to significant toxicity and adverse effects. In contrast, Nadecnemab offers a more refined immunotherapeutic approach, harnessing the body’s natural defense mechanisms to fight cancer while minimizing off-target effects.
Furthermore, Nadecnemab’s immune-stimulating properties make it an ideal candidate for combination therapies. When used alongside immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 agents, Nadecnemab can enhance the overall immune response, leading to improved treatment efficacy. Additionally, preclinical models suggest that combining Nadecnemab with chemotherapeutic agents may further potentiate its tumor-killing effects, providing a multifaceted approach to cancer therapy that could benefit a broad range of patients.
3.) Clinical Applications of Nadecnemab
Nadecnemab has demonstrated significant potential in the treatment of various malignancies, particularly hematologic cancers, where immune evasion via CD47 overexpression is a common challenge. Clinical trials have shown promising results in several blood cancers, making it a viable option for patients with relapsed or refractory disease.
Hematologic Malignancies:
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Patients with AML often exhibit high CD47 expression, which correlates with aggressive disease progression and poor prognosis. Nadecnemab has shown efficacy in improving immune recognition and destruction of leukemic cells, leading to better treatment responses.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL): Preclinical and early-phase clinical studies suggest that Nadecnemab can enhance macrophage-mediated clearance of lymphoma cells, particularly in cases resistant to standard therapies.
- Multiple Myeloma: By disrupting the CD47-mediated immune evasion mechanism, Nadecnemab has demonstrated potential in overcoming treatment resistance in multiple myeloma patients.
Solid Tumors: Emerging research suggests that Nadecnemab’s therapeutic benefits may extend beyond hematologic cancers to include solid tumors. Several ongoing clinical trials are investigating its efficacy in:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): CD47 blockade in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in improving response rates in NSCLC patients.
- Ovarian Cancer: Studies indicate that Nadecnemab may enhance immune-mediated tumor clearance in ovarian cancer, particularly in conjunction with other immunotherapies.
- Pancreatic Cancer: Due to the aggressive nature of pancreatic cancer and its resistance to conventional therapies, researchers are exploring CD47 inhibition as a novel strategy to improve patient outcomes.
While further research is needed to optimize dosing strategies and combination regimens, early findings suggest that Nadecnemab could become a valuable addition to the evolving landscape of immuno-oncology therapies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Nadecnemab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product highly similar to an already approved reference drug. Biosimilars offer a cost-effective alternative while maintaining equivalent efficacy and safety profiles.
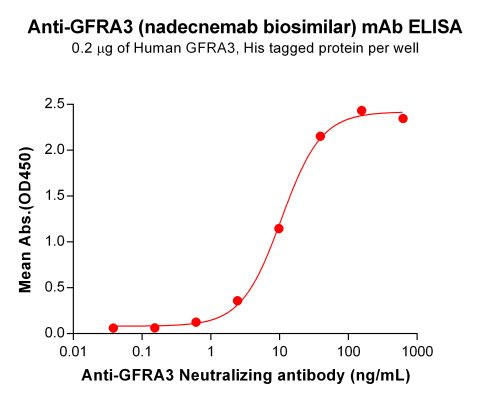
| Nadecnemab (Anti-GFRA3) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GFRA3 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Nadecnemab Biosimilar Compares
Our biosimilar product, Nadecnemab Biosimilar, mirrors the reference monoclonal antibody’s structure and function. Designed for research use only, it provides researchers with a valuable tool to study CD47-targeting therapies in various experimental models.
Benefits of Nadecnemab Biosimilar in Research
- Affordability: Offers a cost-effective alternative for non-clinical studies.
- Reliability: Ensures consistency in immuno-oncology research.
- Innovation: Supports drug development and biomarker discovery.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Nadecnemab Biosimilar is intended for research purposes only and is not for human therapeutic use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



