Lemzoparlimab: Targeting CD47 for Cancer Immunotherapy Advancements
Quick Facts About Lemzoparlimab
What is Lemzoparlimab?
Lemzoparlimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a protein known for its role in helping tumors evade the immune system. By binding to CD47, Lemzoparlimab facilitates immune recognition and destruction of cancer cells.
What is the mechanism of action for Lemzoparlimab?
Lemzoparlimab binds to CD47 on cancer cells, blocking the "don’t eat me" signal that prevents the immune system from attacking tumors. This enhances macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of cancerous cells.
What are the clinical applications of Lemzoparlimab?
Lemzoparlimab is being explored in clinical trials for its efficacy in treating hematologic cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and for its potential in solid tumors.
1.) Understanding Lemzoparlimab
Lemzoparlimab is a promising monoclonal antibody that targets CD47, a protein expressed on the surface of many tumor cells. CD47 acts as a "don’t eat me" signal to macrophages, preventing them from engulfing and destroying cancer cells. By blocking this interaction, Lemzoparlimab enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack tumors. This immune modulation is a key aspect of cancer immunotherapy and represents an innovative approach to treating cancers that have developed resistance to traditional therapies.
The significance of Lemzoparlimab lies in its ability to target CD47 specifically, which is often overexpressed in various malignancies, including hematologic cancers such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Unlike conventional chemotherapy, which indiscriminately affects both cancerous and healthy cells, Lemzoparlimab selectively targets tumor cells, reducing the potential for off-target effects and toxicity. This selectivity positions Lemzoparlimab as an attractive option for patients who may not respond well to traditional treatments or who experience severe side effects.
As an investigational drug, Lemzoparlimab is still in the early phases of clinical development. However, it has shown promise in preclinical studies and early clinical trials, particularly in combination with other immunotherapies and chemotherapy. The ongoing research into its safety, efficacy, and optimal treatment regimens is crucial for establishing its role in the broader cancer immunotherapy landscape. As these studies progress, Lemzoparlimab may emerge as a critical treatment option for patients with hard-to-treat cancers, offering hope where other therapies have failed.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Lemzoparlimab
Lemzoparlimab works by targeting CD47, a cell surface protein that plays a critical role in immune evasion. Under normal conditions, CD47 interacts with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, a type of immune cell. This interaction sends a "don’t eat me" signal that prevents macrophages from engulfing and destroying cells expressing CD47, including cancer cells. Tumor cells often exploit this mechanism to avoid immune surveillance, allowing them to proliferate and spread unchecked.
Lemzoparlimab disrupts this signaling pathway by binding directly to CD47 on the surface of cancer cells, thereby blocking its interaction with SIRPα. Without this inhibitory signal, macrophages are able to recognize and ingest the cancer cells, leading to their destruction. This process is known as macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, a crucial mechanism by which the immune system fights off malignancies. The ability of Lemzoparlimab to activate the immune system and enhance tumor cell clearance makes it a potent tool in the fight against cancer.
In addition to its direct effects on tumor cells, Lemzoparlimab may also work synergistically with other immune-based therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors. By combining Lemzoparlimab with these agents, researchers hope to further enhance its therapeutic effects, leading to improved treatment outcomes for patients with cancers that are resistant to traditional therapies. As clinical trials continue, understanding the full scope of Lemzoparlimab’s mechanisms will be critical for optimizing its use in cancer immunotherapy.
3.) Clinical Applications of Lemzoparlimab
Lemzoparlimab has garnered attention for its potential in treating a variety of cancers, particularly hematologic malignancies. The drug’s ability to target CD47 has made it a strong candidate for use in diseases such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), both of which are difficult to treat with conventional therapies. Early clinical trials have shown that Lemzoparlimab can enhance the body’s immune response to these cancers, offering a new hope for patients who have limited treatment options.
In AML, Lemzoparlimab is being studied in combination with chemotherapy, as researchers aim to assess whether the drug can improve the effectiveness of standard treatments. By blocking the CD47-mediated immune evasion, Lemzoparlimab may help the immune system recognize and destroy leukemia cells that are otherwise protected. Similarly, in NHL, Lemzoparlimab’s ability to target CD47-expressing tumor cells could provide a much-needed alternative for patients who have failed previous therapies.
Emerging research is also expanding the use of Lemzoparlimab into solid tumors. While its potential in hematologic cancers is well-established, ongoing studies are investigating its efficacy in solid cancers such as breast and lung cancer, where CD47 expression is also elevated. These cancers often have immune evasion mechanisms that make them resistant to conventional therapies, and Lemzoparlimab’s ability to enhance immune recognition could offer new treatment options.
As clinical trials continue to investigate the safety and efficacy of Lemzoparlimab, researchers are optimistic that it will become an integral part of the cancer treatment arsenal. By leveraging the power of the immune system, Lemzoparlimab has the potential to significantly improve outcomes for patients with cancers that are resistant to traditional therapies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Lemzoparlimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality. Biosimilars offer a more affordable alternative to the original biologic drugs, providing a cost-effective way to access life-saving treatments.
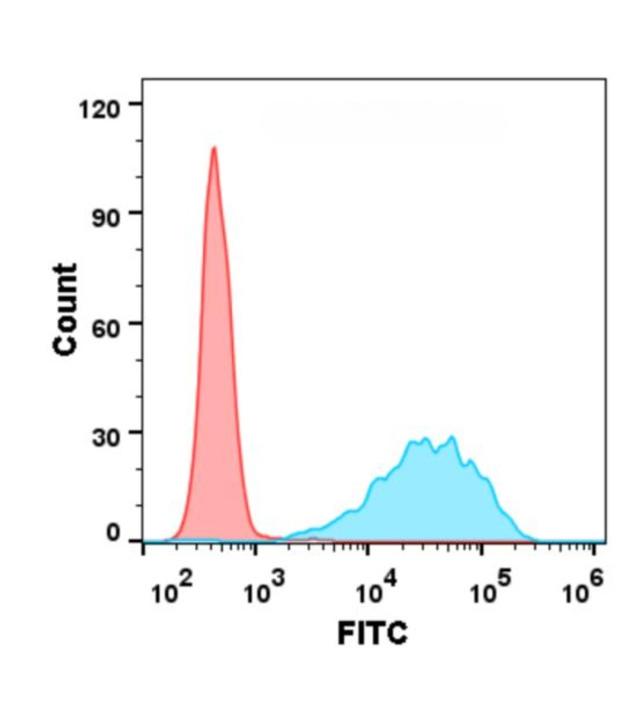
| Lemzoparlimab (Anti-CD47) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD47 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Comparison Between Lemzoparlimab and Its Biosimilar
While Lemzoparlimab is an investigational therapy targeting CD47, the Lemzoparlimab biosimilar shares the same therapeutic target and mechanism of action. Both aim to block the CD47-SIRPα interaction, enhancing immune system-mediated tumor cell destruction. The biosimilar version undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it matches the reference product’s efficacy and safety profile, making it an invaluable research tool for scientists studying cancer immunotherapy.
Benefits of Lemzoparlimab Biosimilar in Research
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Please note that Lemzoparlimab biosimilar is available strictly for research purposes and should not be used for clinical treatment.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



