Codrituzumab: Unveiling Its Role in Cancer Research and Treatment
What You Need to Know About Codrituzumab
What is Codrituzumab?
Codrituzumab is an investigational monoclonal antibody targeting CD47, an immune checkpoint that regulates immune responses in cancer cells. It plays a critical role in the immune evasion mechanisms of tumors.
What is the mechanism of action for Codrituzumab?
Codrituzumab works by binding to CD47 on cancer cells, blocking its interaction with the SIRPα receptor on macrophages, which leads to enhanced immune cell activity and tumor cell phagocytosis.
What are the clinical applications of Codrituzumab?
Codrituzumab is currently under investigation for its potential use in treating various cancers, including hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, with ongoing clinical trials exploring its efficacy and safety.
1.) Understanding Codrituzumab
Codrituzumab is an experimental cancer immunotherapy that leverages the power of the immune system to recognize and eliminate tumor cells. Its primary mechanism revolves around targeting CD47, a key protein on the surface of many cancer cells that acts as a "don't eat me" signal. This signal enables tumors to evade detection by the immune system, allowing cancer cells to survive and proliferate unchecked. By blocking the interaction between CD47 and its receptor, SIRPα, on macrophages, Codrituzumab removes this immune inhibition, enabling macrophages to recognize and engulf cancer cells, thereby enhancing the body’s immune response against tumors.
This approach represents a significant innovation in cancer treatment, particularly in immuno-oncology. Unlike traditional chemotherapy or radiation therapies, which often come with severe side effects and non-specific targeting, Codrituzumab specifically targets the immune evasion mechanisms employed by tumors, offering a more precise and potentially less toxic alternative. By harnessing the body's natural immune defenses, Codrituzumab works to stimulate the immune system, making it a promising candidate for cancers that have been resistant to conventional therapies.
The drug’s potential extends to a variety of cancers, particularly those that overexpress CD47, which include both hematological malignancies like lymphoma and leukemia, and solid tumors such as breast cancer. Researchers are exploring Codrituzumab’s effectiveness in both monotherapy and combination therapies, where it may work synergistically with other cancer treatments to overcome tumor resistance and improve clinical outcomes. Its ability to target immune evasion in tumors has positioned Codrituzumab as an exciting and innovative option in the rapidly evolving field of cancer immunotherapy.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Codrituzumab
Codrituzumab operates by targeting CD47, a protein that is often overexpressed on the surface of many types of cancer cells. CD47 functions as a "don’t eat me" signal, which communicates to immune cells, specifically macrophages, that the cancer cells are "self" and should not be destroyed. This immune evasion mechanism is one of the reasons why tumors can grow and metastasize without being targeted by the immune system. By binding directly to CD47, Codrituzumab blocks the interaction between CD47 and its receptor, SIRPα, on macrophages. This disruption of the CD47-SIRPα interaction removes the signal that prevents macrophages from engulfing the cancer cells.
As a result, macrophages are activated to recognize and phagocytose tumor cells, leading to their destruction. This mechanism enhances the body’s innate immune response, increasing the ability of immune cells to clear malignant cells from the body. Moreover, the blockage of CD47 may also lead to the recruitment of other immune components to the tumor site, further amplifying the body’s anti-cancer immune response. This makes Codrituzumab particularly effective in treating cancers that rely on CD47-mediated immune evasion.
Research into Codrituzumab has shown promise in various preclinical and clinical studies, particularly for cancers that are traditionally difficult to treat. The drug’s ability to modulate the immune system at a critical checkpoint has generated significant interest in its potential as part of a broader cancer immunotherapy strategy. It is being investigated for its effectiveness both as a standalone treatment and in combination with other therapies, such as chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, to further enhance tumor-targeting immune responses and overcome resistance mechanisms commonly seen in cancer treatment.
3.) Clinical Applications of Codrituzumab
Codrituzumab is currently undergoing extensive clinical trials for its potential to treat a wide array of cancers. Its primary application is in hematological malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), both of which are known to express high levels of CD47. In these cancers, CD47 plays a pivotal role in immune evasion, allowing tumor cells to avoid being attacked by the immune system. By targeting CD47, Codrituzumab works to block this mechanism, enhancing macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of cancer cells, and thereby improving treatment efficacy.
Codrituzumab is also being explored in clinical trials for solid tumors, including breast cancer, which is often resistant to conventional therapies such as chemotherapy and radiation. These cancers can also exploit CD47-mediated immune evasion, making them particularly well-suited for treatment with Codrituzumab. Early-phase trials have shown that Codrituzumab can enhance immune responses in both hematological and solid tumors, potentially offering a new line of defense for patients with advanced or refractory cancers. By blocking CD47 and activating macrophages to target tumor cells, Codrituzumab holds the potential to overcome many of the challenges faced in treating resistant cancer types.
In addition to monotherapy, Codrituzumab is being studied in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors. The combination of Codrituzumab with these therapies may help overcome common resistance mechanisms, improve patient outcomes, and reduce the likelihood of tumor recurrence. Early-stage clinical data suggest that Codrituzumab may also enhance the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors, which work by removing the "brakes" on the immune system, thus allowing for a more robust anti-cancer immune response. As clinical trials continue to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Codrituzumab, it is increasingly seen as a promising candidate in the next generation of cancer immunotherapies. Its potential to target CD47 and enhance macrophage activity presents a novel therapeutic approach with the ability to improve clinical outcomes, offering hope for patients with cancers that are resistant to conventional treatments.
4.) Advancing Research on Codrituzumab with Biosimilars
In recent years, biosimilars have emerged as an essential tool in expanding access to innovative therapies. Codrituzumab biosimilars offer a unique opportunity for researchers and clinicians to explore the potential of CD47 blockade in cancer therapy at a lower cost and with greater accessibility.
A Codrituzumab biosimilar closely mirrors the original anti-CD47 antibody in terms of its molecular structure, mechanism of action, and therapeutic potential. While the biosimilar retains the core biological activity of Codrituzumab, it may provide additional benefits, such as improved production scalability and cost-effectiveness. This makes the biosimilar an attractive option for research-focused applications, where affordability and availability are crucial for advancing studies in cancer immunotherapy.
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product, such as Codrituzumab. It is produced through recombinant DNA technology and undergoes rigorous testing to demonstrate that it is as effective, safe, and consistent as the reference product. Biosimilars are developed to meet the growing demand for biologic therapies, providing more affordable options for patients and researchers alike.
For researchers, Codrituzumab biosimilars serve as a valuable tool in expanding cancer research. These biosimilars offer the same therapeutic potential as the original drug, making them an essential asset in studies exploring new treatment regimens and patient populations. However, it is important to note that Codrituzumab biosimilars are intended for research use only and are not approved for clinical use outside of investigational settings.
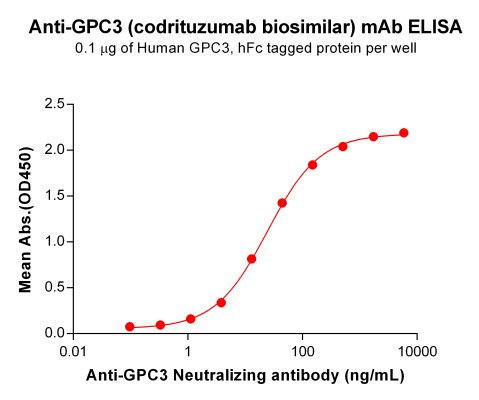
| Codrituzumab (Anti-GPC3) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | GPC3 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Benefits for Research:
The primary advantage of Codrituzumab biosimilar in research lies in its affordability and availability. By providing a more accessible version of the original product, researchers can conduct large-scale studies and clinical trials more efficiently, accelerating the development of new cancer therapies. The biosimilar offers the same benefits in terms of immune modulation and tumor targeting as the original product, ensuring that studies remain relevant and impactful.
By enabling more widespread research, Codrituzumab biosimilars play a pivotal role in advancing cancer treatment and identifying optimal therapeutic combinations. These products contribute to a growing body of knowledge in oncology and provide researchers with the tools they need to make significant strides in cancer immunotherapy.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By David Lee, PhD
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



