Inebilizumab: Advancing Research and Clinical Applications
What You Need to Know About Inebilizumab
What is Inebilizumab?
How does Inebilizumab work?
It depletes B cells by binding to CD19, reducing inflammation and modulating immune responses.
What are the clinical applications of Inebilizumab?
It is primarily approved for treating Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD) in adults.
Is Inebilizumab safe?
Yes, it has demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with common side effects being mild-to-moderate and manageable.
1.) Understanding Inebilizumab
2.) Mechanism of Action of Inebilizumab
Inebilizumab’s mechanism of action is centered on its ability to selectively deplete B cells by targeting CD19, a receptor expressed on nearly all B cell subsets, including memory B cells, plasmablasts, and some plasma cells. This broader range of activity sets Inebilizumab apart from CD20-targeting therapies like rituximab, which do not effectively eliminate plasma cells that produce pathogenic autoantibodies. This distinction makes Inebilizumab especially effective in treating autoimmune disorders driven by autoantibodies.
Upon binding to CD19, Inebilizumab initiates both antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), leading to the targeted destruction of B cells. By efficiently depleting these cells, Inebilizumab plays a crucial role in modulating autoimmune processes, particularly in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD). In NMOSD, autoreactive B cells produce anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) autoantibodies, which drive inflammatory damage in the central nervous system. By eliminating these pathogenic B cells, Inebilizumab helps prevent relapses, reduce disease progression, and improve patient outcomes.
An important distinction of Inebilizumab is its selectivity in sparing regulatory B cells (Bregs), which are essential for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive immune activation. This targeted depletion strategy minimizes the risks associated with broad immunosuppression, such as opportunistic infections and long-term immune dysfunction. As a result, Inebilizumab offers a more precise and safer approach to treating autoimmune conditions.
Beyond NMOSD, research is ongoing to explore Inebilizumab’s therapeutic potential in other B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, and multiple sclerosis. Its ability to offer sustained B cell depletion while preserving key immune functions makes it a promising candidate for next-generation immunotherapies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Inebilizumab
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD):
The FDA approved Inebilizumab in 2020 for NMOSD based on the pivotal N-MOmentum trial. The study demonstrated a significant reduction in relapses compared to placebo, with a safety profile that reinforced its suitability for long-term use.
Myasthenia Gravis (MG):
Inebilizumab is undergoing phase 2 trials for MG, a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness. Preliminary results indicate potential efficacy in reducing autoantibody production, a hallmark of MG pathology.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
Although primarily studied in NMOSD, Inebilizumab’s mechanism suggests potential applications in MS. Its ability to deplete pathogenic B cells without completely compromising humoral immunity is a promising feature for MS treatment.
Lupus and Other Autoimmune Disorders:
Emerging research is evaluating the role of Inebilizumab in lupus and related conditions. Its broad targeting of CD19-positive cells may offer advantages over current therapies in controlling disease flares and progression.
4.) Advancing Research on Inebilizumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Biosimilars offer cost-effective alternatives, expanding access to advanced therapies while supporting ongoing research.
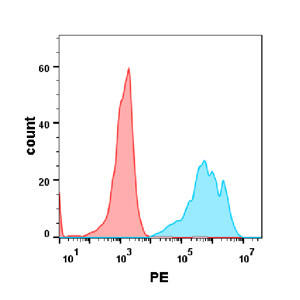
| Inebilizumab (Anti-CD19) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | CD19 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does Inebilizumab Biosimilar Compare?
Our Inebilizumab biosimilar mirrors the original’s structure and function, ensuring comparable efficacy and safety profiles. However, its primary application is in research, enabling scientists to investigate new therapeutic avenues and optimize existing treatment protocols.
Benefits of Inebilizumab Biosimilar for Research
- Cost-Effective: Provides an affordable alternative for preclinical and exploratory studies.
- Accessibility: Expands the availability of high-quality biologics for academic and industrial research.
- Advancing Discovery: Facilitates the development of next-generation therapies and personalized medicine approaches.
Note: The Inebilizumab biosimilar is for research use only and not intended for clinical application.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


