Canakinumab: Unraveling Its Role in Inflammatory Disease and Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Canakinumab
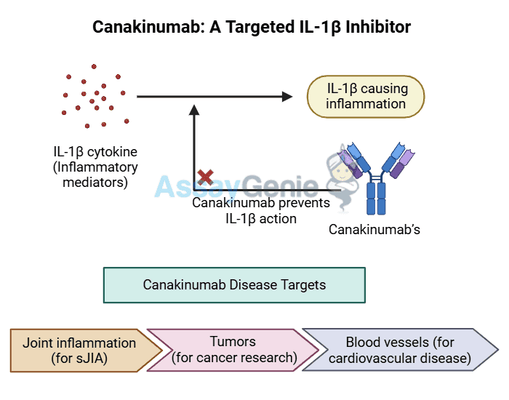
What is Canakinumab?
Canakinumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), reducing inflammation associated with various diseases.
How Does Canakinumab Work?
It neutralizes IL-1β, a key inflammatory mediator, preventing downstream inflammatory responses that contribute to conditions like systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), periodic fever syndromes, and cardiovascular disease.
What Are the Clinical Applications of Canakinumab?
Canakinumab is FDA-approved for treating autoinflammatory syndromes, including sJIA, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS), and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF). It has also shown promise in reducing cardiovascular events and is being explored for cancer therapy.
1.) Understanding Canakinumab
Canakinumab (brand name: Ilaris) is a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively targets and neutralizes interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), a key cytokine involved in the inflammatory response. IL-1β plays a crucial role in autoinflammatory diseases, where excessive activity contributes to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and disease progression. By blocking IL-1β, Canakinumab helps manage these conditions and improve patient outcomes.
Originally developed by Novartis, Canakinumab has been a breakthrough therapy for rare genetic inflammatory disorders, such as Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS), including Muckle-Wells Syndrome and Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome. It has also shown efficacy in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (SJIA) and Adult-Onset Still’s Disease (AOSD), conditions characterized by systemic inflammation and severe symptoms.
Beyond its established use in autoinflammatory diseases, Canakinumab has gained significant attention in cardiovascular research. The Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS) demonstrated that targeting inflammation with Canakinumab could reduce recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction. This landmark study highlighted the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis and suggested that Canakinumab may provide cardiovascular benefits without altering lipid levels, unlike traditional therapies such as statins.
Additionally, ongoing research is exploring Canakinumab’s potential in oncology. IL-1β is implicated in tumor progression, angiogenesis, and metastasis, making its inhibition a promising therapeutic strategy. Studies are investigating Canakinumab as an adjunct therapy in lung cancer and other IL-1β-driven malignancies, assessing its ability to improve outcomes in combination with existing treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. As research progresses, Canakinumab may emerge as a key player in anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer strategies.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Canakinumab

Canakinumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that functions by selectively binding to interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), a key pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in the innate immune response. By neutralizing IL-1β, Canakinumab prevents its interaction with the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R), thereby blocking downstream signaling pathways responsible for inflammation. This inhibition curtails the inflammatory cascade that leads to disease progression in autoinflammatory and immune-mediated conditions.
IL-1β plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases by inducing the release of other pro-inflammatory cytokines, promoting leukocyte recruitment, and activating endothelial cells. Uncontrolled IL-1β activity is associated with fever, joint inflammation, systemic inflammatory responses, and tissue damage. By specifically targeting IL-1β, Canakinumab disrupts this cycle, reducing cytokine-induced fever, alleviating joint inflammation, and mitigating systemic inflammatory damage.
The pharmacokinetics of Canakinumab further enhance its therapeutic advantages. With a long elimination half-life of approximately 26 days, it allows for extended dosing intervals, typically administered every 4 to 8 weeks via subcutaneous injection. This extended half-life reduces the frequency of administration compared to other biologics, improving patient compliance and convenience.
Unlike non-specific anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids and NSAIDs, which broadly suppress immune function and can lead to significant side effects, Canakinumab provides highly targeted therapy. This specificity minimizes systemic side effects, such as immunosuppression and gastrointestinal toxicity, while effectively managing chronic inflammation. Due to its precision and prolonged action, Canakinumab represents a significant advancement in the treatment of autoinflammatory diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and potentially even cancer-related inflammation.
3.) Clinical Applications of Canakinumab
Canakinumab is FDA-approved for the treatment of several autoinflammatory disorders, where excessive IL-1β activity contributes to chronic inflammation and disease progression.
- Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (sJIA): Canakinumab reduces joint inflammation, systemic symptoms, and flare-ups in children with this severe form of juvenile arthritis. By inhibiting IL-1β, it helps manage fever, rash, and arthritis symptoms, improving long-term outcomes.
- Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS): This group of rare genetic disorders includes Muckle-Wells Syndrome and Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome, which are characterized by recurrent fevers, rash, arthritis, and amyloidosis. Canakinumab effectively controls these symptoms by neutralizing IL-1β and preventing disease progression.
- Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF): In patients resistant to colchicine therapy, Canakinumab helps manage recurrent fever episodes and inflammatory complications, reducing the risk of amyloidosis and improving quality of life.
The CANTOS trial (Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study) provided groundbreaking evidence that targeting inflammation with Canakinumab could significantly reduce major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in patients with a history of myocardial infarction. Unlike traditional cardiovascular treatments that focus on lipid reduction, Canakinumab demonstrated that lowering inflammation alone could confer cardiovascular benefits, paving the way for novel anti-inflammatory approaches in cardiovascular medicine.
Emerging research suggests that IL-1β plays a key role in tumor progression, making Canakinumab a promising candidate for oncology applications:
- Lung Cancer: Ongoing clinical trials are investigating Canakinumab’s ability to modify the tumor microenvironment by reducing inflammation-driven tumor growth and enhancing response to existing treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
- Atherosclerosis-related Cancer Risks: Chronic inflammation is linked to increased cancer incidence, particularly in patients with cardiovascular disease. By mitigating systemic inflammation, Canakinumab may lower cancer risk in high-risk populations, offering a potential dual benefit in cardiovascular and oncological health.
As research continues, Canakinumab’s role is expanding beyond its traditional use in autoinflammatory diseases, with growing potential in cardiovascular and cancer therapies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Canakinumab
What is a Biosimilar?
Biosimilars are biologic drugs designed to closely replicate an original biologic therapy. They offer comparable efficacy, safety, and quality while being more cost-effective alternatives for research and clinical applications.
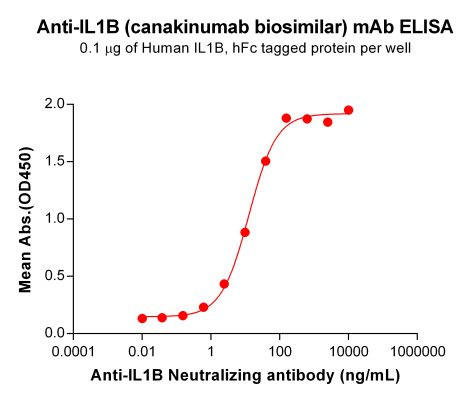
| Canakinumab (Anti-IL1B) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | IL-1B |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Canakinumab Biosimilar Compares to Canakinumab
Biosimilars for Canakinumab are being developed primarily for research purposes. These biosimilars provide:
- Equivalent Binding Affinity: Comparable IL-1β neutralization capacity.
- Cost-effective Research Use: Enabling broader access for preclinical studies.
- Potential for Expanded Applications: Allowing exploration in novel inflammatory and oncological research.
Advancing Research on Canakinumab
Biosimilars facilitate in-depth study of IL-1β inhibition, contributing to:
- Investigating new indications for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
- Understanding long-term effects and resistance mechanisms.
- Developing combination therapies for cancer and cardiovascular conditions.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Biosimilar products for Canakinumab are intended for research use only and not for clinical applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025