Ladiratuzumab Vedotin: Targeting TNBC with Next-Gen ADC Therapy
Quick Facts About Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
What is Ladiratuzumab Vedotin?
What is the mechanism of action of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin?
What are the clinical applications of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin?
1.) Understanding Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
Ladiratuzumab Vedotin represents a novel approach to treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), an aggressive subtype that lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors. This absence of traditional hormone receptors makes TNBC particularly difficult to treat, as standard hormone-based therapies are ineffective. Unlike conventional chemotherapy, which affects both cancerous and healthy cells, Ladiratuzumab Vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) designed to selectively target cancer cells while minimizing damage to normal tissues. This precision reduces systemic toxicity and enhances therapeutic efficacy, offering new hope for TNBC patients.
Ladiratuzumab Vedotin specifically targets LIV-1, a transmembrane protein that is highly expressed in TNBC and other solid tumors. By binding to LIV-1, the ADC facilitates the direct delivery of a potent cytotoxic agent, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), into the cancer cell, disrupting cell division and leading to apoptosis. This targeted delivery system improves the drug's efficacy while reducing adverse effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Developed by Merck and Seagen, Ladiratuzumab Vedotin has undergone extensive clinical evaluations to assess its safety and efficacy in TNBC patients. Early-phase clinical trials demonstrated promising results, including significant tumor shrinkage and disease control. However, its development has faced challenges, including the discontinuation of certain clinical trials due to strategic shifts in research focus and evolving treatment paradigms. Despite these setbacks, Ladiratuzumab Vedotin remains an essential candidate in the pursuit of innovative targeted cancer therapies. Researchers continue to explore its potential, particularly in combination with immunotherapies, to enhance patient outcomes and broaden its application beyond TNBC.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
Ladiratuzumab Vedotin employs a highly specific and multi-step mechanism to combat TNBC effectively. As an ADC, it combines a monoclonal antibody with a cytotoxic drug, allowing for precise tumor targeting while minimizing collateral damage to healthy tissues. Its mechanism of action can be broken down into three critical steps:
1. Targeting LIV-1: The monoclonal antibody component of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin is engineered to recognize and bind to LIV-1, a protein overexpressed in TNBC and other malignancies. LIV-1 plays a role in zinc transport and cellular proliferation, making it a relevant therapeutic target. By attaching to LIV-1, the ADC ensures selective drug delivery to cancerous cells.
2. Internalization and Drug Release: Once bound to the LIV-1 receptor, the entire drug-receptor complex undergoes internalization via endocytosis. Inside the cancer cell, enzymatic processes break down the ADC, releasing its cytotoxic payload, MMAE. MMAE is a potent microtubule inhibitor, which disrupts the structural components necessary for cell division.
3. Inducing Apoptosis: After its release, MMAE binds to tubulin, preventing microtubule polymerization. This disruption halts mitosis, leading to cell cycle arrest and eventual programmed cell death (apoptosis). By selectively targeting LIV-1-expressing cells, Ladiratuzumab Vedotin minimizes off-target effects and reduces systemic toxicity compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Preclinical and clinical data have demonstrated Ladiratuzumab Vedotin’s ability to significantly inhibit tumor growth while maintaining a manageable safety profile. Its targeted mechanism offers a more refined treatment approach, particularly for TNBC patients who lack other viable therapeutic options. Ongoing research is investigating its application in combination with checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab, to amplify immune-mediated tumor destruction. These combination strategies aim to enhance treatment efficacy and improve long-term patient survival.
3.) Clinical Applications of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
Ladiratuzumab Vedotin has been extensively evaluated for its potential role in treating TNBC, a particularly aggressive breast cancer subtype with limited treatment options. Due to its targeted nature, this ADC has demonstrated promise in improving patient outcomes while reducing the harsh side effects associated with conventional chemotherapy. Below are the key aspects of its clinical applications:
Potential Benefits in TNBC Treatment
- Tumor Shrinkage: Early-phase clinical trials have reported significant tumor shrinkage in patients with advanced or metastatic TNBC, highlighting its efficacy as a monotherapy or in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- Combination Therapy Potential: Studies indicate that combining Ladiratuzumab Vedotin with pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1 therapy) may enhance immune response and improve overall survival rates in TNBC patients.
- Reduced Systemic Toxicity: Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which affects both cancerous and healthy cells, the targeted mechanism of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin minimizes systemic toxicity, improving patients’ quality of life.
Challenges and Ongoing Research
- Clinical Trial Discontinuations: Despite early promise, some clinical trials evaluating Ladiratuzumab Vedotin have been discontinued due to strategic shifts in research priorities rather than efficacy concerns. These discontinuations highlight the evolving nature of cancer treatment research.
- Optimizing Patient Selection: Researchers are actively working to identify biomarkers that predict which patients will benefit most from Ladiratuzumab Vedotin, ensuring a more personalized approach to therapy.
- Expanding Applications: Beyond TNBC, studies are exploring the potential of Ladiratuzumab Vedotin in other solid tumors expressing LIV-1, broadening its therapeutic scope.
Although the drug’s development has faced challenges, Ladiratuzumab Vedotin remains a key player in targeted cancer therapy. Ongoing research aims to optimize dosing strategies, refine combination treatments, and identify patient subgroups that will benefit most from its use. These efforts will help maximize its clinical utility and potentially expand its indications beyond TNBC.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
What is a Biosimilar?
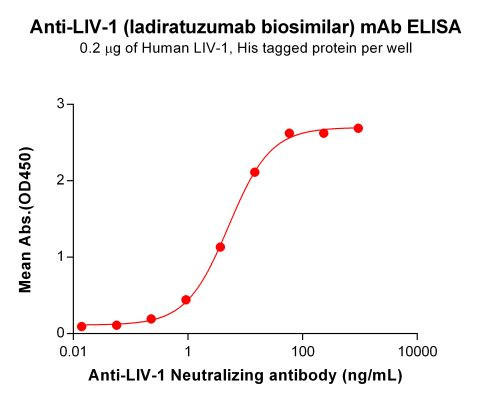
| Ladiratuzumab (Anti-LIV-1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | LIV-1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Ladiratuzumab Biosimilar Compares to Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
- Similarity: The biosimilar retains the same mechanism of action, targeting LIV-1 and delivering MMAE to cancer cells.
- Differences: As a research-use-only product, the biosimilar is not intended for clinical applications but serves as a valuable tool for studying ADCs.
- Advantages: Biosimilars help reduce research costs, increase accessibility, and facilitate further advancements in targeted therapies.
Advancing Research on Ladiratuzumab Vedotin
Biosimilars play a crucial role in accelerating cancer research by providing scientists with cost-effective alternatives for preclinical and translational studies. They allow for:
- Investigating novel ADC combinations.
- Enhancing drug development pipelines.
- Improving understanding of LIV-1 as a therapeutic target.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



