Atezolizumab: Unveiling the Role of Anti-PD-L1 in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Atezolizumab
What is Atezolizumab?
Atezolizumab is an anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody used in immunotherapy to treat various cancers by enhancing the immune system's ability to attack tumors.
What is the mechanism of action for Atezolizumab?
Atezolizumab blocks the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1, restoring T-cell activity and promoting anti-tumor immunity.
What are the clinical applications of Atezolizumab?
It is approved for cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), and urothelial carcinoma, among others.
1.) Understanding Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, marketed as Tecentriq, is a pioneering PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor developed by Roche, marking a significant advancement in cancer treatment. It works by targeting the PD-L1 protein, found on tumor cells and immune cells, which normally helps tumors evade immune detection. By blocking the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 receptors on T-cells, Atezolizumab reactivates the immune system, allowing T-cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
This immunotherapy has proven effective in treating a wide range of cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), bladder cancer, and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), as well as some hematologic malignancies. It is often used in combination with other treatments like chemotherapy to enhance its therapeutic effects.
Atezolizumab’s approval for multiple indications has made it a cornerstone in immuno-oncology, offering a less toxic alternative to traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation. It provides hope for long-term remission in some patients, making it a promising tool in the fight against cancer. Its success highlights the growing role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in modern cancer therapy, offering new avenues for patients with difficult-to-treat cancers. As research evolves, Atezolizumab may play an even larger role in personalized cancer care.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Atezolizumab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab functions as a PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor by specifically blocking the interaction between the PD-L1 protein and two key receptors on T-cells: PD-1 and B7.1. Under normal conditions, the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1 on T-cells suppresses immune activity, allowing tumors to evade detection and destruction by the immune system. By inhibiting this interaction, Atezolizumab effectively reactivates T-cells, enabling them to recognize and attack cancer cells. This process is essential for overcoming the immune evasion mechanisms employed by tumors.
Atezolizumab is particularly selective in targeting PD-L1 without affecting PD-1 itself. This selective blockade allows for a more focused immune response against tumor cells while preserving the broader regulatory functions of PD-1, which is critical for maintaining immune homeostasis. As a result, this mechanism minimizes the risk of unwanted, generalized immune activation and reduces the likelihood of severe immune-related side effects compared to therapies that target PD-1 directly.
The unique mechanism of Atezolizumab complements other therapies, such as immune homeostasisimmune homeostasis like bevacizumab. When combined, these therapies target different pathways in the tumor microenvironment, improving the overall efficacy of cancer treatment regimens. VEGF inhibitors help reduce tumor vascularization, while Atezolizumab enhances immune surveillance. Together, these therapies can provide a more comprehensive attack on tumors, making combination regimens a promising strategy in modern cancer treatment.

3.) Clinical Applications of Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting PD-L1, continues to demonstrate expanding potential beyond its current approvals. Its mechanism of action, which enhances T-cell-mediated anti-tumor responses, makes it a valuable candidate for exploration in various malignancies and treatment settings.
One area of ongoing investigation is the adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings, where Atezolizumab is being studied for its ability to reduce recurrence risk after surgical resection or as a pre-surgical therapy to shrink tumors. Promising results have been observed in early-phase trials for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), suggesting its potential to improve long-term outcomes.
In addition to approved indications, Atezolizumab is being evaluated in combination with other immunotherapies, such as CTLA-4 inhibitors, to enhance its efficacy. Studies are also exploring its role in combination with novel targeted agents, expanding its application to cancers previously resistant to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Moreover, emerging evidence supports its use in rare and difficult-to-treat cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), gastric cancer, and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Its ability to modulate the tumor microenvironment and promote durable immune responses has led to trials assessing its efficacy in these challenging malignancies.
As the understanding of immune-oncology deepens, Atezolizumab's role is expected to grow, potentially encompassing broader cancer types, earlier treatment settings, and more personalized approaches. Ongoing clinical trials and real-world studies will provide critical insights into maximizing its therapeutic impact.
4.) Advancing Research on Atezolizumab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar alternative to an original biologic drug, offering equivalent safety, purity, and potency. In research, biosimilars are invaluable for studying drug mechanisms, testing combinations, and expanding accessibility.
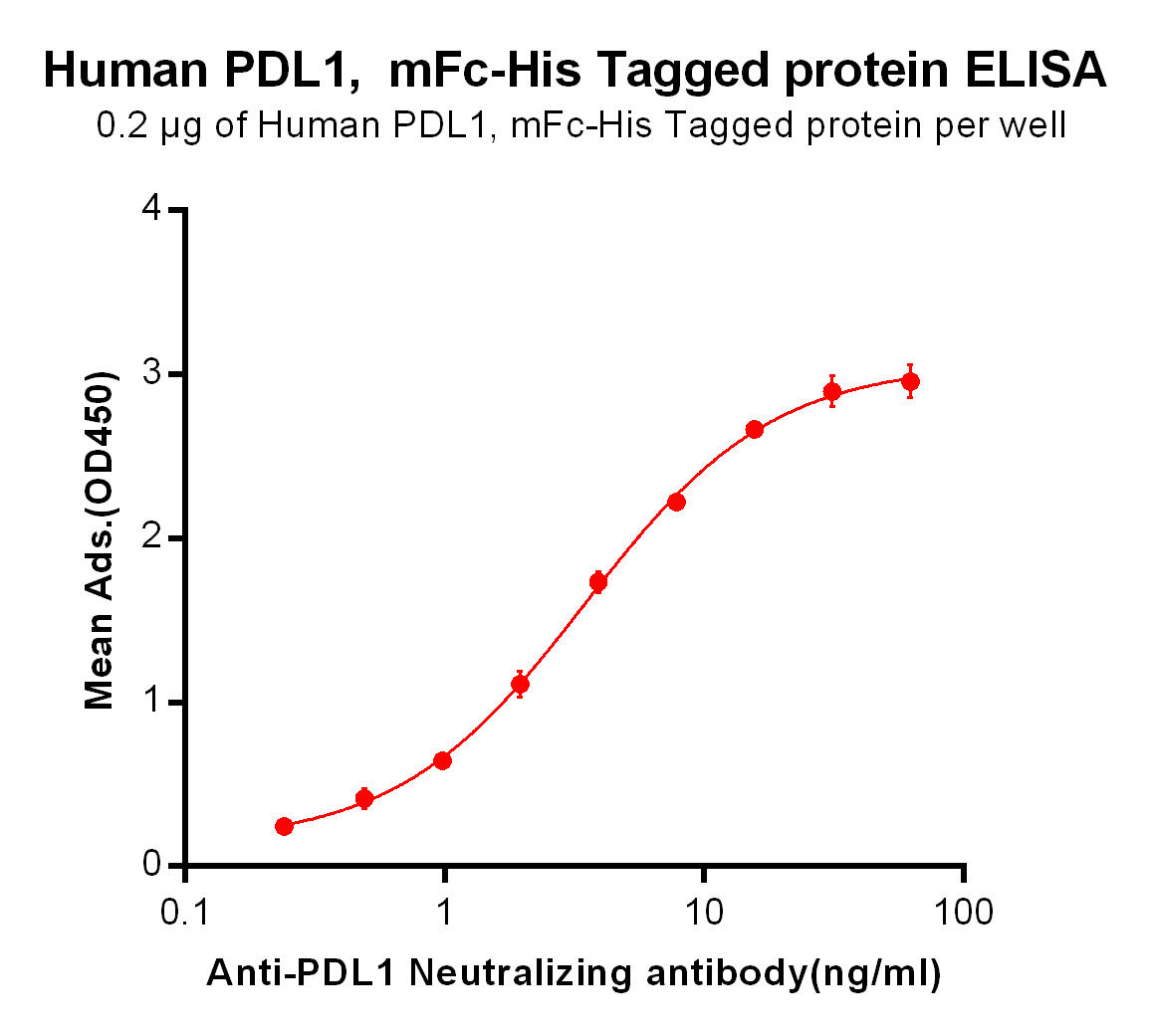
| Atezolizumab (Anti-PDL1) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | PD-L1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
Atezolizumab Biosimilar: A Research Tool
Our Atezolizumab biosimilar enables researchers to investigate PD-L1 pathways efficiently and cost-effectively. This research-use-only product mirrors the binding and activity of the original, facilitating detailed studies on immunotherapy mechanisms.
Benefits for Research:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the financial barriers to accessing cutting-edge research tools.
- High Fidelity: Maintains the specificity and functional properties of the original drug, ensuring accurate experimental results.
- Versatility: Suitable for a variety of research applications, from preclinical trials to in vitro studies.
Note: This biosimilar is strictly for research purposes and not intended for clinical or therapeutic use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD
Miren Ruiz de Eguilaz, PhD, has an extensive academic background, earning a BSc in Biology from UPV/EHU, an MSc in Biotechnology from the University of Oviedo, and a PhD in Chemistry from Dublin City University (DCU). Miren’s expertise lies in biosensor technology and bacterial diagnostics. She currently serves as a Product Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Erenumab: Transforming Migraine Prevention Through CGRP Receptor Inhibition
Quick Facts About ErenumabWhat is Erenumab?Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibo …1st Apr 2025



