Bersanlimab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research with Anti-CD47 Therapeutics
What You Need to Know About Bersanlimab
What is Bersanlimab?
Bersanlimab is a cutting-edge anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody designed to disrupt cancer cells' evasion of immune detection.
What role does Bersanlimab play in targeting CD47?
It inhibits CD47—a “do not eat me” signal used by cancer cells—to enhance macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and immune response.
What are the clinical applications of Bersanlimab?
Bersanlimab is under investigation for treating hematologic malignancies and solid tumors by restoring the immune system’s ability to fight cancer effectively.
1.) Understanding Bersanlimab
Bersanlimab represents a significant advancement in immuno-oncology, specifically within the anti-CD47 therapeutic class. CD47, a cell surface protein, plays a pivotal role as an immune checkpoint by interacting with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages. This interaction allows cancer cells to evade immune clearance by sending a “don’t eat me” signal to the immune system. By targeting and blocking CD47, Bersanlimab disrupts this mechanism, effectively restoring the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This innovative approach underscores its importance in immuno-oncology as it addresses one of the key challenges in cancer treatment: immune evasion by tumor cells.
In preclinical and early clinical studies, Bersanlimab has shown substantial promise, particularly in treating cancers resistant to conventional therapies. Its mechanism of action forms part of a broader movement to develop immune checkpoint inhibitors that target novel pathways beyond the well-established PD-1/PD-L1 axis. By focusing on CD47, Bersanlimab opens up new possibilities for treating aggressive and refractory cancers. The drug’s ability to counteract immune evasion mechanisms makes it a compelling candidate for further investigation and clinical development.
Researchers are also exploring its potential in combination therapies. By integrating Bersanlimab with other immunotherapeutic agents, such as checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1/PD-L1 or CTLA-4, the aim is to achieve synergistic effects that amplify the immune response and overcome resistance mechanisms. These combinations could significantly enhance its efficacy in treating tumors with complex immunosuppressive environments. Ongoing clinical trials and advancements in biomarker research are expected to further refine Bersanlimab’s applications, ensuring its position at the forefront of precision cancer immunotherapy.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Bersanlimab
Bersanlimab’s mechanism of action centers on targeting and disrupting the CD47-SIRPα axis, a pivotal pathway exploited by cancer cells to evade immune detection. CD47, often referred to as the “do not eat me” signal, is highly expressed on the surface of many tumor cells. This overexpression interacts with signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages, effectively suppressing their phagocytic activity. By binding to CD47, Bersanlimab effectively blocks this interaction, neutralizing the inhibitory signal. Consequently, macrophages are reactivated to identify, engulf, and destroy cancer cells, a process known as phagocytosis.
The therapeutic effects of Bersanlimab extend beyond innate immunity, harnessing the body’s adaptive immune system as well. Once macrophages consume tumor cells, they process and present tumor antigens to T-cells, triggering a robust T-cell-mediated immune response. This antigen presentation facilitates the recruitment and activation of cytotoxic T-cells, which seek out and destroy remaining cancer cells, including those distant from the primary tumor site. This cascade amplifies the adaptive immune response, creating a systemic anti-tumor effect that can address metastatic and residual disease.
Bersanlimab’s dual mechanism of action—reviving innate immune functions through phagocytosis and stimulating adaptive immunity via antigen presentation—makes it a promising immuno-oncology agent. It offers a multifaceted approach to treating cancers with high CD47 expression, which are often associated with poor prognosis. By engaging multiple arms of the immune system, Bersanlimab has the potential to overcome significant therapeutic challenges, positioning itself as a cornerstone treatment in the fight against difficult-to-treat malignancies.

3.) Clinical Applications of Bersanlimab
Bersanlimab is being actively investigated for its therapeutic potential across a range of oncologic indications. In hematologic malignancies, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), CD47 overexpression serves as a common mechanism for immune evasion. Early trials have demonstrated that Bersanlimab can effectively target these malignancies, restoring immune function and offering hope for patients with limited treatment options.
In solid tumors, emerging data highlights Bersanlimab’s potential in addressing cancers like colorectal and ovarian cancer. These tumors often exhibit high CD47 expression, making them prime targets for this therapy. The combination of Bersanlimab with other immunotherapies has shown promise, leveraging synergistic effects to enhance overall efficacy. This combination approach is particularly exciting for tumors traditionally considered difficult to treat with single-agent immunotherapies.
Ongoing research emphasizes the importance of patient stratification based on CD47 expression levels, ensuring that treatment is tailored to those most likely to benefit. Additionally, studies aim to optimize dosing strategies to balance efficacy with safety, minimizing on-target, off-tumor side effects such as anemia. The comprehensive exploration of Bersanlimab across diverse cancer types underscores its potential to transform the therapeutic landscape, providing new hope for patients with aggressive and resistant malignancies.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Bersanlimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference product. Biosimilars offer equivalent efficacy and safety, often at a lower cost, making them invaluable in research and therapeutic settings.
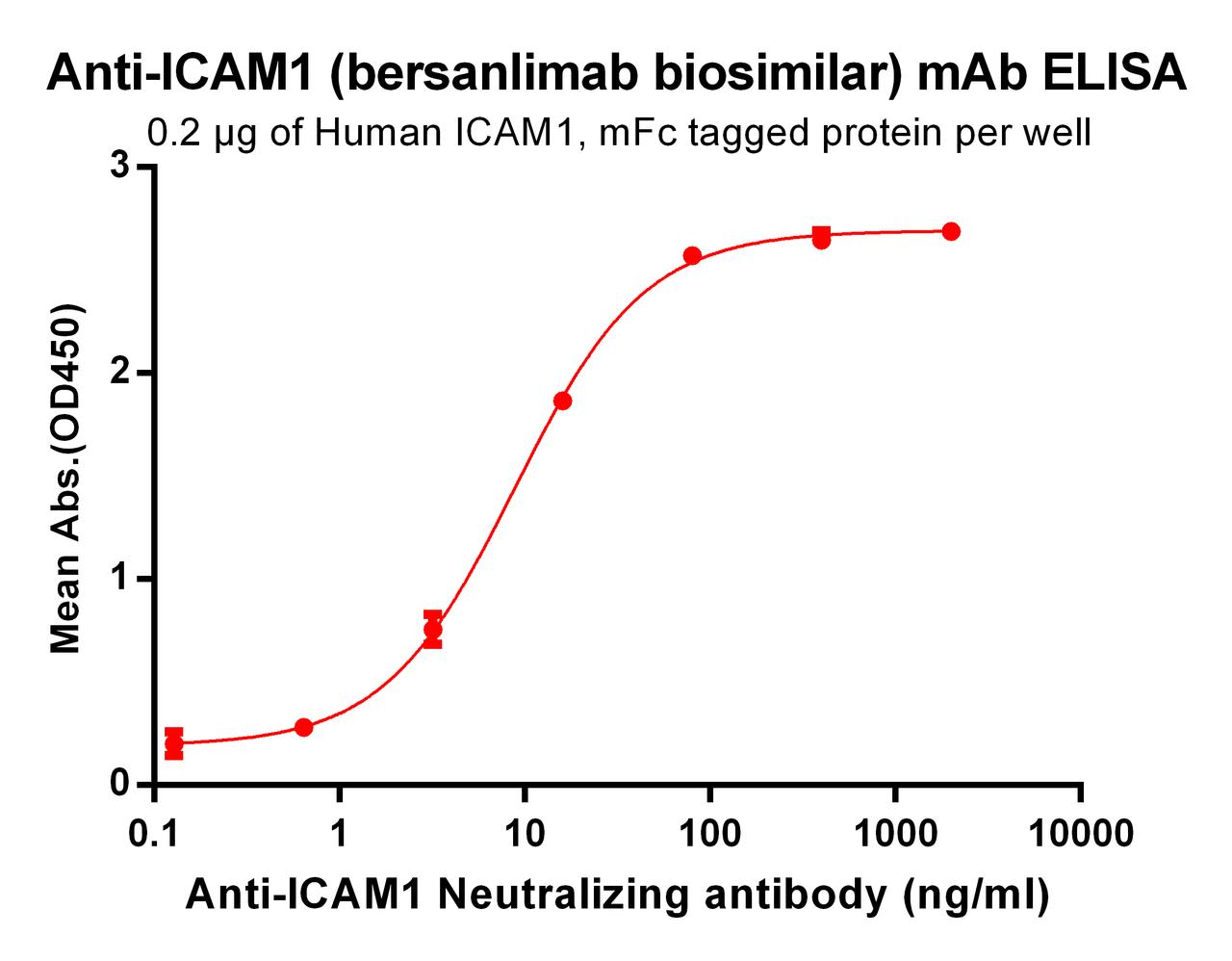
| Bersanlimab (Anti-ICAM1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | ICAM1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Bersanlimab Biosimilar Compares to Bersanlimab
The Bersanlimab biosimilar mirrors the original drug’s structure and function but is specifically designed for research purposes. This similarity allows scientists to:
- Explore new combinations and applications of anti-CD47 therapies.
- Conduct comparative studies to refine dosing and minimize side effects.
Benefits of Bersanlimab Biosimilars in Research
- Accessibility: Biosimilars make cutting-edge research more feasible by reducing costs.
- Scalability: Their availability supports large-scale studies and accelerates discoveries.
Note: The Bersanlimab biosimilar is for research use only and not intended for clinical applications.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Praluzatamab: Unveiling the Promise of CD47-Targeted Therapy in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About PraluzatamabWhat is Praluzatamab?Praluzatamab is an experimental mon …13th May 2025




