Icrucumab: Exploring the Role of Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Icrucumab
What is Icrucumab?
How Does Icrucumab Work?
What Are the Clinical Applications of Icrucumab?
1.) Understanding Icrucumab
Icrucumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody developed to target vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR-1), a crucial mediator of tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is essential for tumor progression and metastasis, as it provides the necessary oxygen and nutrients to sustain cancer cell proliferation. Many tumors exploit VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) signaling to stimulate blood vessel formation, making anti-angiogenic strategies a key focus in oncology drug development.
Unlike traditional anti-angiogenic therapies, which primarily inhibit VEGF-A, Icrucumab directly blocks VEGFR-1, preventing its interaction with multiple angiogenic ligands such as VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and placental growth factor (PlGF). This approach aims to broaden the inhibition of tumor-driven angiogenesis, potentially leading to more effective tumor control. Additionally, by targeting the receptor rather than the ligand, Icrucumab may influence immune cell dynamics, contributing to an improved tumor microenvironment.
Despite its theoretical advantages, Icrucumab’s clinical development has faced setbacks. Initial trials in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) showed limited efficacy as a monotherapy. The complexity of angiogenic signaling networks and tumor adaptation mechanisms have made VEGFR-1 inhibition challenging in isolation. As a result, researchers are now exploring combination strategies, pairing VEGFR-1 blockade with immune checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy to enhance therapeutic effectiveness.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Icrucumab
Icrucumab exerts its effects by selectively binding to VEGFR-1, blocking its interaction with pro-angiogenic VEGF ligands, including VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and PlGF. This inhibition prevents endothelial cell activation, thereby disrupting tumor-driven blood vessel formation and reducing oxygen and nutrient supply to malignant tissues. By limiting angiogenesis, Icrucumab inhibits tumor growth and metastasis, positioning it as a potential therapeutic agent for various solid tumors.
A unique aspect of Icrucumab’s mechanism is that it targets VEGFR-1 directly, rather than neutralizing VEGF-A like bevacizumab. This approach offers potential advantages, such as:
1. Broader Anti-Angiogenic Activity – Since VEGFR-1 binds multiple VEGF ligands, blocking the receptor itself ensures a wider inhibition of angiogenic signaling.
2. Immune Modulation – VEGFR-1 is expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells, and endothelial cells, meaning its inhibition could influence immune cell recruitment and polarization, potentially shifting the tumor microenvironment toward enhanced immune surveillance.
3. Combination Therapy Potential – By normalizing tumor vasculature, Icrucumab may improve immune cell infiltration, making immune checkpoint inhibitors and chemotherapy more effective.
Despite its scientific promise, challenges persist. Tumors can adapt by activating alternative angiogenic pathways, such as VEGFR-2, fibroblast growth factors (FGF), and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF), which can limit the long-term effectiveness of VEGFR-1 blockade. Furthermore, off-target effects on normal vasculature and wound healing raise concerns about treatment tolerability and side effects.
To overcome these challenges, current research efforts focus on:
- Refining dosing strategies to minimize resistance.
- Identifying biomarkers to select patients who may respond better.
- Developing combination regimens with other targeted therapies to enhance efficacy.
3.) Clinical Applications of Icrucumab
Icrucumab has been primarily studied in oncology, particularly for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These cancers are highly dependent on angiogenesis, making them prime candidates for VEGFR-1 inhibition strategies. However, early-phase clinical trials revealed that while Icrucumab was well-tolerated, its efficacy as a monotherapy was limited, prompting a re-evaluation of its therapeutic potential.
One of the most promising areas of research is its combination with other treatments, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and chemotherapy. Preclinical and clinical studies suggest that VEGFR-1 blockade may:
- Enhance immune infiltration into tumors, making checkpoint blockade therapy (such as anti-PD-1 or anti-CTLA-4) more effective.
- Improve drug delivery by normalizing tumor vasculature, allowing chemotherapeutic agents to penetrate tumors more efficiently.
- Reduce tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and immune-suppressive cells, potentially shifting the tumor microenvironment toward increased immune activation.
Despite these theoretical advantages, clinical development has slowed, and no major trials are currently active for Icrucumab. The challenges in VEGFR-1 targeting have led to explorations of alternative anti-angiogenic strategies, including dual VEGFR-1/VEGFR-2 blockade and multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that inhibit multiple angiogenic and growth factor pathways.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Icrucumab
What is a Biosimilar?
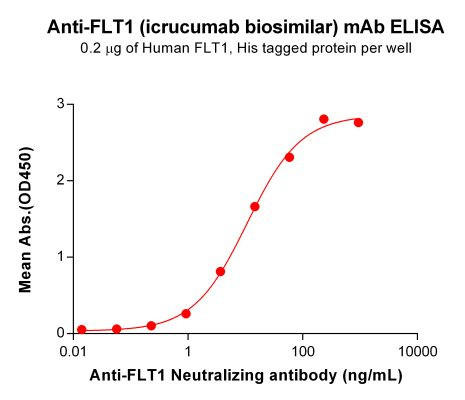
| Icrucumab (Anti-FLT1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | FLT1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Icrucumab Biosimilar Compares to Icrucumab
Advantages of Icrucumab Biosimilar for Research
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


