Avizakimab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-CD47 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Avizakimab
What is Avizakimab?
Avizakimab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target the CD47 protein, a key checkpoint in immune regulation, particularly in cancer therapy.
What is the mechanism of action for Avizakimab?
Avizakimab works by blocking the CD47 "don't eat me" signal, allowing immune cells, especially macrophages, to target and eliminate cancer cells.
What are the clinical applications of Avizakimab?
Avizakimab has shown promise in clinical trials for treating various cancers, including solid tumors and hematological malignancies, by enhancing immune system responses against tumor cells.
1.) Understanding Avizakimab
Avizakimab is an innovative monoclonal antibody designed to target CD47, a key immune checkpoint protein that plays a critical role in helping tumors evade the body's natural immune response. CD47 is often referred to as a "don’t eat me" signal because it binds to the SIRPα receptor on macrophages, inhibiting their phagocytic activity. Tumors exploit this mechanism to avoid detection and destruction by immune cells, allowing cancer cells to proliferate unchecked. By blocking this CD47-SIRPα interaction, Avizakimab effectively removes this inhibitory signal, enabling the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells more efficiently.
This antibody's mechanism of action is particularly significant in the context of both solid tumors and hematologic malignancies, as CD47 is widely overexpressed in many cancer types, including breast cancer, lymphoma, and leukemia. Its ability to enhance macrophage-mediated phagocytosis makes it a promising candidate for immune modulation in cancer therapy. Furthermore, Avizakimab has been shown to work synergistically with other cancer treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors and chemotherapies, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of existing therapies.
Beyond its direct effects on tumor cells, Avizakimab’s impact on the immune microenvironment is of particular interest. By stimulating the immune system to overcome tumor-induced immunosuppression, it holds the potential to restore the body’s natural immune defenses. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing Avizakimab's therapeutic potential, including exploring its use in combination with other immunotherapies and targeted therapies. This research could position Avizakimab as a cornerstone of next-generation cancer immunotherapy, offering hope for improved treatment outcomes in patients with resistant or advanced cancers.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Avizakimab
Avizakimab operates through a cutting-edge mechanism by targeting CD47, a transmembrane protein that plays a crucial role in immune evasion. CD47 sends a "don’t eat me" signal to immune cells, specifically macrophages, inhibiting their ability to engulf and destroy cancer cells. This immune evasion strategy is commonly exploited by various cancers, as CD47 is overexpressed in many solid tumors and hematologic malignancies, including breast, lung, and blood cancers. By binding to CD47, Avizakimab blocks this protective signal, effectively "unmasking" the tumor cells and allowing macrophages and other immune cells to recognize and attack the cancer cells. The subsequent process of phagocytosis leads to the destruction of tumor cells.
What sets Avizakimab apart from conventional cancer therapies is its immune-based mechanism of action. Unlike traditional chemotherapies or radiation therapies that directly target and kill cancer cells, Avizakimab boosts the body's natural immune response to fight cancer. This approach may reduce the toxic side effects commonly associated with cytotoxic treatments, such as nausea, hair loss, and immunosuppression. Moreover, Avizakimab's potential synergy with other immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies, makes it a powerful candidate for combination therapies. By combining Avizakimab with other treatments, researchers aim to enhance its efficacy, broaden its therapeutic impact, and improve patient outcomes, especially for those with cancers resistant to conventional therapies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Avizakimab
The clinical applications of Avizakimab are wide-ranging, with significant potential in the treatment of various cancers, both solid and hematologic. Early clinical trials have demonstrated promising efficacy across different cancer types, including lung cancer, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and hematologic malignancies like lymphoma and leukemia. Avizakimab’s ability to block CD47 and stimulate the immune system positions it as a promising therapeutic option for cancers that commonly evade immune detection. By enhancing macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, it offers a novel approach to treating tumors that may be resistant to traditional therapies.
Emerging studies have highlighted the potential of Avizakimab in overcoming resistance to standard chemotherapy and radiation, especially in advanced or refractory cancers. These cancers often exploit the CD47-SIRPα pathway to suppress immune responses, leading to treatment failure. Avizakimab, by neutralizing this pathway, may restore immune surveillance and enable the body’s natural defenses to target cancer cells more effectively.
Clinical trials are actively exploring Avizakimab’s use as both a monotherapy and in combination with other therapies, such as chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors. These studies aim to refine treatment regimens, optimize dosing strategies, and identify the patient populations that would benefit most from Avizakimab therapy. Additionally, ongoing research is investigating biomarkers that can predict which patients will respond best to Avizakimab, further improving its potential as a precision cancer therapy.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Avizakimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic product that is highly similar to an already-approved reference biologic, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, efficacy, or immunogenicity. Biosimilars are crucial for improving access to biologic therapies, offering cost-effective alternatives while maintaining high therapeutic standards. In research settings, biosimilars provide an invaluable tool for exploring the mechanisms of action and clinical applications of drugs like Avizakimab.
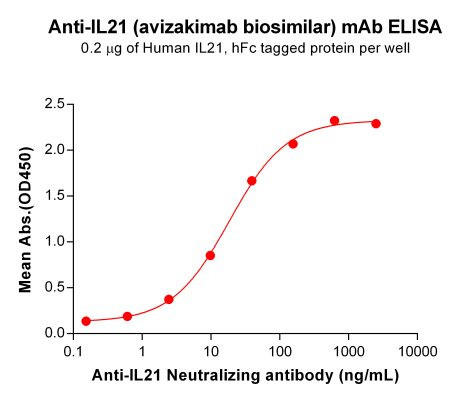
| Avizakimab (Anti-IL21) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | IL-21 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Avizakimab Biosimilar Compares to Avizakimab
Avizakimab biosimilars are designed to replicate the structure and function of the original Avizakimab antibody, offering the same therapeutic benefits while providing researchers with an affordable alternative. These biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to ensure they match the reference product in terms of quality, efficacy, and safety. For researchers, the availability of biosimilars opens new opportunities for large-scale studies and preclinical research, enhancing our understanding of Avizakimab's role in cancer immunotherapy.
Benefits of Avizakimab Biosimilars in Research
The introduction of Avizakimab biosimilars to the research landscape provides numerous benefits. Researchers can now conduct studies with high-quality, cost-effective versions of the drug, which can accelerate the pace of discovery and facilitate large-scale experiments. Biosimilars also offer a reliable alternative for researchers studying the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of Avizakimab in a variety of settings.
As with all biosimilars, the research use only disclaimer applies, ensuring these products are used exclusively for preclinical and clinical research purposes. The growing availability of biosimilars expands the toolkit available to scientists investigating cancer immunotherapies, providing both a sustainable and scalable option for advancing research.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025


